Abstract
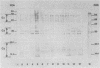
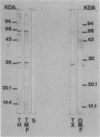
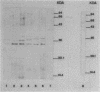
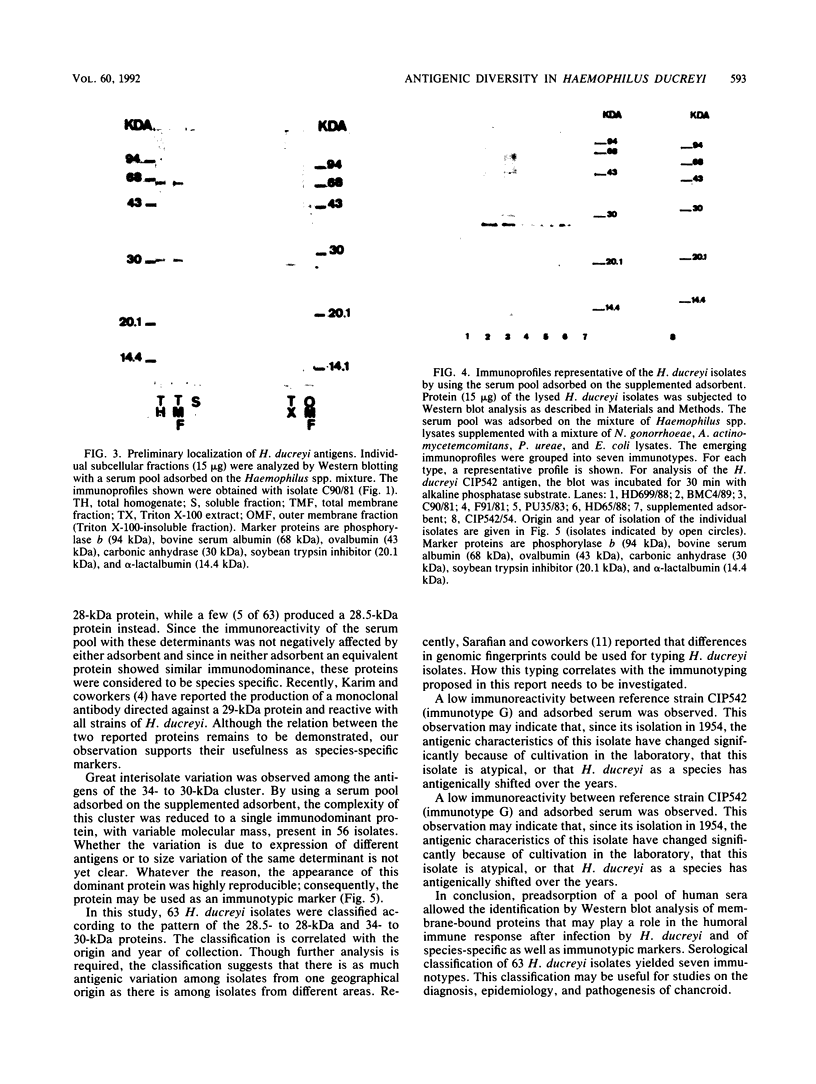
The antigenic diversity within a panel of 63 Haemophilus ducreyi isolates was examined by Western blot (immunoblot) analysis with a pool of 238 well-characterized human antisera. When a serum pool adsorbed on a mixture of Haemophilus influenzae, H. parainfluenzae, and H. parahaemolyticus was used, the immunoprofiles suggested that prominent antigenic proteins involved in the human immune response have apparent molecular masses of 63, 42, 34 to 30, and 28.5 to 28 kDa. Preliminary subcellular localization revealed that these antigens are associated with the cellular membrane. Two subsets of antigens were discriminated by detergent extraction. There was no evidence that the antigen composition is altered by changing the growth conditions. With a serum pool adsorbed on the Haemophilus spp. mixture supplemented with Actinobacillus actinomycetemcomitans, Pasteurella ureae, Neisseria gonorrhoeae, and Escherichia coli, antigenic determinants more specific for H. ducreyi were identified. An immunodominant 28.5- to 28-kDa protein was expressed by all H. ducreyi isolates. In the range from 34 to 30 kDa, 56 isolates revealed a dominant protein with variable molecular mass. By using both proteins (28.5 to 28 kDa and 34 to 30 kDa) as immunotypic markers, seven different immunopatterns were identified. Antigenic diversity among isolates from different geographical origins as well as from a single area was observed.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bradford M. M. A rapid and sensitive method for the quantitation of microgram quantities of protein utilizing the principle of protein-dye binding. Anal Biochem. 1976 May 7;72:248–254. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(76)90527-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dunn S. D. Effects of the modification of transfer buffer composition and the renaturation of proteins in gels on the recognition of proteins on Western blots by monoclonal antibodies. Anal Biochem. 1986 Aug 15;157(1):144–153. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(86)90207-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Karim Q. N., Finn G. Y., Easmon C. S., Dangor Y., Dance D. A., Ngeow Y. F., Ballard R. C. Rapid detection of Haemophilus ducreyi in clinical and experimental infections using monoclonal antibody: a preliminary evaluation. Genitourin Med. 1989 Dec;65(6):361–365. doi: 10.1136/sti.65.6.361. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laemmli U. K. Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature. 