Abstract
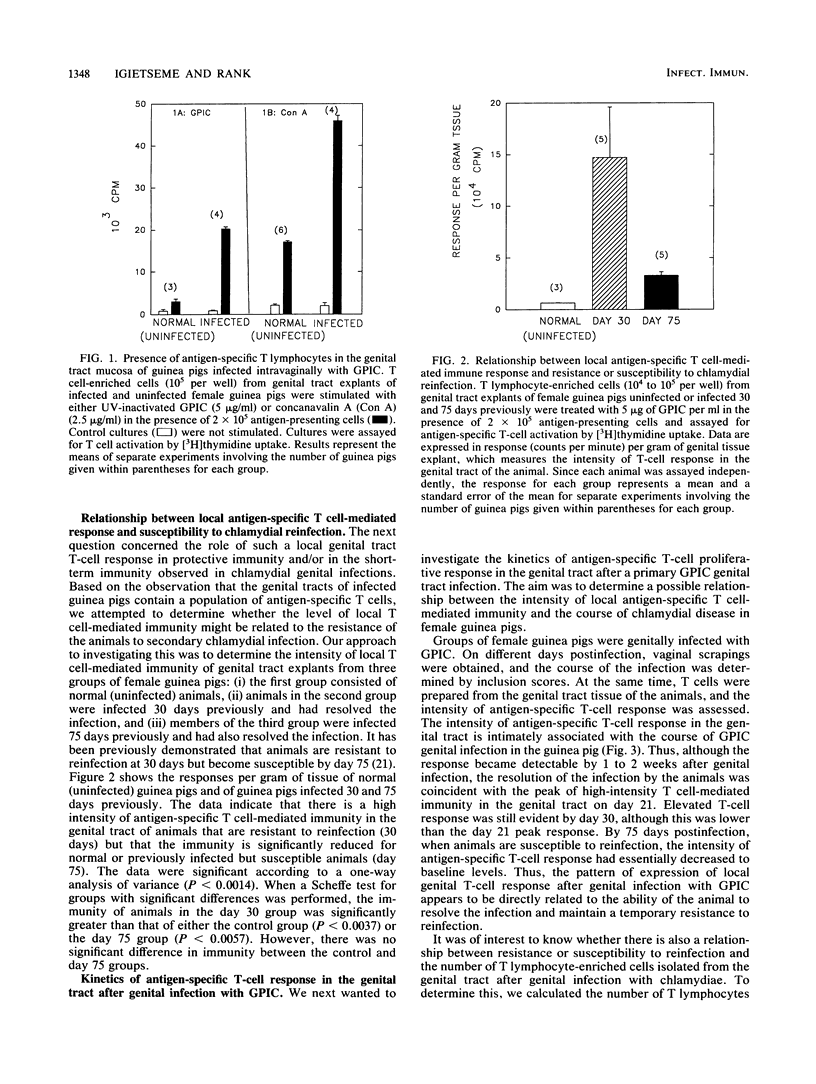
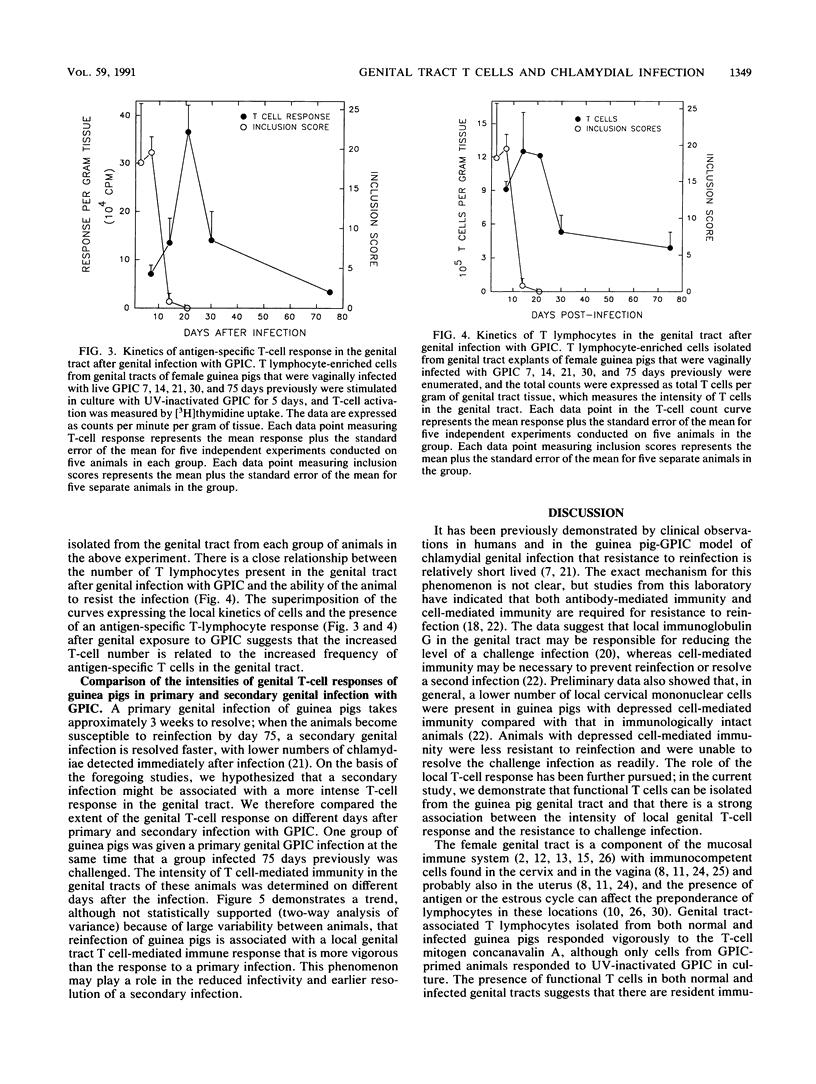
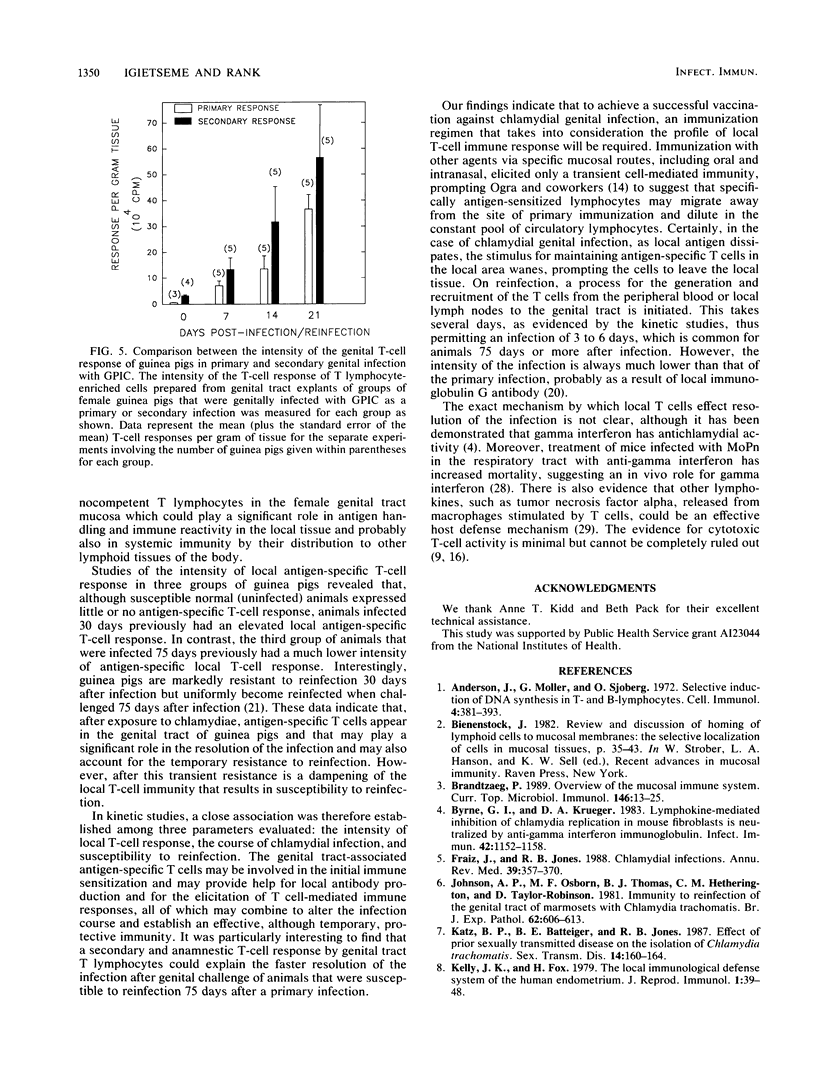
We tested the hypothesis that the intensity of specific antichlamydial T cell-mediated immunity in the genital tract of female guinea pigs infected intravaginally with the chlamydial agent of guinea pig inclusion conjunctivitis would determine the resistance or susceptibility to reinfection after a primary chlamydial infection. T cell-enriched lymphocytes were isolated by collagenase treatment of genital tract tissues from either infected or control uninfected female guinea pigs at various times after infection. The nylon wool-enriched T lymphocytes were evaluated for expression of antigen-specific T cell-mediated immunity in vitro by using a blast transformation assay. Both uninfected and infected genital tracts contained T cells, as evidenced by reactivity to concanavalin A, although a greater number of T lymphocytes was detected in the genital tracts of infected animals compared with that in controls. Significant antigen-specific T-cell activity could be detected in the genital tract tissue by 7 days after a primary genital tract infection with the chlamydial agent of guinea pig inclusion conjunctivitis. When antigen-specific activity was assessed at different times after infection, the intensity of the response of genital tract-associated T lymphocytes was directly proportional to the degree of resistance of the animals to genital challenge. Thus, susceptibility of animals to reinfection by chlamydiae appears to be associated with the intensity of the local T cell-mediated immune responses in the genital tract of infected animals.
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Andersson J., Möller G., Sjöberg O. Selective induction of DNA synthesis in T and B lymphocytes. Cell Immunol. 1972 Aug;4(4):381–393. doi: 10.1016/0008-8749(72)90040-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brandtzaeg P. Overview of the mucosal immune system. Curr Top Microbiol Immunol. 