Abstract
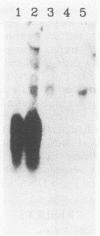
Coordinate regulation of gene expression in Bordetella pertussis is controlled by the products of the vir locus, BvgA and BvgS. In the presence of modulating signals such as MgSO4 and nicotinic acid, expression of vir-activated genes (vag) is reduced, while expression of vir-repressed genes (vrg) is maximal. We have cloned one of these vir-repressed genes, vrg-6, in Escherichia coli. DNA sequencing has shown that vrg-6 is contained on a single EcoRI restriction endonuclease fragment and is predicted to code for a protein of 105 amino acids with a molecular weight of 11,441. The predicted protein product appears to have two domains, one consisting of seven hydrophobic proline-rich pentameric repeats and the other consisting of five alkaline trimeric repeats. Southern blot analysis has revealed vrg-6-homologous sequences in the chromosomes of Bordetella bronchiseptica and Bordetella parapertussis, but, unlike Bordetella pertussis, these species do not express vrg-6-homologous RNA when grown under modulating conditions. In order to assess the role of vrg gene products in B. pertussis pathogenesis, two 18323 derivatives which harbor TnphoA insertions in vrg genes were analyzed in a mouse model of respiratory infection. Strain SK6, which carries a vrg-6::TnphoA mutation, failed to induce lymphocytosis and was significantly less able to colonize lungs and trachea than its parent strain 18323 or than SK18, which harbors a TnphoA fusion in the vrg-18 locus. This is the first evidence that a vir-repressed gene may play an important role in the virulence of B. pertussis and the pathogenesis of whooping cough.
Full text
PDF




Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Aricò B., Rappuoli R. Bordetella parapertussis and Bordetella bronchiseptica contain transcriptionally silent pertussis toxin genes. J Bacteriol. 1987 Jun;169(6):2847–2853. doi: 10.1128/jb.169.6.2847-2853.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Beattie D. T., Knapp S., Mekalanos J. J. Evidence that modulation requires sequences downstream of the promoters of two vir-repressed genes of Bordetella pertussis. J Bacteriol. 1990 Dec;172(12):6997–7004. doi: 10.1128/jb.172.12.6997-7004.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Charles I. G., Dougan G., Pickard D., Chatfield S., Smith M., Novotny P., Morrissey P., Fairweather N. F. Molecular cloning and characterization of protective outer membrane protein P.69 from Bordetella pertussis. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 May;86(10):3554–3558. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.10.3554. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cheers C., Gray D. F. Macrophage behaviour during the complaisant phase of murine pertussis. Immunology. 1969 Dec;17(6):875–887. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Devereux J., Haeberli P., Smithies O. A comprehensive set of sequence analysis programs for the VAX. Nucleic Acids Res. 1984 Jan 11;12(1 Pt 1):387–395. doi: 10.1093/nar/12.1part1.387. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DiRita V. J., Parsot C., Jander G., Mekalanos J. J. Regulatory cascade controls virulence in Vibrio cholerae. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1991 Jun 15;88(12):5403–5407. doi: 10.1073/pnas.88.12.5403. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ewanowich C. A., Melton A. R., Weiss A. A., Sherburne R. K., Peppler M. S. Invasion of HeLa 229 cells by virulent Bordetella pertussis. Infect Immun. 1989 Sep;57(9):2698–2704. doi: 10.1128/iai.57.9.2698-2704.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Finn T. M., Shahin R., Mekalanos J. J. Characterization of vir-activated TnphoA gene fusions in Bordetella pertussis. Infect Immun. 1991 Sep;59(9):3273–3279. doi: 10.1128/iai.59.9.3273-3279.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Friedman A. M., Long S. R., Brown S. E., Buikema W. J., Ausubel F. M. Construction of a broad host range cosmid cloning vector and its use in the genetic analysis of Rhizobium mutants. Gene. 1982 Jun;18(3):289–296. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(82)90167-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Knapp S., Mekalanos J. J. Two trans-acting regulatory genes (vir and mod) control antigenic modulation in Bordetella pertussis. J Bacteriol. 1988 Nov;170(11):5059–5066. doi: 10.1128/jb.170.11.5059-5066.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LACEY B. W. Antigenic modulation of Bordetella pertussis. J Hyg (Lond) 1960 Mar;58:57–93. doi: 10.1017/s0022172400038134. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lee C. K., Roberts A. L., Finn T. M., Knapp S., Mekalanos J. J. A new assay for invasion of HeLa 229 cells by Bordetella pertussis: effects of inhibitors, phenotypic modulation, and genetic alterations. Infect Immun. 1990 Aug;58(8):2516–2522. doi: 10.1128/iai.58.8.2516-2522.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Leininger E., Roberts M., Kenimer J. G., Charles I. G., Fairweather N., Novotny P., Brennan M. J. Pertactin, an Arg-Gly-Asp-containing Bordetella pertussis surface protein that promotes adherence of mammalian cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1991 Jan 15;88(2):345–349. doi: 10.1073/pnas.88.2.345. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miller S. I., Kukral A. M., Mekalanos J. J. A two-component regulatory system (phoP phoQ) controls Salmonella typhimurium virulence. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 Jul;86(13):5054–5058. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.13.5054. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miller S. I., Mekalanos J. J. Constitutive expression of the phoP regulon attenuates Salmonella virulence and survival within macrophages. J Bacteriol. 1990 May;172(5):2485–2490. doi: 10.1128/jb.172.5.2485-2490.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miller S. I. PhoP/PhoQ: macrophage-specific modulators of Salmonella virulence? Mol Microbiol. 1991 Sep;5(9):2073–2078. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2958.1991.tb02135.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miller V. L., Mekalanos J. J. A novel suicide vector and its use in construction of insertion mutations: osmoregulation of outer membrane proteins and virulence determinants in Vibrio cholerae requires toxR. J Bacteriol. 1988 Jun;170(6):2575–2583. doi: 10.1128/jb.170.6.2575-2583.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mooi F. R. Virulence factors of Bordetella pertussis. Antonie Van Leeuwenhoek. 1988;54(5):465–474. doi: 10.1007/BF00461865. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Patel A. H., Nowlan P., Weavers E. D., Foster T. Virulence of protein A-deficient and alpha-toxin-deficient mutants of Staphylococcus aureus isolated by allele replacement. Infect Immun. 1987 Dec;55(12):3103–3110. doi: 10.1128/iai.55.12.3103-3110.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Peppler M. S. Isolation and characterization of isogenic pairs of domed hemolytic and flat nonhemolytic colony types of Bordetella pertussis. Infect Immun. 1982 Mar;35(3):840–851. doi: 10.1128/iai.35.3.840-851.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pierschbacher M. D., Ruoslahti E. Variants of the cell recognition site of fibronectin that retain attachment-promoting activity. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 Oct;81(19):5985–5988. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.19.5985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Recsei P., Kreiswirth B., O'Reilly M., Schlievert P., Gruss A., Novick R. P. Regulation of exoprotein gene expression in Staphylococcus aureus by agar. Mol Gen Genet. 1986 Jan;202(1):58–61. doi: 10.1007/BF00330517. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Relman D. A., Domenighini M., Tuomanen E., Rappuoli R., Falkow S. Filamentous hemagglutinin of Bordetella pertussis: nucleotide sequence and crucial role in adherence. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 Apr;86(8):2637–2641. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.8.2637. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Saukkonen K., Cabellos C., Burroughs M., Prasad S., Tuomanen E. Integrin-mediated localization of Bordetella pertussis within macrophages: role in pulmonary colonization. J Exp Med. 1991 May 1;173(5):1143–1149. doi: 10.1084/jem.173.5.1143. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stibitz S., Aaronson W., Monack D., Falkow S. Phase variation in Bordetella pertussis by frameshift mutation in a gene for a novel two-component system. Nature. 1989 Mar 16;338(6212):266–269. doi: 10.1038/338266a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weiss A. A., Goodwin M. S. Lethal infection by Bordetella pertussis mutants in the infant mouse model. Infect Immun. 1989 Dec;57(12):3757–3764. doi: 10.1128/iai.57.12.3757-3764.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weiss A. A., Hewlett E. L., Myers G. A., Falkow S. Tn5-induced mutations affecting virulence factors of Bordetella pertussis. Infect Immun. 1983 Oct;42(1):33–41. doi: 10.1128/iai.42.1.33-41.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weiss A. A., Hewlett E. L. Virulence factors of Bordetella pertussis. Annu Rev Microbiol. 1986;40:661–686. doi: 10.1146/annurev.mi.40.100186.003305. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weiss A. A., Melton A. R., Walker K. E., Andraos-Selim C., Meidl J. J. Use of the promoter fusion transposon Tn5 lac to identify mutations in Bordetella pertussis vir-regulated genes. Infect Immun. 1989 Sep;57(9):2674–2682. doi: 10.1128/iai.57.9.2674-2682.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yanisch-Perron C., Vieira J., Messing J. Improved M13 phage cloning vectors and host strains: nucleotide sequences of the M13mp18 and pUC19 vectors. Gene. 1985;33(1):103–119. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(85)90120-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- von Gabain A., Belasco J. G., Schottel J. L., Chang A. C., Cohen S. N. Decay of mRNA in Escherichia coli: investigation of the fate of specific segments of transcripts. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1983 Feb;80(3):653–657. doi: 10.1073/pnas.80.3.653. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]