Abstract
The P2 porin protein is the major outer membrane protein of nontypeable Haemophilus influenzae. Five monoclonal antibodies to P2 of four strains of nontypeable H. influenzae were developed by immunizing mice with whole bacterial cells. All five antibodies recognized epitopes on P2 in immunoblot assays of whole organism lysates, purified outer membrane, and purified P2. Competitive enzyme-linked immunosorbent assays and immunoblot assays of cyanogen bromide-digested P2 showed that two antibodies to the P2 protein of strain 1479 recognized different epitopes on the molecule. Immunofluorescence and immunoelectron microscopy demonstrated that each of the five antibodies recognized epitopes that were abundantly expressed on the bacterial surface. Analysis of 120 H. influenzae strains indicated that three of the five antibodies were reactive exclusively with the homologous strain. The remaining two antibodies were reactive with less than 3% of the strains. These studies indicate that the P2 protein expresses a highly strain-specific and immunodominant epitope on the bacterial surface. The expression of strain-specific and immunodominant epitopes on the bacterial surface may represent a mechanism by which the bacterium induces antibodies that will protect against recurrent infection by the homologous strain but will not protect against infection by heterologous strains.
Full text
PDF


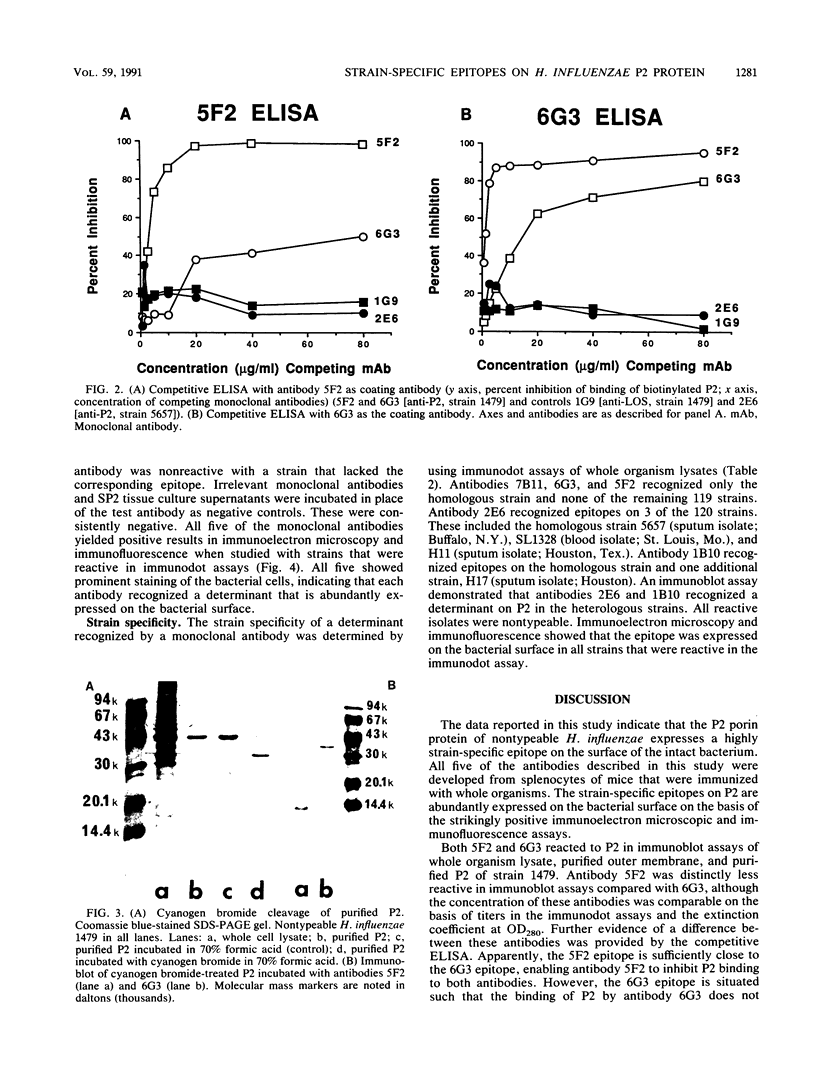
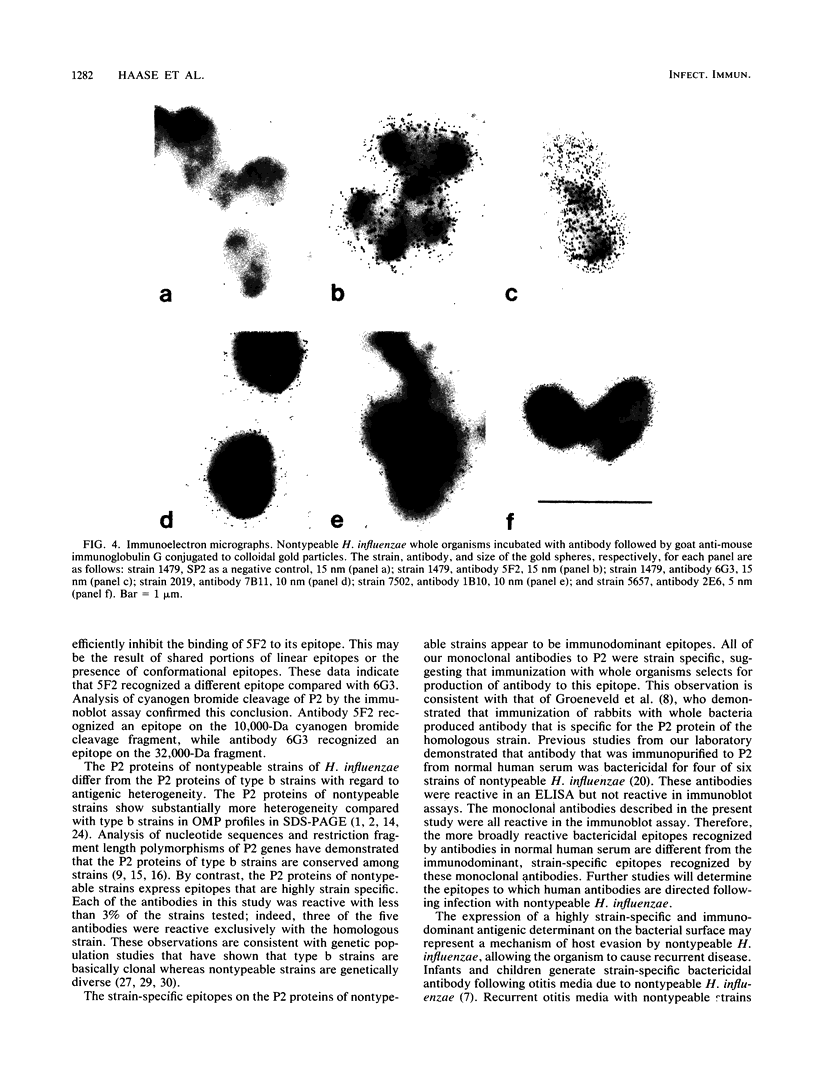


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Barenkamp S. J., Munson R. S., Jr, Granoff D. M. Outer membrane protein and biotype analysis of pathogenic nontypable Haemophilus influenzae. Infect Immun. 1982 May;36(2):535–540. doi: 10.1128/iai.36.2.535-540.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Barenkamp S. J., Munson R. S., Jr, Granoff D. M. Subtyping isolates of Haemophilus influenzae type b by outer-membrane protein profiles. J Infect Dis. 1981 May;143(5):668–676. doi: 10.1093/infdis/143.5.668. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Berk S. L., Holtsclaw S. A., Wiener S. L., Smith J. K. Nontypeable Haemophilus influenzae in the elderly. Arch Intern Med. 1982 Mar;142(3):537–539. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bluestone C. D. Otitis media in children: to treat or not to treat? N Engl J Med. 1982 Jun 10;306(23):1399–1404. doi: 10.1056/NEJM198206103062305. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Burns J. L., Mendelman P. M., Levy J., Stull T. L., Smith A. L. A permeability barrier as a mechanism of chloramphenicol resistance in Haemophilus influenzae. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1985 Jan;27(1):46–54. doi: 10.1128/aac.27.1.46. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Faden H., Bernstein J., Brodsky L., Stanievich J., Krystofik D., Shuff C., Hong J. J., Ogra P. L. Otitis media in children. I. The systemic immune response to nontypable Hemophilus influenzae. J Infect Dis. 1989 Dec;160(6):999–1004. doi: 10.1093/infdis/160.6.999. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Groeneveld K., van Alphen L., Voorter C., Eijk P. P., Jansen H. M., Zanen H. C. Antigenic drift of Haemophilus influenzae in patients with chronic obstructive pulmonary disease. Infect Immun. 1989 Oct;57(10):3038–3044. doi: 10.1128/iai.57.10.3038-3044.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hansen E. J., Pelzel S. E., Orth K., Moomaw C. R., Radolf J. D., Slaughter C. A. Structural and antigenic conservation of the P2 porin protein among strains of Haemophilus influenzae type b. Infect Immun. 1989 Nov;57(11):3270–3275. doi: 10.1128/iai.57.11.3270-3275.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Howie V. M., Ploussard J. H., Sloyer J. The "otitis-prone" condition. Am J Dis Child. 1975 Jun;129(6):676–678. doi: 10.1001/archpedi.1975.02120430016006. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kennett R. H. Cell fusion. Methods Enzymol. 1979;58:345–359. doi: 10.1016/s0076-6879(79)58149-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Klingman K. L., Jansen E. M., Murphy T. F. Nearest neighbor analysis of outer membrane proteins of nontypeable Haemophilus influenzae. Infect Immun. 1988 Dec;56(12):3058–3063. doi: 10.1128/iai.56.12.3058-3063.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laemmli U. K. Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature. 1970 Aug 15;227(5259):680–685. doi: 10.1038/227680a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Loeb M. R., Smith D. H. Outer membrane protein composition in disease isolates of Haemophilus influenzae: pathogenic and epidemiological implications. Infect Immun. 1980 Dec;30(3):709–717. doi: 10.1128/iai.30.3.709-717.1980. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Munson R. S., Jr, Shenep J. L., Barenkamp S. J., Granoff D. M. Purification and comparison of outer membrane protein P2 from Haemophilus influenzae type b isolates. J Clin Invest. 1983 Aug;72(2):677–684. doi: 10.1172/JCI111017. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Munson R., Jr, Bailey C., Grass S. Diversity of the outer membrane protein P2 gene from major clones of Haemophilus influenzae type b. Mol Microbiol. 1989 Dec;3(12):1797–1803. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2958.1989.tb00165.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Munson R., Jr, Tolan R. W., Jr Molecular cloning, expression, and primary sequence of outer membrane protein P2 of Haemophilus influenzae type b. Infect Immun. 1989 Jan;57(1):88–94. doi: 10.1128/iai.57.1.88-94.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Murphy T. F., Apicella M. A. Antigenic heterogeneity of outer membrane proteins of nontypable Haemophilus influenzae is a basis for a serotyping system. Infect Immun. 1985 Oct;50(1):15–21. doi: 10.1128/iai.50.1.15-21.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Murphy T. F., Apicella M. A. Nontypable Haemophilus influenzae: a review of clinical aspects, surface antigens, and the human immune response to infection. Rev Infect Dis. 1987 Jan-Feb;9(1):1–15. doi: 10.1093/clinids/9.1.1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Murphy T. F., Bartos L. C., Campagnari A. A., Nelson M. B., Apicella M. A. Antigenic characterization of the P6 protein of nontypable Haemophilus influenzae. Infect Immun. 