Abstract
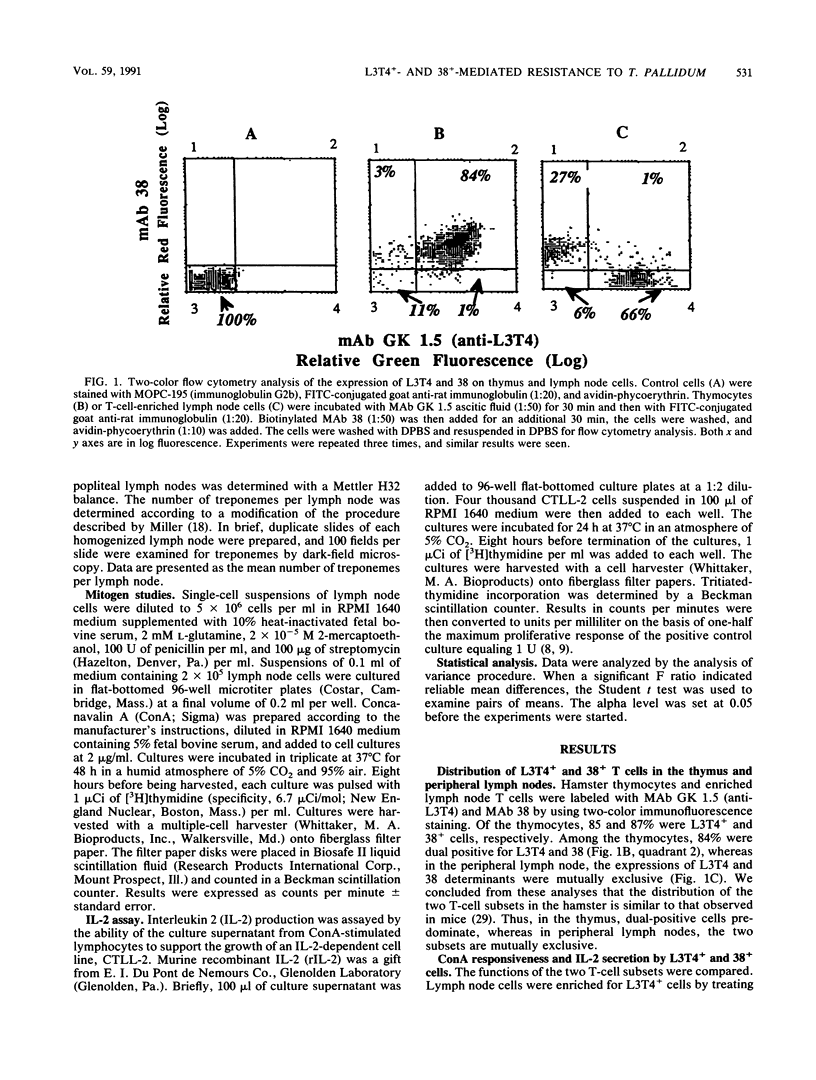
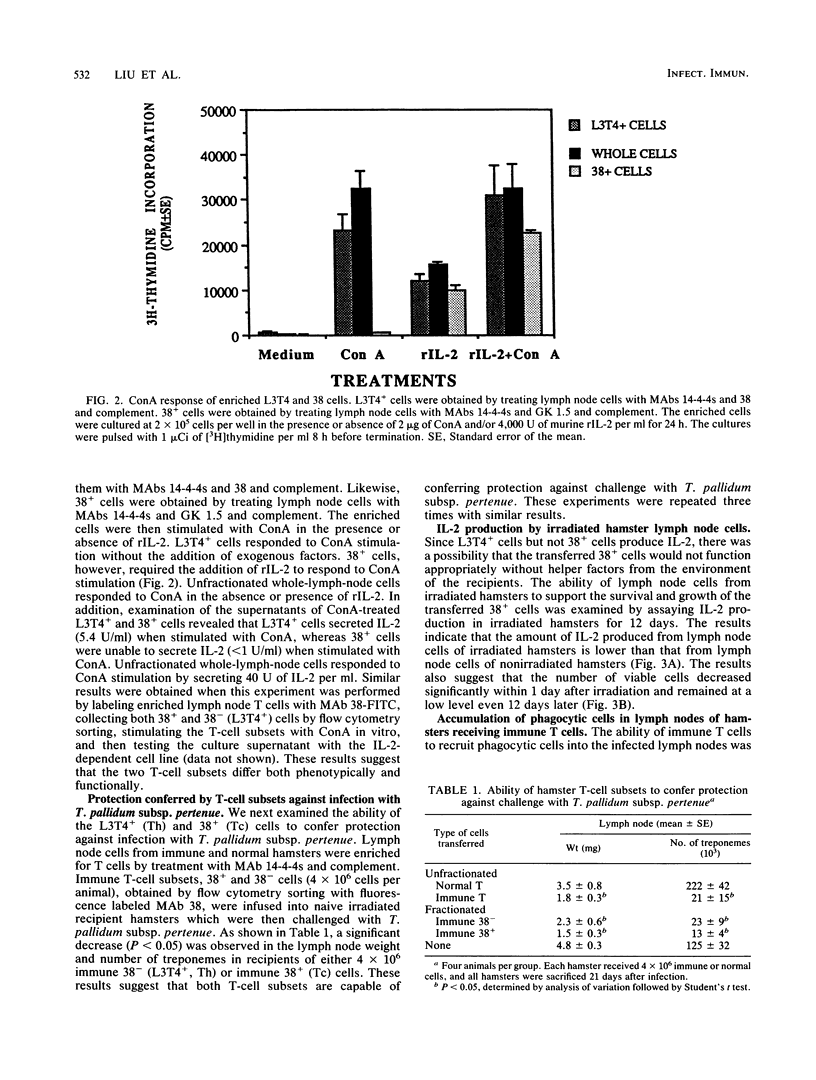
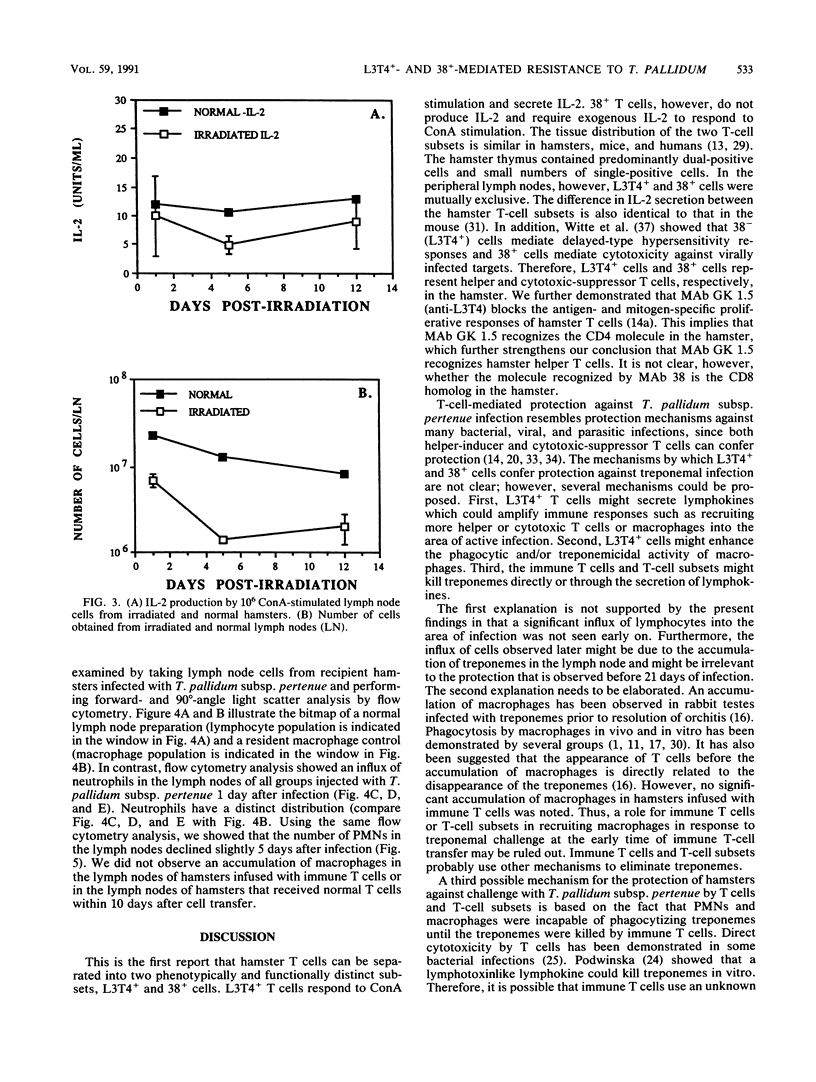
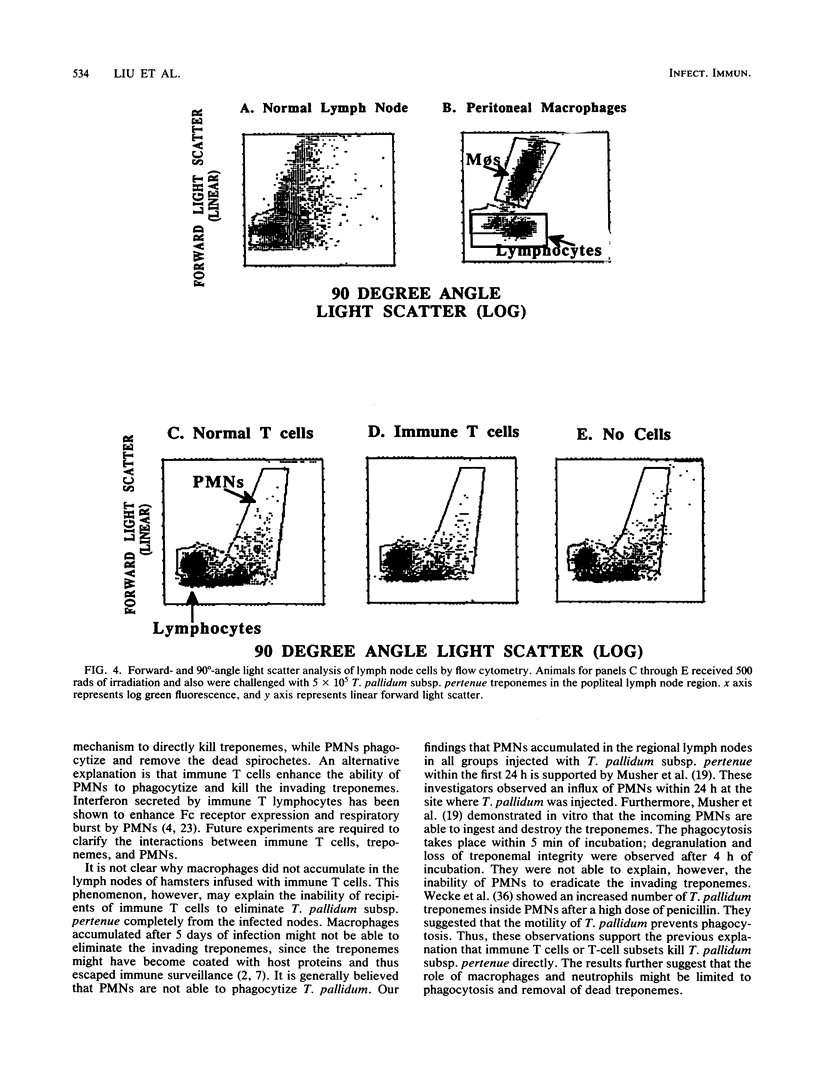
The protective immunity conferred by T-cell subsets against infection with Treponema pallidum subsp. pertenue was studied. We demonstrated that hamster T cells can be separated into two subsets by monoclonal antibody (MAb) GK 1.5 (anti-L3T4) and MAb 38. Eighty-five percent of hamster thymocytes were L3T4+ and 87% were 38+ cells; 84% were dual positive for MAbs anti-L3T4 and 38. In the peripheral lymph nodes, however, the L3T4+ and 38+ T cells were mutually exclusive according to two-color immunofluorescence analysis. The two T-cell subsets were found to be functionally distinct according to their secretion of interleukin 2 (IL-2) when stimulated with concanavalin A. The L3T4+ cells secreted IL-2 and had characteristics of T helper cells, while the 38+ cells did not secrete IL-2 and appeared to be T cytotoxic-suppressor cells. Transfer of 4 x 10(6) helper or cytotoxic-suppressor T lymphocytes from T. pallidum subsp. pertenue-immune hamsters protected irradiated naive hamsters against challenge with this subspecies. IL-2 production could still be detected in the irradiated recipients 12 days after irradiation of naive recipients, although at a low level. This suggests that the remaining lymph node cells could support the survival and expansion of the infused cytotoxic-suppressor T cells. No accumulation of macrophages was observed in regional lymph nodes of immune T-cell recipients within 10 days of infection. Instead, there was an influx of polymorphonuclear neutrophils in all animals injected with T. pallidum subsp. pertenue. This report demonstrates that hamster T cells can be separated into two phenotypically and functionally distinct subsets and that both T-cell subsets confer protection against challenge with T. pallidum subsp. pertenue.
