Abstract
Enteropathogenic Escherichia coli (EPEC) are a class of diarrheagenic organisms that induce a characteristic attaching and effacing lesion in enterocytes and various cultured cell lines. Infection of cultured HEp-2 cells by EPEC isolates 2036-80 (serotype O119) and E2348-69 (serotype O127) resulted in significant elevation of intracellular free calcium levels, determined quantitatively with the fluorescent calcium indicator dye 2-([2-bis(carboxymethyl)amino-5-methylphenoxy]methyl)-6-methoxy-8- bis(carboxymethyl)aminoquinoline. This effect, which was not observed on infection with non-lesion-forming E. coli strains, was inhibited by dantrolene, a drug that prevents calcium mobilization from intracellular stores. Moreover, activated protein kinase C in infected cells was dissociated from cell membranes by a process that was inhibited by cyclosporin A, suggesting involvement of the calcium-dependent protease calpain. A qualitative method for observing intracellular calcium fluxes by fluorescence microscopy with the recently described fluorescein-based indicator fluo-3 was used to screen a collection of well-characterized E. coli isolates from patients with infantile enteritis. Increased localized calcium-dependent fluo-3 fluorescence was observed only in HEp-2 cells infected with known lesion-forming EPEC strains. We propose that enhancement of intracellular free calcium levels in enterocytes infected with EPEC would result in formation of the characteristic lesion by calcium-dependent activation of actin-depolymerizing proteins, with eventual loss of absorptive capacity.
Full text
PDF

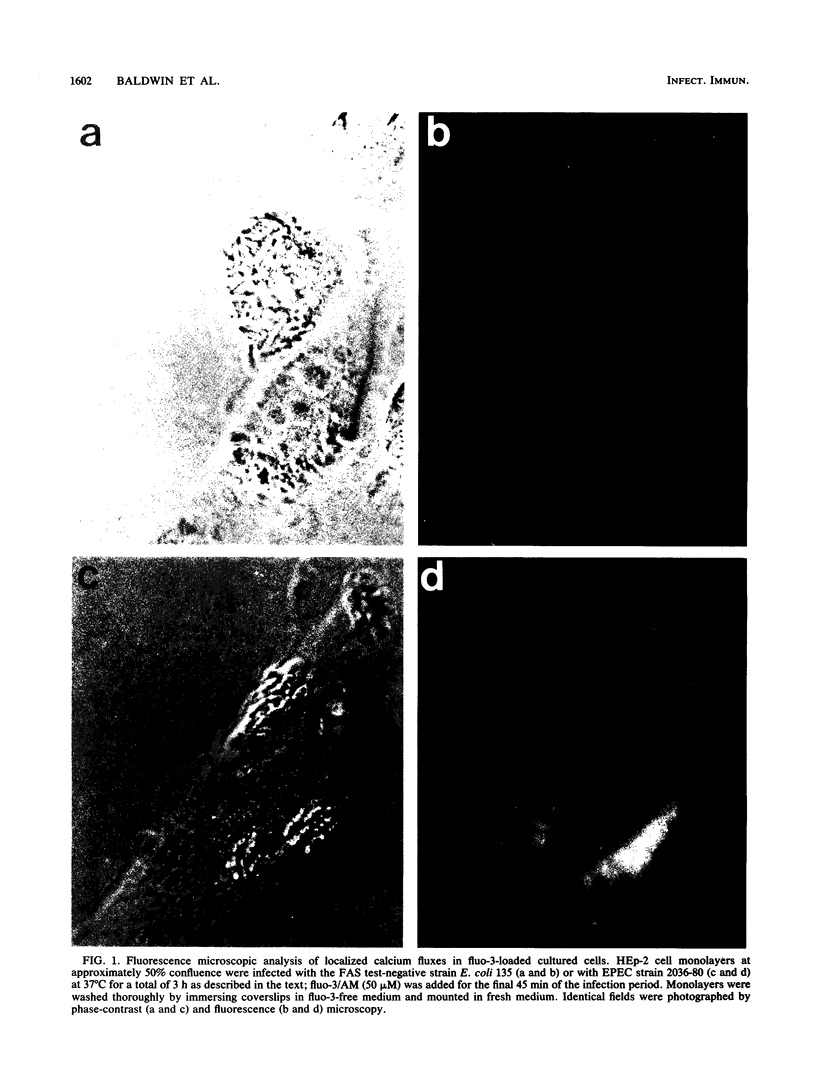


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Baldassare J. J., Bakshian S., Knipp M. A., Fisher G. J. Inhibition of fibrinogen receptor expression and serotonin release by leupeptin and antipain. J Biol Chem. 1985 Sep 5;260(19):10531–10535. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baldini M. M., Nataro J. P., Kaper J. B. Localization of a determinant for HEp-2 adherence by enteropathogenic Escherichia coli. Infect Immun. 1986 Apr;52(1):334–336. doi: 10.1128/iai.52.1.334-336.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baldwin T. J., Brooks S. F., Knutton S., Manjarrez Hernandez H. A., Aitken A., Williams P. H. Protein phosphorylation by protein kinase C in HEp-2 cells infected with enteropathogenic Escherichia coli. Infect Immun. 1990 Mar;58(3):761–765. doi: 10.1128/iai.58.3.761-765.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Berridge M. J. Inositol trisphosphate and diacylglycerol: two interacting second messengers. Annu Rev Biochem. 1987;56:159–193. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.56.070187.001111. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bretscher A., Weber K. Villin is a major protein of the microvillus cytoskeleton which binds both G and F actin in a calcium-dependent manner. Cell. 1980 Jul;20(3):839–847. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(80)90330-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bretscher A., Weber K. Villin: the major microfilament-associated protein of the intestinal microvillus. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 May;76(5):2321–2325. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.5.2321. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cabot M. C., Welsh C. J., Zhang Z. C., Cao H. T. Evidence for a protein kinase C-directed mechanism in the phorbol diester-induced phospholipase D pathway of diacylglycerol generation from phosphatidylcholine. FEBS Lett. 1989 Mar 13;245(1-2):85–90. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(89)80197-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Collins M. K., Rozengurt E. Homologous and heterologous mitogenic desensitization of Swiss 3T3 cells to phorbol esters and vasopressin: role of receptor and postreceptor steps. J Cell Physiol. 1984 Feb;118(2):133–142. doi: 10.1002/jcp.1041180205. