Abstract
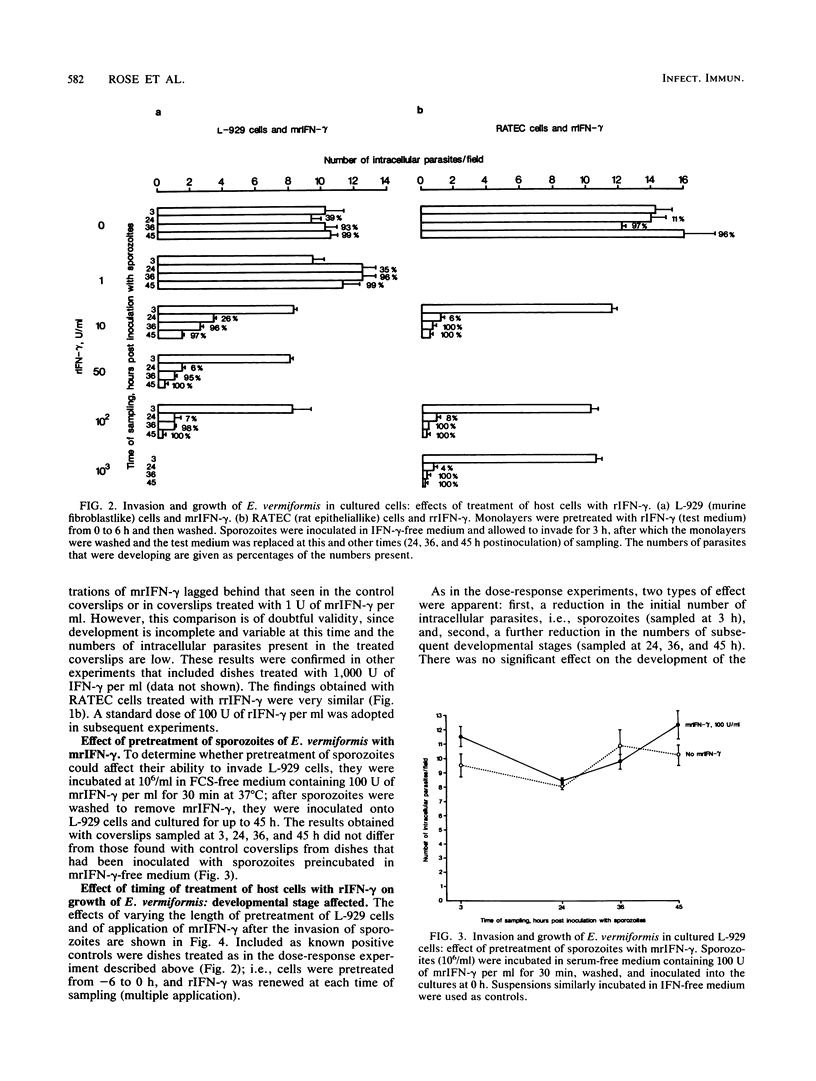
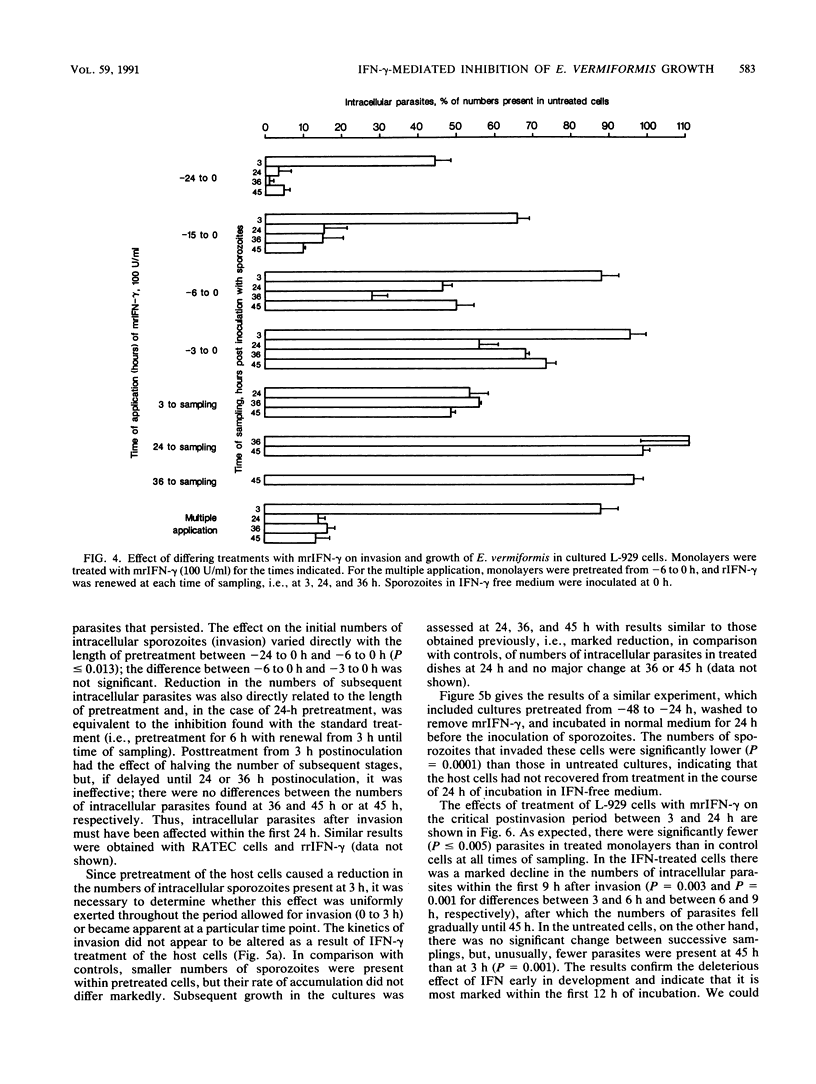
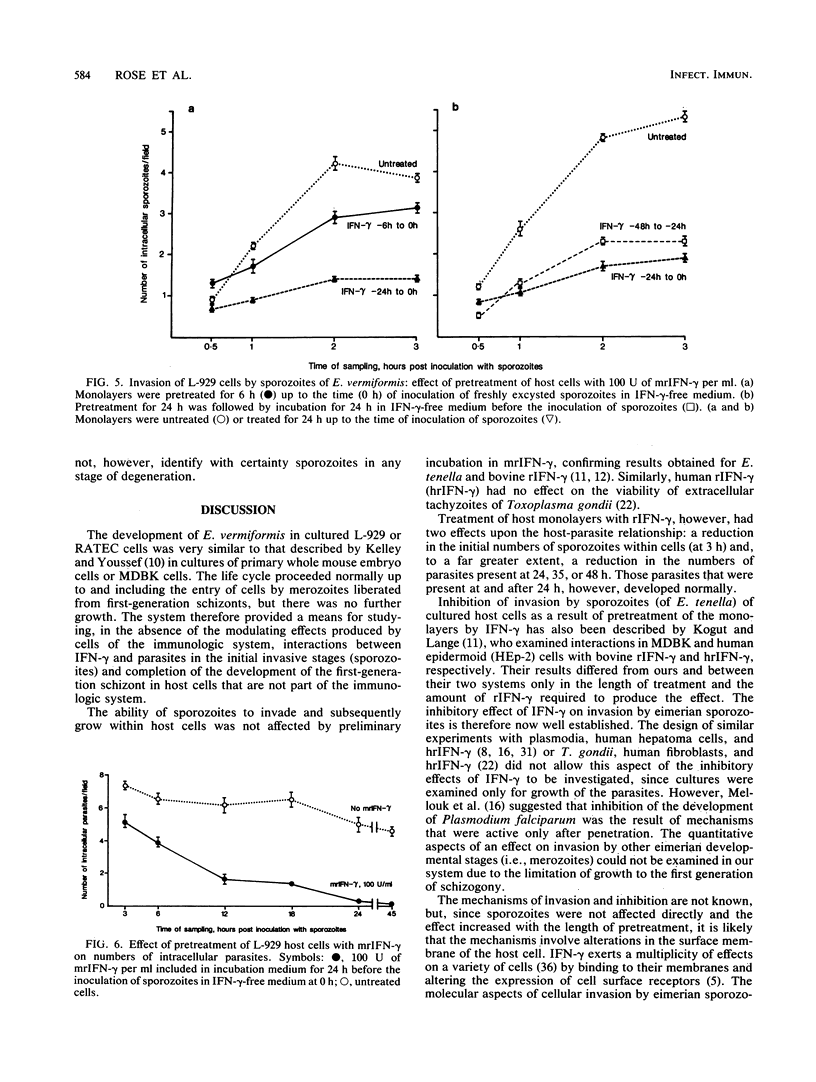
The growth of Eimeria vermiformis within cultured murine fibroblastlike (L-929) or rat epithelial-like (RATEC) cells was inhibited by treatment of the cells with the appropriate recombinant gamma interferon. The effect was apparent as a reduction in both the initial numbers of intracellular sporozoites and, to a much greater extent, the numbers of subsequent developmental stages. Pretreatment of the host cells was more effective than treatment in the early postinvasive period, and recombinant gamma interferon had no effect on the development of the parasite if added 24 h or later after the inoculation of sporozoites. Incubation of sporozoites in medium containing recombinant gamma interferon in no way affected their ability to invade or to grow within host cells. These findings indicate that the inhibitory effects of recombinant gamma interferon on the growth of E. vermiformis are mediated via the host cell and are directed mainly against the transforming sporozoite, although the ability of the sporozoite to invade the host cell was also reduced to some extent. The later developmental stages were refractory to the effects of this lymphokine.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Augustine P. C., Danforth H. D. A study of the dynamics of the invasion of immunized birds by Eimeria sporozoites. Avian Dis. 1986 Apr-Jun;30(2):347–351. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Balkwill F. R., Burke F. The cytokine network. Immunol Today. 1989 Sep;10(9):299–304. doi: 10.1016/0167-5699(89)90085-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chang E. H., Grollman E. F., Jay F. T., Lee G., Kohn L. D., Friedman R. M. Membrane alterations following interferon treatment. Adv Exp Med Biol. 1978;110:85–99. doi: 10.1007/978-1-4615-9080-4_8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chapman H. D. Studies on the excystation of different species of Eimeria in vitro. Z Parasitenkd. 1978 Jul 4;56(2):115–121. doi: 10.1007/BF00930742. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dijkema R., van der Meide P. H., Pouwels P. H., Caspers M., Dubbeld M., Schellekens H. Cloning and expression of the chromosomal immune interferon gene of the rat. EMBO J. 1985 Mar;4(3):761–767. