Abstract
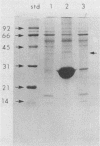
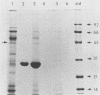
The ability of Escherichia coli K-12(K88ab) to adhere to immobilized porcine small intestine mucus was examined. E. coli K-12(K88ab) but not the isogenic E. coli K-12 strain was found to adhere readily to immobilized crude mucus but not to bovine serum albumin. The adhesion of E. coli K-12(K88ab) was inhibited in a specific fashion by anti-K88 antiserum. Adhesion was also inhibited by pretreatment of receptor-containing crude mucus preparations with sodium metaperiodate or proteolytic enzymes. Removal of glycolipids from crude mucus by chloroform-methanol extraction did not affect the ability of E. coli K-12(K88ab) to bind to mucus preparations. Adsorption of crude mucus preparations with K88ab fimbriae but not type 1 fimbriae resulted in the removal of K88-specific receptors. Analysis of the pelleted fimbriae-receptor complex by sodium dodecyl sulfate-polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis, together with gel filtration chromatography of crude mucus preparations, suggest that the K88-specific receptor present in porcine small intestine mucus is a 40- to 42-kDa glycoprotein.
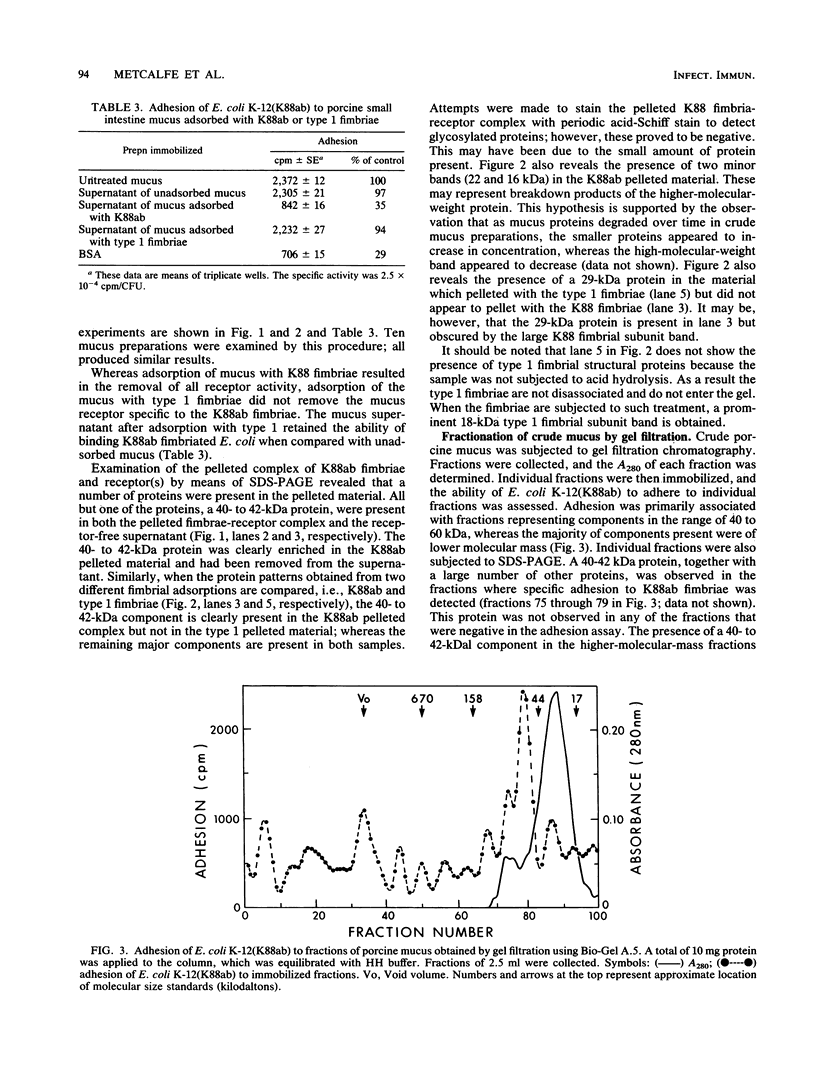
Full text
PDF




Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Anderson M. J., Whitehead J. S., Kim Y. S. Interaction of Escherichia coli K88 antigen with porcine intestinal brush border membranes. Infect Immun. 1980 Sep;29(3):897–901. doi: 10.1128/iai.29.3.897-901.1980. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bijlsma I. G., de Nijs A., van der Meer C., Frik J. F. Different pig phenotypes affect adherence of Escherichia coli to jejunal brush borders by K88ab, K88ac, or K88ad antigen. Infect Immun. 1982 Sep;37(3):891–894. doi: 10.1128/iai.37.3.891-894.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Conway P. L., Welin A., Cohen P. S. Presence of K88-specific receptors in porcine ileal mucus is age dependent. Infect Immun. 1990 Oct;58(10):3178–3182. doi: 10.1128/iai.58.10.3178-3182.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- De Graaf F. K., Mooi F. R. The fimbrial adhesins of Escherichia coli. Adv Microb Physiol. 1986;28:65–143. doi: 10.1016/s0065-2911(08)60237-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dean E. A., Whipp S. C., Moon H. W. Age-specific colonization of porcine intestinal epithelium by 987P-piliated enterotoxigenic Escherichia coli. Infect Immun. 1989 Jan;57(1):82–87. doi: 10.1128/iai.57.1.82-87.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Drumm B., Roberton A. M., Sherman P. M. Inhibition of attachment of Escherichia coli RDEC-1 to intestinal microvillus membranes by rabbit ileal mucus and mucin in vitro. Infect Immun. 1988 Sep;56(9):2437–2442. doi: 10.1128/iai.56.9.2437-2442.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eshdat Y., Silverblatt F. J., Sharon N. Dissociation and reassembly of Escherichia coli type 1 pili. J Bacteriol. 1981 Oct;148(1):308–314. doi: 10.1128/jb.148.1.308-314.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eshdat Y., Speth V., Jann K. Participation of pili and cell wall adhesion in the yeast agglutination activity of Escherichia coli. Infect Immun. 1981 Dec;34(3):980–986. doi: 10.1128/iai.34.3.980-986.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gaastra W., de Graaf F. K. Host-specific fimbrial adhesins of noninvasive enterotoxigenic Escherichia coli strains. Microbiol Rev. 1982 Jun;46(2):129–161. doi: 10.1128/mr.46.2.129-161.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gibbons R. A., Jones G. W., Sellwood R. An attempt to identify the intestinal receptor for the K88 adhesin by means of a haemagglutination inhibition test using glycoproteins and fractions from sow colostrum. J Gen Microbiol. 1975 Feb;86(2):228–240. doi: 10.1099/00221287-86-2-228. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Guinée P. A., Jansen W. H. Behavior of Escherichia coli K antigens K88ab, K88ac, and K88ad in immunoelectrophoresis, double diffusion, and hemagglutination. Infect Immun. 1979 Mar;23(3):700–705. doi: 10.1128/iai.23.3.700-705.1979. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Klemm P. Fimbrial adhesions of Escherichia coli. Rev Infect Dis. 1985 May-Jun;7(3):321–340. doi: 10.1093/clinids/7.3.321. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Krivan H. C., Ginsburg V., Roberts D. D. Pseudomonas aeruginosa and Pseudomonas cepacia isolated from cystic fibrosis patients bind specifically to gangliotetraosylceramide (asialo GM1) and gangliotriaosylceramide (asialo GM2). Arch Biochem Biophys. 1988 Jan;260(1):493–496. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(88)90473-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kyogashima M., Ginsburg V., Krivan H. C. Escherichia coli K99 binds to N-glycolylsialoparagloboside and N-glycolyl-GM3 found in piglet small intestine. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1989 Apr;270(1):391–397. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(89)90042-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laemmli U. K. Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature. 1970 Aug 15;227(5259):680–685. doi: 10.1038/227680a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laux D. C., McSweegan E. F., Williams T. J., Wadolkowski E. A., Cohen P. S. Identification and characterization of mouse small intestine mucosal receptors for Escherichia coli K-12(K88ab). Infect Immun. 1986 Apr;52(1):18–25. doi: 10.1128/iai.52.1.18-25.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mooi F. R., de Graaf F. K. Molecular biology of fimbriae of enterotoxigenic Escherichia coli. Curr Top Microbiol Immunol. 1985;118:119–138. doi: 10.1007/978-3-642-70586-1_7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mouricout M. A., Julien R. A. Pilus-mediated binding of bovine enterotoxigenic Escherichia coli to calf small intestinal mucins. Infect Immun. 1987 May;55(5):1216–1223. doi: 10.1128/iai.55.5.1216-1223.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ono E., Abe K., Nakazawa M., Naiki M. Ganglioside epitope recognized by K99 fimbriae from enterotoxigenic Escherichia coli. Infect Immun. 1989 Mar;57(3):907–911. doi: 10.1128/iai.57.3.907-911.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Oudega B., De Graaf F. K. Genetic organization and biogenesis of adhesive fimbriae of Escherichia coli. Antonie Van Leeuwenhoek. 1988;54(4):285–299. doi: 10.1007/BF00393521. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sellwood R., Gibbons R. A., Jones G. W., Rutter J. M. Adhesion of enteropathogenic Escherichia coli to pig intestinal brush borders: the existence of two pig phenotypes. J Med Microbiol. 1975 Aug;8(3):405–411. doi: 10.1099/00222615-8-3-405. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sellwood R. The interaction of the K88 antigen with porcine intestinal epithelial cell brush borders. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1980 Oct 1;632(2):326–335. doi: 10.1016/0304-4165(80)90090-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smit H., Gaastra W., Kamerling J. P., Vliegenthart J. F., de Graaf F. K. Isolation and structural characterization of the equine erythrocyte receptor for enterotoxigenic Escherichia coli K99 fimbrial adhesin. Infect Immun. 1984 Nov;46(2):578–584. doi: 10.1128/iai.46.2.578-584.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith H. W., Linggood M. A. Further observations on Escherichia coli enterotoxins with particular regard to those produced by atypical piglet strains and by calf and lamb strains: the transmissible nature of these enterotoxins and of a K antigen possessed by calf and lamb strains. J Med Microbiol. 1972 May;5(2):243–250. doi: 10.1099/00222615-5-2-243. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Staley T. E., Wilson I. B. Soluble pig intestinal cell membrane components with affinities for E. coli K88+ antigen. Mol Cell Biochem. 1983;52(2):177–189. doi: 10.1007/BF00224926. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stirm S., Orskov F., Orskov I., Mansa B. Episome-carried surface antigen K88 of Escherichia coli. II. Isolation and chemical analysis. J Bacteriol. 1967 Feb;93(2):731–739. doi: 10.1128/jb.93.2.731-739.1967. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Svennerholm L., Fredman P. A procedure for the quantitative isolation of brain gangliosides. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1980 Jan 18;617(1):97–109. doi: 10.1016/0005-2760(80)90227-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]