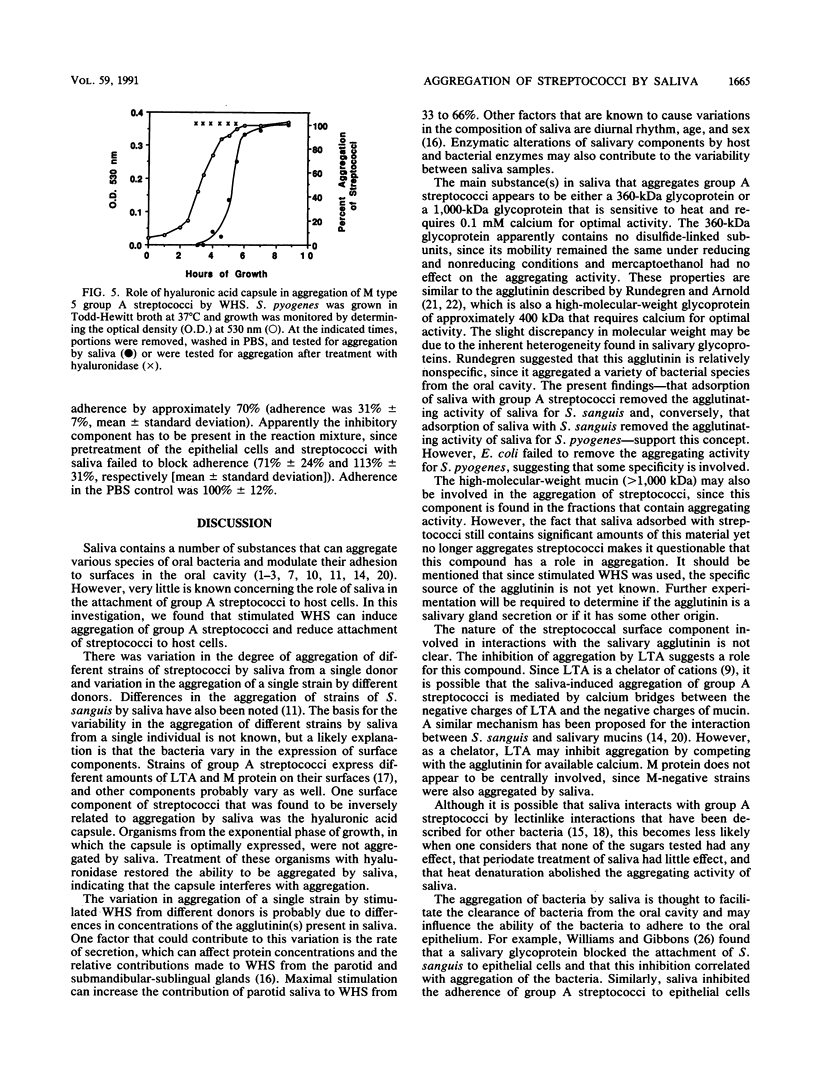
Abstract
The aggregation of group A streptococci by whole, stimulated human saliva (WHS) and the effect of saliva on streptococcal adherence to host cells was investigated. WHS samples from 11 individuals were found to aggregate both M+ and M- group A streptococci to various degrees. The aggregating activity was sensitive to heat, EDTA, EGTA [ethylene glycol-bis(beta-aminoethyl ether)-N,N,N',N'-tetraacetic acid], sodium dodecyl sulfate, and lipoteichoic acid. None of the simple sugars tested, mercaptoethanol, albumin, or nonionic detergents had any effect on aggregation. The aggregating activity of EDTA-treated saliva was restored by 0.1 mM Ca2+ and 1.0 mM Mn2+ but not by up to 5 mM Mg2+. Only streptococci from the stationary phase were aggregated. Hyaluronidase treatment of streptococci from the exponential phase of growth restored their ability to be aggregated, suggesting that the hyaluronic acid capsule interferes with agglutination. Adsorption of WHS by one strain of Streptococcus pyogenes removed aggregating activity for other strains of S. pyogenes and Streptococcus sanguis but not agglutinins for Escherichia coli, suggesting that the agglutinin is specific for certain gram-positive bacteria. Molecular sieve chromatography of WHS and identification of streptococcus-binding components of saliva suggest that either a glycoprotein of approximately 360 kDa or a mucin of saliva of greater than 1,000 kDa mediates aggregation of streptococci. WHS also inhibited adherence of S. pyogenes to buccal epithelial cells.