1989;146:13–25. doi: 10.1007/978-3-642-74529-4_2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Byrne G. I., Krueger D. A. Lymphokine-mediated inhibition of Chlamydia replication in mouse fibroblasts is neutralized by anti-gamma interferon immunoglobulin. Infect Immun. 1983 Dec;42(3):1152–1158. doi: 10.1128/iai.42.3.1152-1158.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fraiz J., Jones R. B. Chlamydial infections. Annu Rev Med. 1988;39:357–370. doi: 10.1146/annurev.me.39.020188.002041. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Johnson A. P., Osborn M. F., Thomas B. J., Hetherington C. M., Taylor-Robinson D. Immunity to reinfection of the genital tract of marmosets with Chlamydia trachomatis. Br J Exp Pathol. 1981 Dec;62(6):606–613. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Katz B. P., Batteiger B. E., Jones R. B. Effect of prior sexually transmitted disease on the isolation of Chlamydia trachomatis. Sex Transm Dis. 1987 Jul-Sep;14(3):160–164. doi: 10.1097/00007435-198707000-00008. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kelly J. K., Fox H. The local immunological defence system of the human endometrium. J Reprod Immunol. 1979 Jan-Feb;1(1):39–45. doi: 10.1016/0165-0378(79)90028-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lammert J. K. Cytotoxic cells induced after Chlamydia psittaci infection in mice. Infect Immun. 1982 Mar;35(3):1011–1017. doi: 10.1128/iai.35.3.1011-1017.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Larsen B., Markovetz A. J., Galask R. P. Quantitative alterations in the genital microflora of female rats in relation to the estrous cycle. J Infect Dis. 1976 Nov;134(5):486–489. doi: 10.1093/infdis/134.5.486. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McDermott M. R., Bienenstock J. Evidence for a common mucosal immunologic system. I. Migration of B immunoblasts into intestinal, respiratory, and genital tissues. J Immunol. 1979 May;122(5):1892–1898. