Abstract
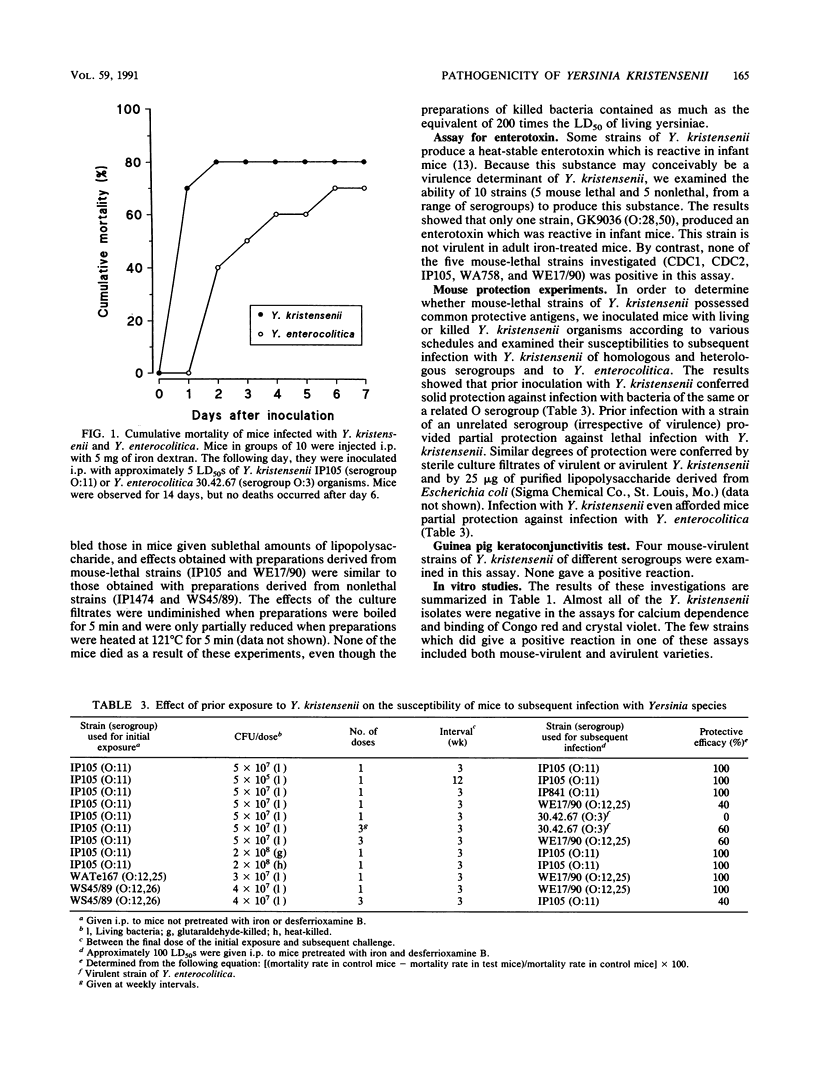
Forty-seven strains of Yersinia kristensenii from widely differing sources, representing all known O serogroups of this species, were investigated for virulence with a variety of animal and in vitro assays. Twenty-four (51%) of the isolates were lethal for mice pretreated with iron dextran. Mouse-lethal strains occurred predominantly within O serogroups O:11, O:12,25, and O:16. Virulent Y. kristensenii strains generally did not express the virulence-associated phenotype (Ca2+ dependence and binding of Congo red and crystal violet) which characterizes virulent strains of Y. enterocolitica, nor did they carry the Yersinia virulence plasmid. Although all strains hybridized with a DNA probe derived from the inv (invasin) gene of Y. enterocolitica, none was able to invade HEp-2 epithelial cell culture. Y. kristensenii strains were virulent only when inoculated parenterally into iron-loaded mice. Animals infected in this way succumbed rapidly to infection, generally within 24 h. This finding suggested that the pathogenicity of these bacteria may be attributable to a secreted toxin, but a search for such a substance and for other in vitro correlates of pathogenicity was unsuccessful. These observations indicate that some strains of Y. kristensenii kill mice by a mechanism not previously recognized in yersiniae.
