Abstract
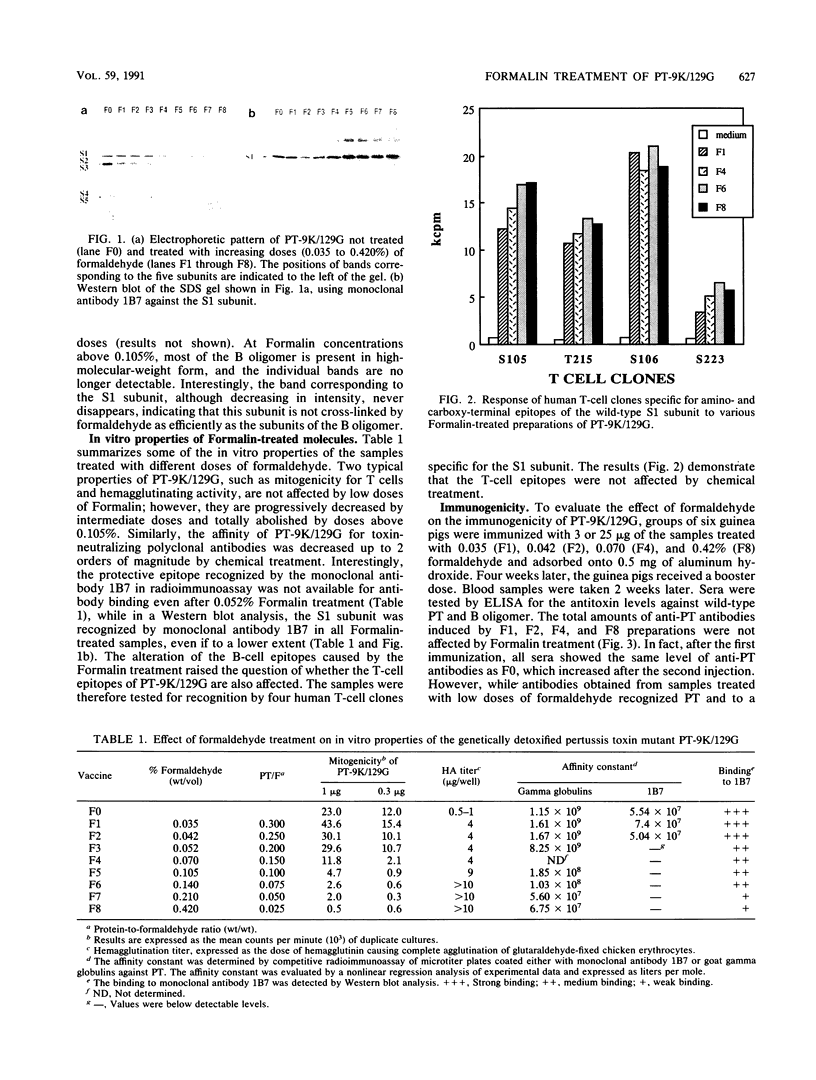
Formaldehyde treatment is a method routinely used to detoxify diphtheria, tetanus, and pertussis toxins as well as other molecules suitable for vaccine production. To investigate whether chemical detoxification alters the immunological properties of vaccine components, we have treated the pertussis toxin mutant PT-9K/129G with formaldehyde and tested the properties of the resulting molecules. Very low concentrations of formaldehyde stabilize the molecule without affecting the physicochemical and immunological parameters. Increasing doses of formaldehyde abolish the mitogenic and hemagglutinating activities of PT-9K/129G. At the same time, the molecule loses the ability to be recognized by a monoclonal antibody specific for a major protective epitope on the S1 subunit of pertussis toxin and its affinity for anti-pertussis toxin polyclonal antibodies is also reduced. In marked contrast, the ability of PT-9K/129G to be recognized by human T-cell clones is not affected by Formalin treatment. In vivo, the formaldehyde-treated molecules induce amounts of specific antibodies comparable with those of untreated molecules but significantly lower levels of toxin-neutralizing antibodies. Furthermore, the formaldehyde-treated molecules also show a reduced protective activity in the intracerebral challenge assay.