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McDermott M. R., Clark D. A., Bienenstock J. Evidence for a common mucosal immunologic system. II. Influence of the estrous cycle on B immunoblast migration into genital and intestinal tissues. J Immunol. 1980 Jun;124(6):2536–2539. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ogra P. L., Chiba Y., Beutner K. R., Morag A. Vaccination by non-parenteral routes: characteristics of immune response. Dev Biol Stand. 1976;33:19–26. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pavia C. S., Schachter J. Failure to detect cell-mediated cytotoxicity against Chlamydia trachomatis-infected cells. Infect Immun. 1983 Mar;39(3):1271–1274. doi: 10.1128/iai.39.3.1271-1274.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ramsey K. H., Soderberg L. S., Rank R. G. Resolution of chlamydial genital infection in B-cell-deficient mice and immunity to reinfection. Infect Immun. 1988 May;56(5):1320–1325. doi: 10.1128/iai.56.5.1320-1325.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rank R. G., Barron A. L. Effect of antithymocyte serum on the course of chlamydial genital infection in female guinea pigs. Infect Immun. 1983 Aug;41(2):876–879. doi: 10.1128/iai.41.2.876-879.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rank R. G., Barron A. L. Humoral immune response in acquired immunity to chlamydial genital infection of female guinea pigs. Infect Immun. 1983 Jan;39(1):463–465. doi: 10.1128/iai.39.1.463-465.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rank R. G., Batteiger B. E. Protective role of serum antibody in immunity to chlamydial genital infection. Infect Immun. 1989 Jan;57(1):299–301. doi: 10.1128/iai.57.1.299-301.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rank R. G., Batteiger B. E., Soderberg L. S. Susceptibility to reinfection after a primary chlamydial genital infection. Infect Immun. 1988 Sep;56(9):2243–2249. doi: 10.1128/iai.56.9.2243-2249.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rank R. G., Soderberg L. S., Sanders M. M., Batteiger B. E. Role of cell-mediated immunity in the resolution of secondary chlamydial genital infection in guinea pigs infected with the agent of guinea pig inclusion conjunctivitis. Infect Immun. 