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1985.tb03694.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ferreira A., Schofield L., Enea V., Schellekens H., van der Meide P., Collins W. E., Nussenzweig R. S., Nussenzweig V. Inhibition of development of exoerythrocytic forms of malaria parasites by gamma-interferon. Science. 1986 May 16;232(4752):881–884. doi: 10.1126/science.3085218. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hughes H. P., Speer C. A., Kyle J. E., Dubey J. P. Activation of murine macrophages and a bovine monocyte cell line by bovine lymphokines to kill the intracellular pathogens Eimeria bovis and Toxoplasma gondii. Infect Immun. 1987 Mar;55(3):784–791. doi: 10.1128/iai.55.3.784-791.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kelley G. L., Youssef N. N. Development in cell cultures of Eimeria vermiformis Ernst, Chobotar and Hammond, 1971. Z Parasitenkd. 1977 Aug 25;53(1):23–29. doi: 10.1007/BF00383111. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kogut M. H., Lange C. Interferon-gamma-mediated inhibition of the development of Eimeria tenella in cultured cells. J Parasitol. 1989 Apr;75(2):313–317. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kogut M. H., Lange C. Recombinant interferon-gamma inhibits cell invasion by Eimeria tenella. J Interferon Res. 1989 Feb;9(1):67–77. doi: 10.1089/jir.1989.9.67. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lillehoj H. S., Kang S. Y., Keller L., Sevoian M. Eimeria tenella and E. acervulina: lymphokines secreted by an avian T cell lymphoma or by sporozoite-stimulated immune T lymphocytes protect chickens against avian coccidiosis. Exp Parasitol. 1989 Jul;69(1):54–64. doi: 10.1016/0014-4894(89)90171-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McCabe R. E., Luft B. J., Remington J. S. Effect of murine interferon gamma on murine toxoplasmosis. J Infect Dis. 1984 Dec;150(6):961–962. doi: 10.1093/infdis/150.6.961. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mellouk S., Maheshwari R. K., Rhodes-Feuillette A., Beaudoin R. L., Berbiguier N., Matile H., Miltgen F., Landau I., Pied S., Chigot J. P. Inhibitory activity of interferons and interleukin 1 on the development of Plasmodium falciparum in human hepatocyte cultures. J Immunol. 1987 Dec 15;139(12):4192–4195. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Murray H. W., Rubin B. Y., Rothermel C. D. Killing of intracellular Leishmania donovani by lymphokine-stimulated human mononuclear phagocytes. Evidence that interferon-gamma is the activating lymphokine. J Clin Invest. 1983 Oct;72(4):1506–1510. doi: 10.1172/JCI111107. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Murray H. W., Spitalny G. L., Nathan C. F. Activation of mouse peritoneal macrophages in vitro and in vivo by interferon-gamma. J Immunol. 1985 Mar;134(3):1619–1622. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Onaga H., Tajima M., Ishii T. Activation of macrophages by culture fluid of antigen-stimulated spleen cells collected from chickens immunized with Eimeria tenella. Vet Parasitol. 1983 Aug;13(1):1–11. doi: 10.1016/0304-4017(83)90015-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Patton W. H. Eimeria tenella: cultivation of the asexual stages in cultured animal cells. Science. 1965 Nov 5;150(3697):767–769. doi: 10.1126/science.150.3697.767. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pfefferkorn E. R., Guyre P. M. Inhibition of growth of Toxoplasma gondii in cultured fibroblasts by human recombinant gamma interferon. Infect Immun. 1984 May;44(2):211–216. doi: 10.1128/iai.44.2.211-216.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reed S. G. In vivo administration of recombinant IFN-gamma induces macrophage activation, and prevents acute disease, immune suppression, and death in experimental Trypanosoma cruzi infections. J Immunol. 1988 Jun 15;140(12):4342–4347. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Riley D., Fernando M. A. Eimeria maxima (Apicomplexa): a comparison of sporozoite transport in naive and immune chickens. J Parasitol. 1988 Feb;74(1):103–110. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rose M. E., Lawn A. M., Millard B. J. The effect of immunity on the early events in the life-cycle of Eimeria tenella in the caecal mucosa of the chicken. Parasitology. 1984 Apr;88(Pt 2):199–210. doi: 10.1017/s0031182000054470. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rose M. E., Owen D. G., Hesketh P. Susceptibility to coccidiosis: effect of strain of mouse on reproduction of Eimeria vermiformis. Parasitology. 1984 Feb;88(Pt 1):45–54. doi: 10.1017/s0031182000054330. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rose M. E., Wakelin D., Hesketh P. Gamma interferon controls Eimeria vermiformis primary infection in BALB/c mice. Infect Immun. 