Abstract
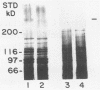
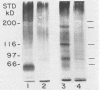
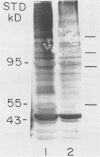
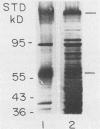
Strains of Candida albicans, selected on the basis of their reduced agglutination with a polyclonal anti-Candida antiserum, were tested for their adherence to human buccal epithelial cells (BEC). Of four strains, one (A9V2) had reduced binding to BEC in vitro. Adherence of wild type (wt) yeast cells (A9), as measured by the percentage of BEC with adhering Candida cells, was 73.4% +/- 3.8% compared with 49.3% +/- 3.1% for A9V2 (P less than 0.01). From yeast cells of A9 and A9V2, whole-cell extracts and dithiothreitol-, Zymolyase-, or beta-mercaptoethanol-solubilized cell extracts were compared by sodium dodecyl sulfate-polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis and Western blotting (immunoblotting). From dithiothreitol-solubilized cell extracts, proteins with molecular masses of 55 to 60, 80 to 84, 115, and 165 kDa were observed from wt (A9) cells but were highly reduced in amount or absent from A9V2 cells. Western blot profiles of Zymolyase-solubilized extracts from both A9 and A9V2 were similar in appearance, while 55-, 80- to 84-, 115-, and 165-kDa proteins were observed only in A9 cells extracted with beta-mercaptoethanol. Strain A9V4, also selected by reduced agglutination but which adhered as well as strain A9, lacked the 80- to 84-kDa and 115-kDa proteins but otherwise was similar to strain A9. These results indicate that the 55- to 60- and 165-kDa proteins may be related to an adhesin function in C. albicans. The differences observed in the protein profiles of the wt adhering strain and its derived nonadhering mutant are similar to those described for another matched pair of C. albicans strains.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Calderone R. A., Cihlar R. L., Lee D. D., Hoberg K., Scheld W. M. Yeast adhesion in the pathogenesis of endocarditis due to Candida albicans: studies with adherence-negative mutants. J Infect Dis. 1985 Oct;152(4):710–715. doi: 10.1093/infdis/152.4.710. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Calderone R. A., Lehrer N., Segal E. Adherence of Candida albicans to buccal and vaginal epithelial cells: ultrastructural observations. Can J Microbiol. 1984 Aug;30(8):1001–1007. doi: 10.1139/m84-156. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Calderone R. A., Linehan L., Wadsworth E., Sandberg A. L. Identification of C3d receptors on Candida albicans. Infect Immun. 1988 Jan;56(1):252–258. doi: 10.1128/iai.56.1.252-258.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Calderone R., Wadsworth E. Characterization with crossed immunoelectrophoresis of some antigens differentiating a virulent Candida albicans from its derived, avirulent strain. Proc Soc Exp Biol Med. 1987 Jul;185(3):325–334. doi: 10.3181/00379727-185-42552. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Critchley I. A., Douglas L. J. Role of glycosides as epithelial cell receptors for Candida albicans. J Gen Microbiol. 1987 Mar;133(3):637–643. doi: 10.1099/00221287-133-3-637. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Douglas L. J. Adhesion of Candida species to epithelial surfaces. Crit Rev Microbiol. 1987;15(1):27–43. doi: 10.3109/10408418709104446. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Edwards J. E., Jr, Gaither T. A., O'Shea J. J., Rotrosen D., Lawley T. J., Wright S. A., Frank M. M., Green I. Expression of specific binding sites on Candida with functional and antigenic characteristics of human complement receptors. J Immunol. 1986 Dec 1;137(11):3577–3583. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eigentler A., Schulz T. F., Larcher C., Breitwieser E. M., Myones B. L., Petzer A. L., Dierich M. P. C3bi-binding protein on Candida albicans: temperature-dependent expression and relationship to human complement receptor type 3. Infect Immun. 1989 Feb;57(2):616–622. doi: 10.1128/iai.57.2.616-622.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gilmore B. J., Retsinas E. M., Lorenz J. S., Hostetter M. K. An iC3b receptor on Candida albicans: structure, function, and correlates for pathogenicity. J Infect Dis. 1988 Jan;157(1):38–46. doi: 10.1093/infdis/157.1.38. