Abstract
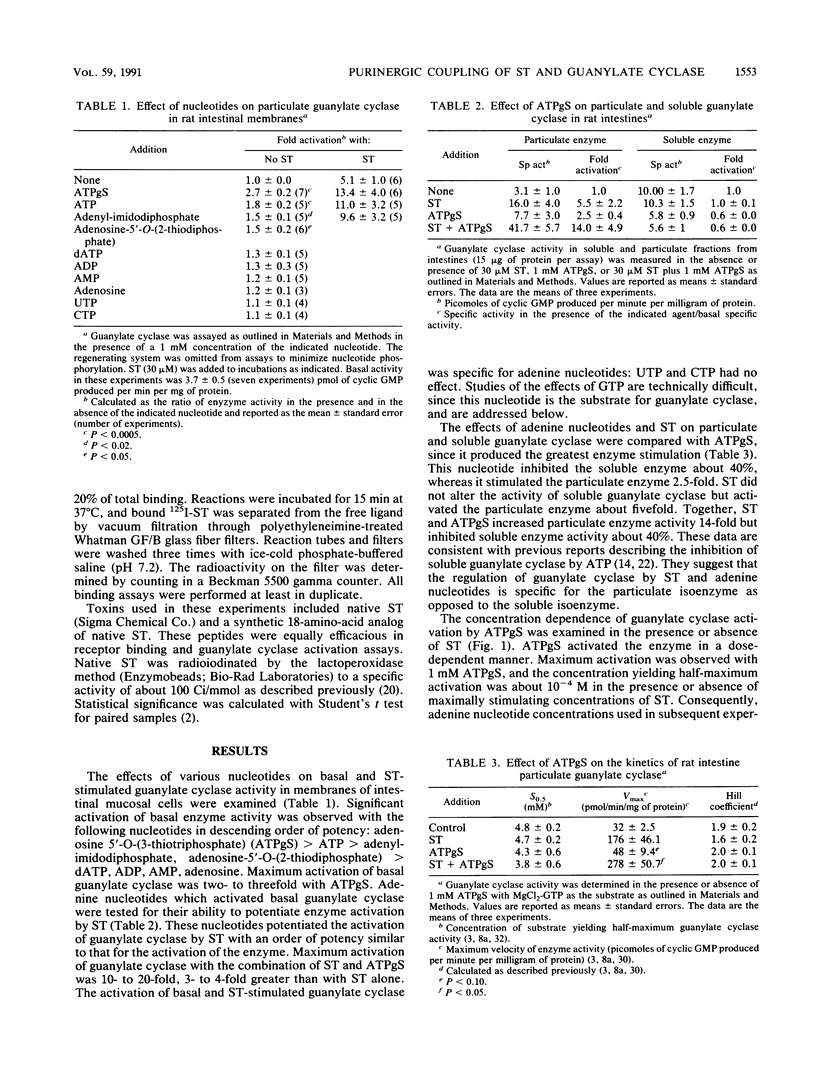
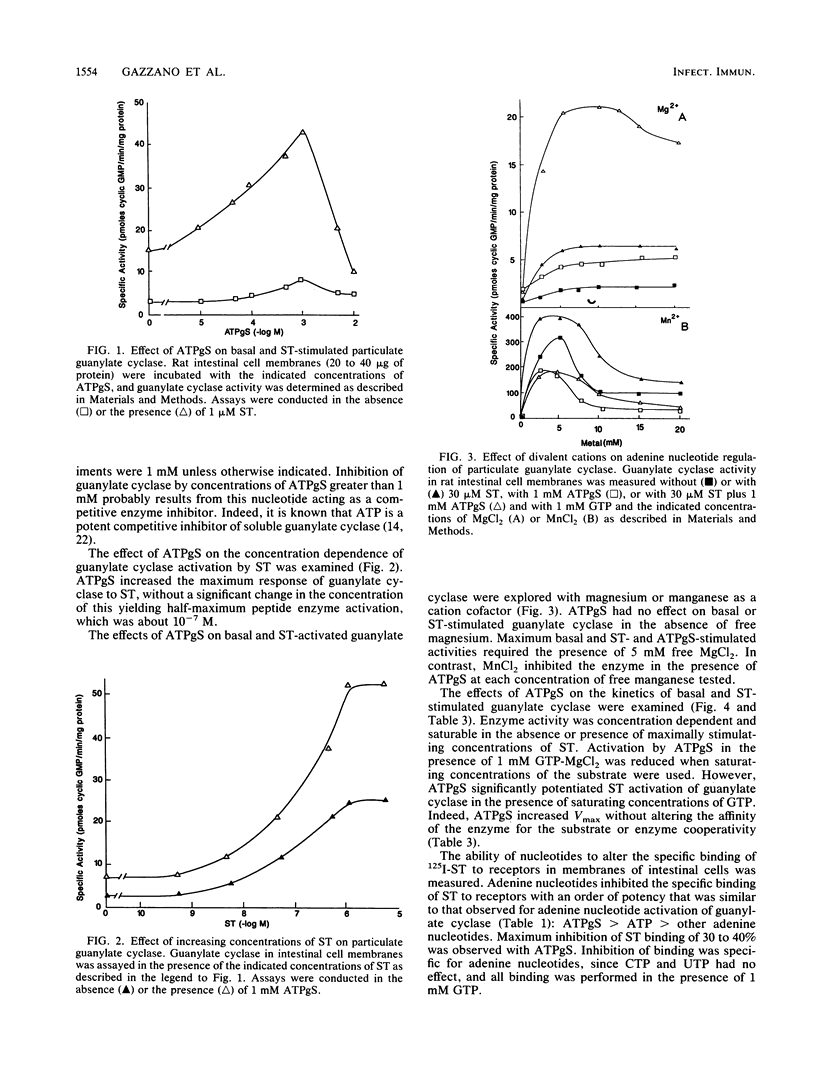
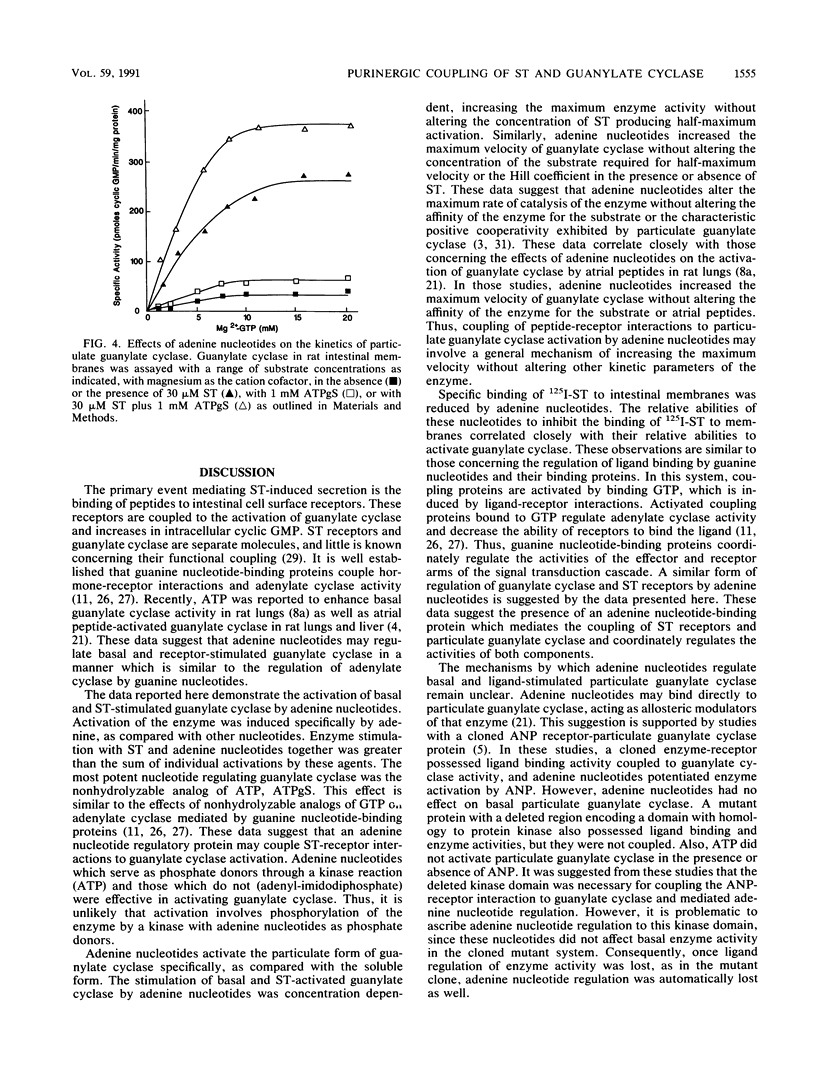
Guanylate cyclase is regulated by adenine nucleotides in membranes of intestinal mucosal cells. Basal guanylate cyclase was activated about twofold by adenine nucleotides. Activation was specific for adenine, as compared with the pyrimidine nucleotides UTP and CTP. In addition, enzyme activation was obtained in the presence of saturating concentrations of GTP, the substrate for guanylate cyclase. The most potent adenine nucleotide was the nonhydrolyzable analog of ATP, adenosine 5'-O-(3-thiotriphosphate). Adenine nucleotide activation was specific for the particulate form of guanylate cyclase, as compared with the soluble form. Also, adenine nucleotides potentiated the activation of guanylate cyclase by the heat-stable enterotoxin produced by Escherichia coli. Indeed, enzyme activation by adenine nucleotides and toxin was greater than the sum of individual activations by these agents. Adenine nucleotides regulate guanylate cyclase by increasing the maximum velocity of the enzyme without altering its affinity for substrate or its cooperativity. In addition to stimulating guanylate cyclase, adenine nucleotides decreased the specific binding of the heat-stable enterotoxin to receptors in intestinal membranes. The coordinated regulation of the toxin-receptor interaction and guanylate cyclase activity by a process utilizing nonhydrolyzable analogs of a purine nucleotide is similar to the mechanisms involved in the hormone regulation of adenylate cyclase by guanine nucleotide-binding proteins. These data suggest that an adenine nucleotide-dependent protein may couple the toxin-receptor interaction to the regulation of particulate guanylate cyclase in intestinal membranes.
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Banwell J. G., Sherr H. Effect of bacterial enterotoxins on the gastrointestinal tract. Gastroenterology. 1973 Sep;65(3):467–497. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carr S., Gazzano H., Waldman S. A. Regulation of particulate guanylate cyclase by Escherichia coli heat-stable enterotoxin: receptor binding and enzyme kinetics. Int J Biochem. 