Full text
PDF



Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bissett M. L. Yersinia enterocolitica isolates from humans in California, 1968-1975. J Clin Microbiol. 1976 Aug;4(2):137–144. doi: 10.1128/jcm.4.2.137-144.1976. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bottone E. J. Atypical Yersinia enterocolitica: clinical and epidemiological parameters. J Clin Microbiol. 1978 Jun;7(6):562–567. doi: 10.1128/jcm.7.6.562-567.1978. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bottone E. J., Robin T. Yersinia enterocolitica: recovery and characterization of two unusual isolates from a case of acute enteritis. J Clin Microbiol. 1977 Mar;5(3):341–345. doi: 10.1128/jcm.5.3.341-345.1977. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chiesa C., Pacifico L., Cianfrano V., Midulla M. Italian experience with yersiniosis (1978-1985). Contrib Microbiol Immunol. 1987;9:76–88. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cornelis G., Laroche Y., Balligand G., Sory M. P., Wauters G. Yersinia enterocolitica, a primary model for bacterial invasiveness. Rev Infect Dis. 1987 Jan-Feb;9(1):64–87. doi: 10.1093/clinids/9.1.64. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Delor I., Kaeckenbeeck A., Wauters G., Cornelis G. R. Nucleotide sequence of yst, the Yersinia enterocolitica gene encoding the heat-stable enterotoxin, and prevalence of the gene among pathogenic and nonpathogenic yersiniae. Infect Immun. 1990 Sep;58(9):2983–2988. doi: 10.1128/iai.58.9.2983-2988.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Falcão D. P. Yersiniosis in Brazil. Summary of the data received at the Reference Laboratory for Yersinia in Brazil. Contrib Microbiol Immunol. 1987;9:68–75. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fletcher K. M., Morris C. M., Noble M. A. Human coproantibody secretory immunoglobulin A response to Yersinia species. J Clin Microbiol. 1988 Feb;26(2):287–292. doi: 10.1128/jcm.26.2.287-292.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hancock G. E., Schaedler R. W., MacDonald T. T. Yersinia enterocolitica infection in resistant and susceptible strains of mice. Infect Immun. 1986 Jul;53(1):26–31. doi: 10.1128/iai.53.1.26-31.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kapperud G. Enterotoxin production at 4 degrees, 22 degrees, and 37 degrees C and Y. enterocolitica-like bacteria. Acta Pathol Microbiol Immunol Scand B. 1982 Jun;90(3):185–189. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lewis A. M., Chattopadhyay B. Faecal carriage rate of Yersinia species. J Hyg (Lond) 1986 Oct;97(2):281–287. doi: 10.1017/s0022172400065372. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mehigh R. J., Sample A. K., Brubaker R. R. Expression of the low calcium response in Yersinia pestis. Microb Pathog. 1989 Mar;6(3):203–217. doi: 10.1016/0882-4010(89)90070-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miller V. L., Farmer J. J., 3rd, Hill W. E., Falkow S. The ail locus is found uniquely in Yersinia enterocolitica serotypes commonly associated with disease. Infect Immun. 1989 Jan;57(1):121–131. doi: 10.1128/iai.57.1.121-131.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miller V. L., Finlay B. B., Falkow S. Factors essential for the penetration of mammalian cells by Yersinia. Curr Top Microbiol Immunol. 1988;138:15–39. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Noble M. A., Barteluk R. L., Freeman H. J., Subramaniam R., Hudson J. B. Clinical significance of virulence-related assay of Yersinia species. J Clin Microbiol. 1987 May;25(5):802–807. doi: 10.1128/jcm.25.5.802-807.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pierson D. E., Falkow S. Nonpathogenic isolates of Yersinia enterocolitica do not contain functional inv-homologous sequences. Infect Immun. 1990 Apr;58(4):1059–1064. doi: 10.1128/iai.58.4.1059-1064.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Portnoy D. A., Martinez R. J. Role of a plasmid in the pathogenicity of Yersinia species. Curr Top Microbiol Immunol. 1985;118:29–51. doi: 10.1007/978-3-642-70586-1_3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Prpic J. K., Robins-Browne R. M., Davey R. B. In vitro assessment of virulence in Yersinia enterocolitica and related species. J Clin Microbiol. 1985 Jul;22(1):105–110. doi: 10.1128/jcm.22.1.105-110.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Robins-Browne R. M., Levine M. M. Effect of chlorpromazine on intestinal secretion mediated by Escherichia coli heat-stable enterotoxin and 8-Br-cyclic GMP in infant mice. Gastroenterology. 1981 Feb;80(2):321–326. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Robins-Browne R. M., Miliotis M. D., Cianciosi S., Miller V. L., Falkow S., Morris J. G., Jr Evaluation of DNA colony hybridization and other techniques for detection of virulence in Yersinia species. J Clin Microbiol. 1989 Apr;27(4):644–650. doi: 10.1128/jcm.27.4.644-650.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Robins-Browne R. M., Prpic J. K. Effects of iron and desferrioxamine on infections with Yersinia enterocolitica. Infect Immun. 1985 Mar;47(3):774–779. doi: 10.1128/iai.47.3.774-779.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Robins-Browne R. M., Prpic J. K., Stuart S. J. Yersiniae and iron. A study in host-parasite relationships. Contrib Microbiol Immunol. 1987;9:254–258. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shayegani M., Parsons L. M. Epidemiology and pathogenicity of Yersinia enterocolitica in New York State. Contrib Microbiol Immunol. 1987;9:41–47. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stuart S. J., Prpic J. K., Robins-Browne R. M. Production of aerobactin by some species of the genus Yersinia. J Bacteriol. 1986 Jun;166(3):1131–1133. doi: 10.1128/jb.166.3.1131-1133.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Une T., Brubaker R. R. In vivo comparison of avirulent Vwa- and Pgm- or Pstr phenotypes of yersiniae. Infect Immun. 1984 Mar;43(3):895–900. doi: 10.1128/iai.43.3.895-900.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Urbaschek R., Urbaschek B. Tumor necrosis factor and interleukin 1 as mediators of endotoxin-induced beneficial effects. Rev Infect Dis. 1987 Sep-Oct;9 (Suppl 5):S607–S615. doi: 10.1093/clinids/9.supplement_5.s607. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Van Noyen R., Selderslaghs R., Wauters G., Vandepitte J. Comparative epidemiology of Yersinia enterocolitica and related species in patients and healthy controls. Contrib Microbiol Immunol. 1987;9:61–67. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