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Heidenreich F., Dierich M. P. Candida albicans and Candida stellatoidea, in contrast to other Candida species, bind iC3b and C3d but not C3b. Infect Immun. 1985 Nov;50(2):598–600. doi: 10.1128/iai.50.2.598-600.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hoberg K. A., Cihlar R. L., Calderone R. A. Characterization of cerulenin-resistant mutants of Candida albicans. Infect Immun. 1986 Jan;51(1):102–109. doi: 10.1128/iai.51.1.102-109.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hostetter M. K., Lorenz J. S., Preus L., Kendrick K. E. The iC3b receptor on Candida albicans: subcellular localization and modulation of receptor expression by glucose. J Infect Dis. 1990 Apr;161(4):761–768. doi: 10.1093/infdis/161.4.761. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- King R. D., Lee J. C., Morris A. L. Adherence of Candida albicans and other Candida species to mucosal epithelial cells. Infect Immun. 1980 Feb;27(2):667–674. doi: 10.1128/iai.27.2.667-674.1980. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lee J. C., King R. D. Characterization of Candida albicans adherence to human vaginal epithelial cells in vitro. Infect Immun. 1983 Sep;41(3):1024–1030. doi: 10.1128/iai.41.3.1024-1030.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lee K. L., Buckley H. R., Campbell C. C. An amino acid liquid synthetic medium for the development of mycelial and yeast forms of Candida Albicans. Sabouraudia. 1975 Jul;13(2):148–153. doi: 10.1080/00362177585190271. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lehrer N., Segal E., Cihlar R. L., Calderone R. A. Pathogenesis of vaginal candidiasis: studies with a mutant which has reduced ability to adhere in vitro. J Med Vet Mycol. 1986 Apr;24(2):127–131. doi: 10.1080/02681218680000191. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Linehan L., Wadsworth E., Calderone R. Candida albicans C3d receptor, isolated by using a monoclonal antibody. Infect Immun. 1988 Aug;56(8):1981–1986. doi: 10.1128/iai.56.8.1981-1986.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miyakawa Y., Kagaya K., Kuribayashi T., Suzuki M., Fukazawa Y. Isolation and chemical and biological characterization of antigenic mutants of Candida albicans serotype A. Yeast. 1989 Apr;5(Spec No):S225–S229. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ollert M. W., Calderone R. A. A monoclonal antibody that defines a surface antigen on Candida albicans hyphae cross-reacts with yeast cell protoplasts. Infect Immun. 1990 Mar;58(3):625–631. doi: 10.1128/iai.58.3.625-631.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ollert M. W., Wadsworth E., Calderone R. A. Reduced expression of the functionally active complement receptor for iC3b but not for C3d on an avirulent mutant of Candida albicans. Infect Immun. 1990 Apr;58(4):909–913. doi: 10.1128/iai.58.4.909-913.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ray T. L., Digre K. B., Payne C. D. Adherence of Candida species to human epidermal corneocytes and buccal mucosal cells: correlation with cutaneous pathogenicity. J Invest Dermatol. 1984 Jul;83(1):37–41. doi: 10.1111/1523-1747.ep12261661. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rotrosen D., Calderone R. A., Edwards J. E., Jr Adherence of Candida species to host tissues and plastic surfaces. Rev Infect Dis. 1986 Jan-Feb;8(1):73–85. doi: 10.1093/clinids/8.1.73. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Saxena A., Calderone R. Purification and characterization of the extracellular C3d-binding protein of Candida albicans. Infect Immun. 1990 Feb;58(2):309–314. doi: 10.1128/iai.58.2.309-314.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tronchin G., Bouchara J. P., Robert R. Dynamic changes of the cell wall surface of Candida albicans associated with germination and adherence. Eur J Cell Biol. 1989 Dec;50(2):285–290. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Whelan W. L., Delga J. M., Wadsworth E., Walsh T. J., Kwon-Chung K. J., Calderone R., Lipke P. N. Isolation and characterization of cell surface mutants of Candida albicans. Infect Immun. 1990 Jun;58(6):1552–1557. doi: 10.1128/iai.58.6.1552-1557.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]