1989 Mar;57(3):706–710. doi: 10.1128/iai.57.3.706-710.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rank R. G., White H. J., Barron A. L. Humoral immunity in the resolution of genital infection in female guinea pigs infected with the agent of guinea pig inclusion conjunctivitis. Infect Immun. 1979 Nov;26(2):573–579. doi: 10.1128/iai.26.2.573-579.1979. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rebello R., Green F. H., Fox H. A study of the secretory immune system of the female genital tract. Br J Obstet Gynaecol. 1975 Oct;82(10):812–816. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tourville D. R., Ogra S. S., Lippes J., Tomasi T. B., Jr The human female reproductive tract: immunohistological localization of gamma A, gamma G, gamma M, secretory "piece," and lactoferrin. Am J Obstet Gynecol. 1970 Dec 1;108(7):1102–1108. doi: 10.1016/0002-9378(70)90460-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vaerman J. P., Férin J. Local immunological response in the vagina, cervix and endometrium. Acta Endocrinol Suppl (Copenh) 1975;194:281–305. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Williams D. M., Byrne G. I., Grubbs B., Marshal T. J., Schachter J. Role in vivo for gamma interferon in control of pneumonia caused by Chlamydia trachomatis in mice. Infect Immun. 1988 Nov;56(11):3004–3006. doi: 10.1128/iai.56.11.3004-3006.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Williams D. M., Magee D. M., Bonewald L. F., Smith J. G., Bleicker C. A., Byrne G. I., Schachter J. A role in vivo for tumor necrosis factor alpha in host defense against Chlamydia trachomatis. Infect Immun. 1990 Jun;58(6):1572–1576. doi: 10.1128/iai.58.6.1572-1576.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wira C. R., Merritt K. Effect of the estrous cycle, castration and pseudopregnancy on E. coli in the uterus and uterine secretions of the rat. Biol Reprod. 1977 Nov;17(4):519–522. doi: 10.1095/biolreprod17.4.519. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