Full text
PDF


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- De Magistris M. T., Romano M., Bartoloni A., Rappuoli R., Tagliabue A. Human T cell clones define S1 subunit as the most immunogenic moiety of pertussis toxin and determine its epitope map. J Exp Med. 1989 May 1;169(5):1519–1532. doi: 10.1084/jem.169.5.1519. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- De Magistris M. T., Romano M., Nuti S., Rappuoli R., Tagliabue A. Dissecting human T cell responses against Bordetella species. J Exp Med. 1988 Oct 1;168(4):1351–1362. doi: 10.1084/jem.168.4.1351. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gillenius P., Jätmaa E., Askelöf P., Granström M., Tiru M. The standardization of an assay for pertussis toxin and antitoxin in microplate culture of Chinese hamster ovary cells. J Biol Stand. 1985 Jan;13(1):61–66. doi: 10.1016/s0092-1157(85)80034-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Granström M., Granström G., Gillenius P., Askelöf P. Neutralizing antibodies to pertussis toxin in whooping cough. J Infect Dis. 1985 Apr;151(4):646–649. doi: 10.1093/infdis/151.4.646. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kimura A., Mountzouros K. T., Schad P. A., Cieplak W., Cowell J. L. Pertussis toxin analog with reduced enzymatic and biological activities is a protective immunogen. Infect Immun. 1990 Oct;58(10):3337–3347. doi: 10.1128/iai.58.10.3337-3347.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LOWRY O. H., ROSEBROUGH N. J., FARR A. L., RANDALL R. J. Protein measurement with the Folin phenol reagent. J Biol Chem. 1951 Nov;193(1):265–275. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laemmli U. K. Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature. 1970 Aug 15;227(5259):680–685. doi: 10.1038/227680a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mariani M., Nucci D., Bracci L., Neri P., Antoni G. Determination of antigen-specific immunoglobulin content in ascitic fluids and antisera. J Immunol Methods. 1986 Sep 27;92(2):189–193. doi: 10.1016/0022-1759(86)90165-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nencioni L., Pizza M., Bugnoli M., De Magistris T., Di Tommaso A., Giovannoni F., Manetti R., Marsili I., Matteucci G., Nucci D. Characterization of genetically inactivated pertussis toxin mutants: candidates for a new vaccine against whooping cough. Infect Immun. 1990 May;58(5):1308–1315. doi: 10.1128/iai.58.5.1308-1315.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pizza M., Bugnoli M., Manetti R., Covacci A., Rappuoli R. The subunit S1 is important for pertussis toxin secretion. J Biol Chem. 1990 Oct 15;265(29):17759–17763. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Podda A., Nencioni L., De Magistris M. T., Di Tommaso A., Bossù P., Nuti S., Pileri P., Peppoloni S., Bugnoli M., Ruggiero P. Metabolic, humoral, and cellular responses in adult volunteers immunized with the genetically inactivated pertussis toxin mutant PT-9K/129G. J Exp Med. 1990 Sep 1;172(3):861–868. doi: 10.1084/jem.172.3.861. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sato Y., Cowell J. L., Sato H., Burstyn D. G., Manclark C. R. Separation and purification of the hemagglutinins from Bordetella pertussis. Infect Immun. 1983 Jul;41(1):313–320. doi: 10.1128/iai.41.1.313-320.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sekura R. D., Zhang Y. L., Roberson R., Acton B., Trollfors B., Tolson N., Shiloach J., Bryla D., Muir-Nash J., Koeller D. Clinical, metabolic, and antibody responses of adult volunteers to an investigational vaccine composed of pertussis toxin inactivated by hydrogen peroxide. J Pediatr. 1988 Nov;113(5):806–813. doi: 10.1016/s0022-3476(88)80005-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Storsaeter J., Olin P., Renemar B., Lagergård T., Norberg R., Romanus V., Tiru M. Mortality and morbidity from invasive bacterial infections during a clinical trial of acellular pertussis vaccines in Sweden. Pediatr Infect Dis J. 1988 Sep;7(9):637–645. doi: 10.1097/00006454-198809000-00008. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