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cooper J. A., Loftus D. J., Frieden C., Bryan J., Elson E. L. Localization and mobility of gelsolin in cells. J Cell Biol. 1988 Apr;106(4):1229–1240. doi: 10.1083/jcb.106.4.1229. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Danko S., Kim D. H., Sreter F. A., Ikemoto N. Inhibitors of Ca2+ release from the isolated sarcoplasmic reticulum. II. The effects of dantrolene on Ca2+ release induced by caffeine, Ca2+ and depolarization. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1985 Jun 11;816(1):18–24. doi: 10.1016/0005-2736(85)90388-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goligorsky M. S., Menton D. N., Hruska K. A. Parathyroid hormone-induced changes of the brush border topography and cytoskeleton in cultured renal proximal tubular cells. J Membr Biol. 1986;92(2):151–162. doi: 10.1007/BF01870704. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hauschildt S., Hirt W., Bessler W. Modulation of protein kinase C activity by NaF in bone marrow derived macrophages. FEBS Lett. 1988 Mar 28;230(1-2):121–124. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(88)80654-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Irvine R. F., Letcher A. J., Lander D. J., Berridge M. J. Specificity of inositol phosphate-stimulated Ca2+ mobilization from Swiss-mouse 3T3 cells. Biochem J. 1986 Nov 15;240(1):301–304. doi: 10.1042/bj2400301. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kao J. P., Harootunian A. T., Tsien R. Y. Photochemically generated cytosolic calcium pulses and their detection by fluo-3. J Biol Chem. 1989 May 15;264(14):8179–8184. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Knutton S., Baldini M. M., Kaper J. B., McNeish A. S. Role of plasmid-encoded adherence factors in adhesion of enteropathogenic Escherichia coli to HEp-2 cells. Infect Immun. 1987 Jan;55(1):78–85. doi: 10.1128/iai.55.1.78-85.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Knutton S., Baldwin T., Williams P. H., McNeish A. S. Actin accumulation at sites of bacterial adhesion to tissue culture cells: basis of a new diagnostic test for enteropathogenic and enterohemorrhagic Escherichia coli. Infect Immun. 1989 Apr;57(4):1290–1298. doi: 10.1128/iai.57.4.1290-1298.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Knutton S., Baldwin T., Williams P. H., McNeish A. S. New diagnostic test for enteropathogenic Escherichia coli. Lancet. 1988 Jun 11;1(8598):1337–1337. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(88)92152-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Knutton S., Lloyd D. R., McNeish A. S. Adhesion of enteropathogenic Escherichia coli to human intestinal enterocytes and cultured human intestinal mucosa. Infect Immun. 1987 Jan;55(1):69–77. doi: 10.1128/iai.55.1.69-77.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LENNOX E. S. Transduction of linked genetic characters of the host by bacteriophage P1. Virology. 1955 Jul;1(2):190–206. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(55)90016-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Law D. Virulence factors of enteropathogenic Escherichia coli. J Med Microbiol. 1988 May;26(1):1–10. doi: 10.1099/00222615-26-1-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Matsudaira P. T., Burgess D. R. Partial reconstruction of the microvillus core bundle: characterization of villin as a Ca++-dependent, actin-bundling/depolymerizing protein. J Cell Biol. 1982 Mar;92(3):648–656. doi: 10.1083/jcb.92.3.648. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Matsudaira P., Janmey P. Pieces in the actin-severing protein puzzle. Cell. 1988 Jul 15;54(2):139–140. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(88)90542-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Minta A., Kao J. P., Tsien R. Y. Fluorescent indicators for cytosolic calcium based on rhodamine and fluorescein chromophores. J Biol Chem. 1989 May 15;264(14):8171–8178. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mooseker M. S., Graves T. A., Wharton K. A., Falco N., Howe C. L. Regulation of microvillus structure: calcium-dependent solation and cross-linking of actin filaments in the microvilli of intestinal epithelial cells. J Cell Biol. 1980 Dec;87(3 Pt 1):809–822. doi: 10.1083/jcb.87.3.809. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Polotsky Y. E., Dragunskaya E. M., Seliverstova V. G., Avdeeva T. A., Chakhutinskaya M. G., Kétyi I., Vertényl A., Ralovich B., Emödy L., Málovics I. Pathogenic effect of enterotoxigenic Escherichia coli and Escherichia coli causing infantile diarrhoea. Acta Microbiol Acad Sci Hung. 1977;24(3):221–236. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pontremoli S., Melloni E., Michetti M., Sacco O., Salamino F., Sparatore B., Horecker B. L. Biochemical responses in activated human neutrophils mediated by protein kinase C and a Ca2+-requiring proteinase. J Biol Chem. 1986 Jun 25;261(18):8309–8313. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Robins-Browne R. M. Traditional enteropathogenic Escherichia coli of infantile diarrhea. Rev Infect Dis. 1987 Jan-Feb;9(1):28–53. doi: 10.1093/clinids/9.1.28. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rodriguez-Pena A., Rozengurt E. Disappearance of Ca2+-sensitive, phospholipid-dependent protein kinase activity in phorbol ester-treated 3T3 cells. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1984 May 16;120(3):1053–1059. doi: 10.1016/s0006-291x(84)80213-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rothbaum R. J., Partin J. C., Saalfield K., McAdams A. J. An ultrastructural study of enteropathogenic Escherichia coli infection in human infants. Ultrastruct Pathol. 1983 Jun;4(4):291–304. doi: 10.3109/01913128309140582. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rothbaum R., McAdams A. J., Giannella R., Partin J. C. A clinicopathologic study of enterocyte-adherent Escherichia coli: a cause of protracted diarrhea in infants. Gastroenterology. 1982 Aug;83(2):441–454. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Scaletsky I. C., Silva M. L., Trabulsi L. R. Distinctive patterns of adherence of enteropathogenic Escherichia coli to HeLa cells. Infect Immun. 1984 Aug;45(2):534–536. doi: 10.1128/iai.45.2.534-536.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tsien R. Y., Pozzan T., Rink T. J. Calcium homeostasis in intact lymphocytes: cytoplasmic free calcium monitored with a new, intracellularly trapped fluorescent indicator. J Cell Biol. 1982 Aug;94(2):325–334. doi: 10.1083/jcb.94.2.325. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Van Winkle W. B. Calcium release from skeletal muscle sarcoplasmic reticulum: site of action of dantrolene sodium. Science. 1976 Sep 17;193(4258):1130–1131. doi: 10.1126/science.959824. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Volpe P., Salviati G., Di Virgilio F., Pozzan T. Inositol 1,4,5-trisphosphate induces calcium release from sarcoplasmic reticulum of skeletal muscle. Nature. 1985 Jul 25;316(6026):347–349. doi: 10.1038/316347a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yin H. L. Gelsolin: calcium- and polyphosphoinositide-regulated actin-modulating protein. Bioessays. 1987 Oct;7(4):176–179. doi: 10.1002/bies.950070409. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yin H. L., Stossel T. P. Control of cytoplasmic actin gel-sol transformation by gelsolin, a calcium-dependent regulatory protein. Nature. 1979 Oct 18;281(5732):583–586. doi: 10.1038/281583a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- vonRuecker A. A., Rao G., Bidlingmaier F. Cyclosporin A inhibits proteolytic cleavage and degradation of membrane-bound protein kinase C in hepatocytes after stimulation by phorbol ester. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1988 Mar 30;151(3):997–1003. doi: 10.1016/s0006-291x(88)80464-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]