1986 Dec;54(3):774–779. doi: 10.1128/iai.54.3.774-779.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Murphy T. F., Bartos L. C. Human bactericidal antibody response to outer membrane protein P2 of nontypeable Haemophilus influenzae. Infect Immun. 1988 Oct;56(10):2673–2679. doi: 10.1128/iai.56.10.2673-2679.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Murphy T. F., Bartos L. C. Purification and analysis with monoclonal antibodies of P2, the major outer membrane protein of nontypable Haemophilus influenzae. Infect Immun. 1988 May;56(5):1084–1089. doi: 10.1128/iai.56.5.1084-1089.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Murphy T. F., Bernstein J. M., Dryja D. M., Campagnari A. A., Apicella M. A. Outer membrane protein and lipooligosaccharide analysis of paired nasopharyngeal and middle ear isolates in otitis media due to nontypable Haemophilus influenzae: pathogenetic and epidemiological observations. J Infect Dis. 1987 Nov;156(5):723–731. doi: 10.1093/infdis/156.5.723. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Murphy T. F., Dudas K. C., Mylotte J. M., Apicella M. A. A subtyping system for nontypable Haemophilus influenzae based on outer-membrane proteins. J Infect Dis. 1983 May;147(5):838–846. doi: 10.1093/infdis/147.5.838. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Murphy T. F., Nelson M. B., Dudas K. C., Mylotte J. M., Apicella M. A. Identification of a specific epitope of Haemophilus influenzae on a 16,600-dalton outer membrane protein. J Infect Dis. 1985 Dec;152(6):1300–1307. doi: 10.1093/infdis/152.6.1300. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Musher D. M., Kubitschek K. R., Crennan J., Baughn R. E. Pneumonia and acute febrile tracheobronchitis due to haemophilus influenzae. Ann Intern Med. 1983 Oct;99(4):444–450. doi: 10.7326/0003-4819-99-4-444. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Musser J. M., Barenkamp S. J., Granoff D. M., Selander R. K. Genetic relationships of serologically nontypable and serotype b strains of Haemophilus influenzae. Infect Immun. 1986 Apr;52(1):183–191. doi: 10.1128/iai.52.1.183-191.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Osborn M. J., Gander J. E., Parisi E., Carson J. Mechanism of assembly of the outer membrane of Salmonella typhimurium. Isolation and characterization of cytoplasmic and outer membrane. J Biol Chem. 1972 Jun 25;247(12):3962–3972. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Porras O., Caugant D. A., Gray B., Lagergård T., Levin B. R., Svanborg-Edén C. Difference in structure between type b and nontypable Haemophilus influenzae populations. Infect Immun. 1986 Jul;53(1):79–89. doi: 10.1128/iai.53.1.79-89.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Porras O., Caugant D. A., Lagergård T., Svanborg-Edén C. Application of multilocus enzyme gel electrophoresis to Haemophilus influenzae. Infect Immun. 