1989;21(11):1211–1215. doi: 10.1016/0020-711x(89)90005-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chang C. H., Kohse K. P., Chang B., Hirata M., Jiang B., Douglas J. E., Murad F. Characterization of ATP-stimulated guanylate cyclase activation in rat lung membranes. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1990 Apr 9;1052(1):159–165. doi: 10.1016/0167-4889(90)90071-k. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chinkers M., Garbers D. L. The protein kinase domain of the ANP receptor is required for signaling. Science. 1989 Sep 22;245(4924):1392–1394. doi: 10.1126/science.2571188. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dreyfus L. A., Jaso-Friedmann L., Robertson D. C. Characterization of the mechanism of action of Escherichia coli heat-stable enterotoxin. Infect Immun. 1984 May;44(2):493–501. doi: 10.1128/iai.44.2.493-501.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Field M., Graf L. H., Jr, Laird W. J., Smith P. L. Heat-stable enterotoxin of Escherichia coli: in vitro effects on guanylate cyclase activity, cyclic GMP concentration, and ion transport in small intestine. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1978 Jun;75(6):2800–2804. doi: 10.1073/pnas.75.6.2800. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Frantz J. C., Jaso-Friedman L., Robertson D. C. Binding of Escherichia coli heat-stable enterotoxin to rat intestinal cells and brush border membranes. Infect Immun. 1984 Feb;43(2):622–630. doi: 10.1128/iai.43.2.622-630.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Giannella R. A. Pathogenesis of acute bacterial diarrheal disorders. Annu Rev Med. 1981;32:341–357. doi: 10.1146/annurev.me.32.020181.002013. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gilman A. G. G proteins: transducers of receptor-generated signals. Annu Rev Biochem. 1987;56:615–649. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.56.070187.003151. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Guerrant R. L., Hughes J. M., Chang B., Robertson D. C., Murad F. Activation of intestinal guanylate cyclase by heat-stable enterotoxin of Escherichia coli: studies of tissue specificity, potential receptors, and intermediates. J Infect Dis. 1980 Aug;142(2):220–228. doi: 10.1093/infdis/142.2.220. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hardman J. G., Sutherland E. W. Guanyl cyclase, an enzyme catalyzing the formation of guanosine 3',5'-monophosphate from guanosine trihosphate. J Biol Chem. 1969 Dec 10;244(23):6363–6370. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hughes J. M., Murad F., Chang B., Guerrant R. L. Role of cyclic GMP in the action of heat-stable enterotoxin of Escherichia coli. Nature. 1978 Feb 23;271(5647):755–756. doi: 10.1038/271755a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ishikawa E., Ishikawa S., Davis J. W., Sutherland E. W. Determination of guanosine 3',5'-monophosphate in tissues and of guanyl cyclase in rat intestine. J Biol Chem. 1969 Dec 10;244(23):6371–6376. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ivens K., Gazzano H., O'Hanley P., Waldman S. A. Heterogeneity of intestinal receptors for Escherichia coli heat-stable enterotoxin. Infect Immun. 1990 Jun;58(6):1817–1820. doi: 10.1128/iai.58.6.1817-1820.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kimura H., Murad F. Evidence for two different forms of guanylate cyclase in rat heart. J Biol Chem. 1974 Nov 10;249(21):6910–6916. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kuno T., Andresen J. W., Kamisaki Y., Waldman S. A., Chang L. Y., Saheki S., Leitman D. C., Nakane M., Murad F. Co-purification of an atrial natriuretic factor receptor and particulate guanylate cyclase from rat lung. J Biol Chem. 1986 May 5;261(13):5817–5823. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kuno T., Kamisaki Y., Waldman S. A., Gariepy J., Schoolnik G., Murad F. Characterization of the receptor for heat-stable enterotoxin from Escherichia coli in rat intestine. J Biol Chem. 1986 Jan 25;261(3):1470–1476. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kurose H., Inagami T., Ui M. Participation of adenosine 5'-triphosphate in the activation of membrane-bound guanylate cyclase by the atrial natriuretic factor. FEBS Lett. 1987 Jul 27;219(2):375–379. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(87)80256-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Paul A. K., Marala R. B., Jaiswal R. K., Sharma R. K. Coexistence of guanylate cyclase and atrial natriuretic factor receptor in a 180-kD protein. Science. 1987 Mar 6;235(4793):1224–1226. doi: 10.1126/science.2881352. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sack D. A., Merson M. H., Wells J. G., Sack R. B., Morris G. K. Diarrhoea associated with heat-stable enterotoxin-producing strains of Escherichia coli. Lancet. 1975 Aug 9;2(7928):239–241. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(75)90958-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sack R. B. Human diarrheal disease caused by enterotoxigenic Escherichia coli. Annu Rev Microbiol. 1975;29:333–353. doi: 10.1146/annurev.mi.29.100175.002001. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Steiner A. L., Parker C. W., Kipnis D. M. Radioimmunoassay for cyclic nucleotides. I. Preparation of antibodies and iodinated cyclic nucleotides. J Biol Chem. 1972 Feb 25;247(4):1106–1113. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stryer L., Bourne H. R. G proteins: a family of signal transducers. Annu Rev Cell Biol. 1986;2:391–419. doi: 10.1146/annurev.cb.02.110186.002135. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stryer L. Cyclic GMP cascade of vision. Annu Rev Neurosci. 1986;9:87–119. doi: 10.1146/annurev.ne.09.030186.000511. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Takayanagi R., Inagami T., Snajdar R. M., Imada T., Tamura M., Misono K. S. Two distinct forms of receptors for atrial natriuretic factor in bovine adrenocortical cells. Purification, ligand binding, and peptide mapping. J Biol Chem. 1987 Sep 5;262(25):12104–12113. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Waldman S. A., Kuno T., Kamisaki Y., Chang L. Y., Gariepy J., O'Hanley P., Schoolnik G., Murad F. Intestinal receptor for heat-stable enterotoxin of Escherichia coli is tightly coupled to a novel form of particulate guanylate cyclase. Infect Immun. 1986 Jan;51(1):320–326. doi: 10.1128/iai.51.1.320-326.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Waldman S. A., Murad F. Cyclic GMP synthesis and function. Pharmacol Rev. 1987 Sep;39(3):163–196. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Waldman S. A., O'Hanley P., Falkow S., Schoolnik G., Murad F. A simple, sensitive, and specific assay for the heat-stable enterotoxin of Escherichia coli. J Infect Dis. 1984 Jan;149(1):83–89. doi: 10.1093/infdis/149.1.83. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