Full text
PDF

Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Abraham S. N., Beachey E. H., Simpson W. A. Adherence of streptococcus pyogenes, Escherichia coli, and Pseudomonas aeruginosa to fibronectin-coated and uncoated epithelial cells. Infect Immun. 1983 Sep;41(3):1261–1268. doi: 10.1128/iai.41.3.1261-1268.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Babu J. P., Abraham S. N., Dabbous M. K., Beachey E. H. Interaction of a 60-kilodalton D-mannose-containing salivary glycoprotein with type 1 fimbriae of Escherichia coli. Infect Immun. 1986 Oct;54(1):104–108. doi: 10.1128/iai.54.1.104-108.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Babu J. P., Simpson W. A., Courtney H. S., Beachey E. H. Interaction of human plasma fibronectin with cariogenic and non-cariogenic oral streptococci. Infect Immun. 1983 Jul;41(1):162–168. doi: 10.1128/iai.41.1.162-168.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Beachey E. H., Courtney H. S. Bacterial adherence: the attachment of group A streptococci to mucosal surfaces. Rev Infect Dis. 1987 Sep-Oct;9 (Suppl 5):S475–S481. doi: 10.1093/clinids/9.supplement_5.s475. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Courtney H. S., Ofek I., Simpson W. A., Hasty D. L., Beachey E. H. Binding of Streptococcus pyogenes to soluble and insoluble fibronectin. Infect Immun. 1986 Sep;53(3):454–459. doi: 10.1128/iai.53.3.454-459.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Courtney H. S., Simpson W. A., Beachey E. H. Relationship of critical micelle concentrations of bacterial lipoteichoic acids to biological activities. Infect Immun. 1986 Feb;51(2):414–418. doi: 10.1128/iai.51.2.414-418.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Devine P. L., Warren J. A., Layton G. T. Glycoprotein detection using the periodic acid/Schiff reagent: a microassay using microtitration plates. Biotechniques. 1990 Apr;8(4):354–356. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HILL M. J., JAMES A. M., MAXTED W. R. Some physical investigations of the behaviour of bacterial surfaces. VIII. Studies on the capsular material of Streptococcus pyogenes. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1963 Mar 19;66:264–274. doi: 10.1016/0006-3002(63)91193-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hasty D. L., Simpson W. A. Effects of fibronectin and other salivary macromolecules on the adherence of Escherichia coli to buccal epithelial cells. Infect Immun. 1987 Sep;55(9):2103–2109. doi: 10.1128/iai.55.9.2103-2109.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hughes A. H., Hancock I. C., Baddiley J. The function of teichoic acids in cation control in bacterial membranes. Biochem J. 1973 Jan;132(1):83–93. doi: 10.1042/bj1320083. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Komiyama K., Gibbons R. J. Interbacterial adherence between Actinomyces viscosus and strains of Streptococcus pyogenes, Streptococcus agalactiae, and Pseudomonas aeruginosa. Infect Immun. 1984 Apr;44(1):86–90. doi: 10.1128/iai.44.1.86-90.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Koop H. M., Valentijn-Benz M., Nieuw Amerongen A. V., Roukema P. A., De Graaff J. Aggregation of 27 oral bacteria by human whole saliva. Influence of culture medium, calcium, and bacterial cell concentration, and interference by autoaggregation. Antonie Van Leeuwenhoek. 1989 Mar;55(3):277–290. doi: 10.1007/BF00393856. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kronvall G., Simmons A., Myhre E. B., Jonsson S. Specific absorption of human serum albumin, immunoglobulin A, and immunoglobulin G with selected strains of group A and G streptococci. Infect Immun. 1979 Jul;25(1):1–10. doi: 10.1128/iai.25.1.1-10.1979. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lamont R. J., Rosan B. Adherence of mutans streptococci to other oral bacteria. Infect Immun. 1990 Jun;58(6):1738–1743. doi: 10.1128/iai.58.6.1738-1743.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ligtenberg A. J., Veerman E. C., de Graaff J., Nieuw Amerongen A. V. Influence of the blood group reactive substances in saliva on the aggregation of Streptococcus rattus. Antonie Van Leeuwenhoek. 1990 Feb;57(2):97–107. doi: 10.1007/BF00403161. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miörner H., Johansson G., Kronvall G. Lipoteichoic acid is the major cell wall component responsible for surface hydrophobicity of group A streptococci. Infect Immun. 1983 Jan;39(1):336–343. doi: 10.1128/iai.39.1.336-343.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Murray P. A., Levine M. J., Tabak L. A., Reddy M. S. Specificity of salivary-bacterial interactions: II. Evidence for a lectin on Streptococcus sanguis with specificity for a NeuAc alpha 2, 3Ga1 beta 1, 3Ga1NAc sequence. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1982 May 31;106(2):390–396. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(82)91122-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ofek I., Courtney H. S., Schifferli D. M., Beachey E. H. Enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay for adherence of bacteria to animal cells. J Clin Microbiol. 1986 Oct;24(4):512–516. doi: 10.1128/jcm.24.4.512-516.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rundegren J., Arnold R. R. Differentiation and interaction of secretory immunoglobulin A and a calcium-dependent parotid agglutinin for several bacterial strains. Infect Immun. 1987 Feb;55(2):288–292. doi: 10.1128/iai.55.2.288-292.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rundegren J. Calcium-dependent salivary agglutinin with reactivity to various oral bacterial species. Infect Immun. 1986 Jul;53(1):173–178. doi: 10.1128/iai.53.1.173-178.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Simpson W. A., Beachey E. H. Adherence of group A streptococci to fibronectin on oral epithelial cells. Infect Immun. 1983 Jan;39(1):275–279. doi: 10.1128/iai.39.1.275-279.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Simpson W. A., Hasty D. L., Beachey E. H. Binding of fibronectin to human buccal epithelial cells inhibits the binding of type 1 fimbriated Escherichia coli. Infect Immun. 1985 May;48(2):318–323. doi: 10.1128/iai.48.2.318-323.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Williams R. C., Gibbons R. J. Inhibition of streptococcal attachment to receptors on human buccal epithelial cells by antigenically similar salivary glycoproteins. Infect Immun. 1975 Apr;11(4):711–718. doi: 10.1128/iai.11.4.711-718.1975. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zacharius R. M., Zell T. E., Morrison J. H., Woodlock J. J. Glycoprotein staining following electrophoresis on acrylamide gels. Anal Biochem. 1969 Jul;30(1):148–152. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(69)90383-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]