1986 Jul;53(1):71–78. doi: 10.1128/iai.53.1.71-78.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Straley S. C., Brubaker R. R. Cytoplasmic and membrane proteins of yersiniae cultivated under conditions simulating mammalian intracellular environment. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1981 Feb;78(2):1224–1228. doi: 10.1073/pnas.78.2.1224. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stratton C. W., Hawley H. B., Horsman T. A., Tu K. K., Ackley A., Fernando N. K., Weinstein M. P. Hemophilus influenzae pneumonia in adults: report of five cases caused by ampicillin-resistant strains. Am Rev Respir Dis. 1980 Mar;121(3):595–598. doi: 10.1164/arrd.1980.121.3.595. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Teele D. W., Klein J. O., Rosner B., Bratton L., Fisch G. R., Mathieu O. R., Porter P. J., Starobin S. G., Tarlin L. D., Younes R. P. Middle ear disease and the practice of pediatrics. Burden during the first five years of life. JAMA. 1983 Feb 25;249(8):1026–1029. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vachon V., Kristjanson D. N., Coulton J. W. Outer membrane porin protein of Haemophilus influenzae type b: pore size and subunit structure. Can J Microbiol. 1988 Feb;34(2):134–140. doi: 10.1139/m88-027. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vachon V., Lyew D. J., Coulton J. W. Transmembrane permeability channels across the outer membrane of Haemophilus influenzae type b. J Bacteriol. 1985 Jun;162(3):918–924. doi: 10.1128/jb.162.3.918-924.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Verghese A., Berk S. L. Bacterial pneumonia in the elderly. Medicine (Baltimore) 1983 Sep;62(5):271–285. doi: 10.1097/00005792-198309000-00002. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wald E. R., Milmoe G. J., Bowen A., Ledesma-Medina J., Salamon N., Bluestone C. D. Acute maxillary sinusitis in children. N Engl J Med. 1981 Mar 26;304(13):749–754. doi: 10.1056/NEJM198103263041302. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wallace R. J., Jr, Baker C. J., Quinones F. J., Hollis D. G., Weaver R. E., Wiss K. Nontypable Haemophilus influenzae (biotype 4) as a neonatal, maternal, and genital pathogen. Rev Infect Dis. 1983 Jan-Feb;5(1):123–136. doi: 10.1093/clinids/5.1.123. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wallace R. J., Jr, Musher D. M., Septimus E. J., McGowan J. E., Jr, Quinones F. J., Wiss K., Vance P. H., Trier P. A. Haemophilus influenzae infections in adults: characterization of strains by serotypes, biotypes, and beta-lactamase production. J Infect Dis. 1981 Aug;144(2):101–106. doi: 10.1093/infdis/144.2.101. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weinberg G. A., Ghafoor A., Ishaq Z., Nomani N. K., Kabeer M., Anwar F., Burney M. I., Qureshi A. W., Musser J. M., Selander R. K. Clonal analysis of Hemophilus influenzae isolated from children from Pakistan with lower respiratory tract infections. J Infect Dis. 1989 Oct;160(4):634–643. doi: 10.1093/infdis/160.4.634. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]