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Alder J. D., Daugherty N., Harris O. N., Liu H., Steiner B. M., Schell R. F. Phagocytosis of Treponema pallidum pertenue by hamster macrophages on membrane filters. J Infect Dis. 1989 Aug;160(2):289–297. doi: 10.1093/infdis/160.2.289. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Alderete J. F., Baseman J. B. Surface-associated host proteins on virulent Treponema pallidum. Infect Immun. 1979 Dec;26(3):1048–1056. doi: 10.1128/iai.26.3.1048-1056.1979. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Azadegan A. A., Schell R. F., Steiner B. M., Coe J. E., Chan J. K. Effect of immune serum and its immunoglobulin fractions on hamsters challenged with Treponema pallidum ssp. pertenue. J Infect Dis. 1986 Jun;153(6):1007–1013. doi: 10.1093/infdis/153.6.1007. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Berton G., Zeni L., Cassatella M. A., Rossi F. Gamma interferon is able to enhance the oxidative metabolism of human neutrophils. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1986 Aug 14;138(3):1276–1282. doi: 10.1016/s0006-291x(86)80421-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bjerknes R., Bassøe C. F., Sjursen H., Laerum O. D., Solberg C. O. Flow cytometry for the study of phagocyte functions. Rev Infect Dis. 1989 Jan-Feb;11(1):16–33. doi: 10.1093/clinids/11.1.16. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dialynas D. P., Quan Z. S., Wall K. A., Pierres A., Quintáns J., Loken M. R., Pierres M., Fitch F. W. Characterization of the murine T cell surface molecule, designated L3T4, identified by monoclonal antibody GK1.5: similarity of L3T4 to the human Leu-3/T4 molecule. J Immunol. 1983 Nov;131(5):2445–2451. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fitzgerald T. J., Miller J. N., Repesh L. A., Rice M., Urquhart A. Binding of glycosaminoglycans to the surface of Treponema pallidum and subsequent effects on complement interactions between antigen and antibody. Genitourin Med. 1985 Feb;61(1):13–20. doi: 10.1136/sti.61.1.13. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gillis S., Ferm M. M., Ou W., Smith K. A. T cell growth factor: parameters of production and a quantitative microassay for activity. J Immunol. 1978 Jun;120(6):2027–2032. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gillis S., Smith K. A. Long term culture of tumour-specific cytotoxic T cells. Nature. 1977 Jul 14;268(5616):154–156. doi: 10.1038/268154a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Guesdon J. L., Ternynck T., Avrameas S. The use of avidin-biotin interaction in immunoenzymatic techniques. J Histochem Cytochem. 1979 Aug;27(8):1131–1139. doi: 10.1177/27.8.90074. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hardy P. H., Jr, Graham D. J., Nell E. E., Dannenberg A. M., Jr Macrophages in immunity to syphilis: suppressive effect of concurrent infection with Mycobacterium bovis BCG on the development of syphilitic lesions and growth of Treponema pallidum in tuberculin-positive rabbits. Infect Immun. 1979 Nov;26(2):751–763. doi: 10.1128/iai.26.2.751-763.1979. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Janis E. M., Kaufmann S. H., Schwartz R. H., Pardoll D. M. Activation of gamma delta T cells in the primary immune response to Mycobacterium tuberculosis. Science. 1989 May 12;244(4905):713–716. doi: 10.1126/science.2524098. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lanier L. L., Engleman E. G., Gatenby P., Babcock G. F., Warner N. L., Herzenberg L. A. Correlation of functional properties of human lymphoid cell subsets and surface marker phenotypes using multiparameter analysis and flow cytometry. Immunol Rev. 1983;74:143–160. doi: 10.1111/j.1600-065x.1983.tb01088.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Liu H., Steiner B. M., Alder J. D., Baertschy D. K., Schell R. F. Immune T cells sorted by flow cytometry confer protection against infection with Treponema pallidum subsp. pertenue in hamsters. Infect Immun. 1990 Jun;58(6):1685–1690. doi: 10.1128/iai.58.6.1685-1690.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lukehart S. A., Baker-Zander S. A., Lloyd R. M., Sell S. Characterization of lymphocyte responsiveness in early experimental syphilis. II. Nature of cellular infiltration and Treponema pallidum distribution in testicular lesions. J Immunol. 1980 Jan;124(1):461–467. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lukehart S. A., Miller J. N. Demonstration of the in vitro phagocytosis of Treponema pallidum by rabbit peritoneal macrophages. J Immunol. 1978 Nov;121(5):2014–2024. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Musher D. M., Hague-Park M., Gyorkey F., Anderson D. C., Baughn R. E. The interaction between Treponema pallidum and human polymorphonuclear leukocytes. J Infect Dis. 1983 Jan;147(1):77–86. doi: 10.1093/infdis/147.1.77. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Orme I. M. Characteristics and specificity of acquired immunologic memory to Mycobacterium tuberculosis infection. J Immunol. 1988 May 15;140(10):3589–3593. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ozato K., Mayer N., Sachs D. H. Hybridoma cell lines secreting monoclonal antibodies to mouse H-2 and Ia antigens. J Immunol. 1980 Feb;124(2):533–540. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pavis C. S., Folds J. D., Baseman J. B. Cell-mediated immunity during syphilis. Br J Vener Dis. 1978 Jun;54(3):144–150. doi: 10.1136/sti.54.3.144. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Perussia B., Dayton E. T., Lazarus R., Fanning V., Trinchieri G. Immune interferon induces the receptor for monomeric IgG1 on human monocytic and myeloid cells. J Exp Med. 1983 Oct 1;158(4):1092–1113. doi: 10.1084/jem.158.4.1092. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Podwińska J. Identification of cells producing anti-treponemal lymphotoxin (ATL). Arch Immunol Ther Exp (Warsz) 1987;35(1):63–70. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Powderly W. G., Schreiber J. R., Pier G. B., Markham R. B. T cells recognizing polysaccharide-specific B cells function as contrasuppressor cells in the generation of T cell immunity to Pseudomonas aeruginosa. J Immunol. 1988 Apr 15;140(8):2746–2752. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Radolf J. D., Norgard M. V., Schulz W. W. Outer membrane ultrastructure explains the limited antigenicity of virulent Treponema pallidum. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 Mar;86(6):2051–2055. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.6.2051. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schell R. F., Azadegan A. A., Nitskansky S. G., LeFrock J. L. Acquired resistance of hamsters to challenge with homologous and heterologous virulent treponemes. Infect Immun. 1982 Aug;37(2):617–621. doi: 10.1128/iai.37.2.617-621.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schell R. F., Le Frock J. L., Babu J. P., Chan J. K. Use of CB hamsters in the study of Treponema pertenue. Br J Vener Dis. 1979 Oct;55(5):316–319. doi: 10.1136/sti.55.5.316. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Scollay R., Bartlett P., Shortman K. T cell development in the adult murine thymus: changes in the expression of the surface antigens Ly2, L3T4 and B2A2 during development from early precursor cells to emigrants. Immunol Rev. 1984 Dec;82:79–103. doi: 10.1111/j.1600-065x.1984.tb01118.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sell S., Baker-Zander S., Powell H. C. Experimental syphilitic orchitis in rabbits: ultrastructural appearance of Treponema pallidum during phagocytosis and dissolution by macrophages in vivo. Lab Invest. 1982 Apr;46(4):355–364. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sprent J., Schaefer M., Lo D., Korngold R. Functions of purified L3T4+ and Lyt-2+ cells in vitro and in vivo. Immunol Rev. 1986 Jun;91:195–218. doi: 10.1111/j.1600-065x.1986.tb01489.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stern J. J., Oca M. J., Rubin B. Y., Anderson S. L., Murray H. W. Role of L3T4+ and LyT-2+ cells in experimental visceral leishmaniasis. J Immunol. 1988 Jun 1;140(11):3971–3977. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stähli C., Miggiano V., Stocker J., Staehelin T., Häring P., Takács B. Distinction of epitopes by monoclonal antibodies. Methods Enzymol. 1983;92:242–253. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(83)92023-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Suzuki Y., Remington J. S. Dual regulation of resistance against Toxoplasma gondii infection by Lyt-2+ and Lyt-1+, L3T4+ T cells in mice. J Immunol. 1988 Jun 1;140(11):3943–3946. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wecke J., Bartunek J., Stüttgen G. Treponema pallidum in early syphilitic lesions in humans during high-dosage penicillin therapy. An electron microscopical study. Arch Dermatol Res. 1976 Nov 26;257(1):1–15. doi: 10.1007/BF00569109. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Witte P. L., Stein-Streilein J., Streilein J. W. Description of phenotypically distinct T-lymphocyte subsets which mediate helper/DTH and cytotoxic functions in the Syrian hamster. J Immunol. 1985 May;134(5):2908–2915. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Witte P. L., Streilein J. W. Monoclonal antibodies to hamster class II MHC molecules distinguish T and B cells. J Immunol. 1983 May;130(5):2282–2286. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