1970 Aug 15;227(5259):680–685. doi: 10.1038/227680a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morse S. A. Chancroid and Haemophilus ducreyi. Clin Microbiol Rev. 1989 Apr;2(2):137–157. doi: 10.1128/cmr.2.2.137. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Museyi K., Van Dyck E., Vervoort T., Taylor D., Hoge C., Piot P. Use of an enzyme immunoassay to detect serum IgG antibodies to Haemophilus ducreyi. J Infect Dis. 1988 May;157(5):1039–1043. doi: 10.1093/infdis/157.5.1039. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Müller F., Müller K. H. Immunoglobulin M and G antibody response in rabbits after experimental Haemophilus ducreyi infection. Zentralbl Bakteriol Mikrobiol Hyg A. 1988 Apr;268(2):238–244. doi: 10.1016/s0176-6724(88)80008-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Piot P., Laga M. Genital ulcers, other sexually transmitted diseases, and the sexual transmission of HIV. BMJ. 1989 Mar 11;298(6674):623–624. doi: 10.1136/bmj.298.6674.623. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sarafian S. K., Woods T. C., Knapp J. S., Swaminathan B., Morse S. A. Molecular characterization of Haemophilus ducreyi by ribosomal DNA fingerprinting. J Clin Microbiol. 1991 Sep;29(9):1949–1954. doi: 10.1128/jcm.29.9.1949-1954.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Saunders J. M., Folds J. D. Immunoblot analysis of antigens associated with Haemophilus ducreyi using serum from immunised rabbits. Genitourin Med. 1986 Oct;62(5):321–328. doi: 10.1136/sti.62.5.321. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schalla W. O., Sanders L. L., Schmid G. P., Tam M. R., Morse S. A. Use of dot-immunobinding and immunofluorescence assays to investigate clinically suspected cases of chancroid. J Infect Dis. 1986 May;153(5):879–887. doi: 10.1093/infdis/153.5.879. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schmid G. P., Sanders L. L., Jr, Blount J. H., Alexander E. R. Chancroid in the United States. Reestablishment of an old disease. JAMA. 1987 Dec 11;258(22):3265–3268. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Slootmans L., Vanden Berghe D. A., Piot P. Typing Haemophilus ducreyi by indirect immunofluorescence assay. Genitourin Med. 1985 Apr;61(2):123–126. doi: 10.1136/sti.61.2.123. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Taylor D. N., Duangmani C., Suvongse C., O'Connor R., Pitarangsi C., Panikabutra K., Echeverria P. The role of Haemophilus ducreyi in penile ulcers in Bangkok, Thailand. Sex Transm Dis. 1984 Jul-Sep;11(3):148–151. doi: 10.1097/00007435-198407000-00005. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wagar E. A., Schachter J., Bavoil P., Stephens R. S. Differential human serologic response to two 60,000 molecular weight Chlamydia trachomatis antigens. J Infect Dis. 1990 Oct;162(4):922–927. doi: 10.1093/infdis/162.4.922. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]