1989 May;57(5):1599–1603. doi: 10.1128/iai.57.5.1599-1603.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sadick M. D., Locksley R. M., Tubbs C., Raff H. V. Murine cutaneous leishmaniasis: resistance correlates with the capacity to generate interferon-gamma in response to Leishmania antigens in vitro. J Immunol. 1986 Jan;136(2):655–661. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schellekens H., De Wilde G. A., Weimar W. Production and initial characterization of rat interferon. J Gen Virol. 1980 Jan;46(1):243–247. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-46-1-243. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schmatz D. M., Crane M. S., Murray P. K. Purification of Eimeria sporozoites by DE-52 anion exchange chromatography. J Protozool. 1984 Feb;31(1):181–183. doi: 10.1111/j.1550-7408.1984.tb04314.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schofield L., Ferreira A., Altszuler R., Nussenzweig V., Nussenzweig R. S. Interferon-gamma inhibits the intrahepatocytic development of malaria parasites in vitro. J Immunol. 1987 Sep 15;139(6):2020–2025. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schofield L., Villaquiran J., Ferreira A., Schellekens H., Nussenzweig R., Nussenzweig V. Gamma interferon, CD8+ T cells and antibodies required for immunity to malaria sporozoites. Nature. 1987 Dec 17;330(6149):664–666. doi: 10.1038/330664a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schwartzman J. D., Gonias S. L., Pfefferkorn E. R. Murine gamma interferon fails to inhibit Toxoplasma gondii growth in murine fibroblasts. Infect Immun. 1990 Mar;58(3):833–834. doi: 10.1128/iai.58.3.833-834.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Speer C. A., Reduker D. W., Burgess D. E., Whitmire W. M., Splitter G. A. Lymphokine-induced inhibition of growth of Eimeria bovis and Eimeria papillata (Apicomplexa) in cultured bovine monocytes. Infect Immun. 1985 Nov;50(2):566–571. doi: 10.1128/iai.50.2.566-571.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Suzuki Y., Orellana M. A., Schreiber R. D., Remington J. S. Interferon-gamma: the major mediator of resistance against Toxoplasma gondii. Science. 1988 Apr 22;240(4851):516–518. doi: 10.1126/science.3128869. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



