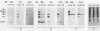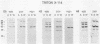Abstract
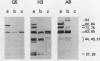
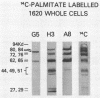
Three monoclonal antibodies (MAbs) were prepared against an arthritogenic strain of Mycoplasma hominis isolated from the joint aspirates of a patient with chronic septic arthritis. Immunoblots of polyacrylamide gel-electrophoresed proteins before and after surface proteolysis showed that the predominant antigenic determinants were on surface-exposed polypeptides. These polypeptides have extensive hydrophobic characteristics, as demonstrated by Triton X-114 phase partitioning. The electrophoresed proteins from cells grown in medium containing [14C]palmitate were blotted onto nitrocellulose which was both reacted with the MAbs and exposed to X-ray film. Superimposable bands on both the immunoblots and the exposed film suggested that the proteins might be acylated. The MAbs were further tested for reactivity with 16 other strains of M. hominis isolated from patients with septic arthritis (1 strain), septicemia (10 strains), or nongonococcal urethritis (1 strain); from the cervix (1 strain), rectum (1 strain), or surgical wound (1 strain) of patients; and from a contaminated cell culture. No single protein was consistently recognized from strain to strain, although a 94-kDa protein from 16 of the 17 strains tested was bound by at least one of the MAbs. The apparent antigenic heterogeneity among strains of M. hominis, including those isolated from the same tissue source and/or from patients with the same type of clinical disease, might be misleading in that all strains express epitopes associated with a discrete number of proteins to which one, two, or all three MAbs bind. The expression of the epitopes on multiple proteins from the same or different strains may reflect a mechanism for generating antigenic diversity.
Full text
PDF





Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Alexander A. G. Analysis of protein antigens of Mycoplasma hominis: detection of polypeptides involved in the human immune response. Isr J Med Sci. 1987 Jun;23(6):608–612. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Andersen H., Birkelund S., Christiansen G., Freundt E. A. Electrophoretic analysis of proteins from Mycoplasma hominis strains detected by SDS-PAGE, two-dimensional gel electrophoresis and immunoblotting. J Gen Microbiol. 1987 Jan;133(1):181–191. doi: 10.1099/00221287-133-1-181. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Barbour A. G., Tessier S. L., Hayes S. F. Variation in a major surface protein of Lyme disease spirochetes. Infect Immun. 1984 Jul;45(1):94–100. doi: 10.1128/iai.45.1.94-100.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Barile M. F., Grabowski M. W., Stephens E. B., O'Brien S. J., Simonson J. M., Izumikawa K., Chandler D. K., Taylor-Robinson D., Tully J. G. Mycoplasma hominis- tissue cell interactions: a review with new observations on phenotypic and genotypic properties. Sex Transm Dis. 1983 Oct-Dec;10(4 Suppl):345–354. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bordier C. Phase separation of integral membrane proteins in Triton X-114 solution. J Biol Chem. 1981 Feb 25;256(4):1604–1607. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Boyer M. J., Wise K. S. Lipid-modified surface protein antigens expressing size variation within the species Mycoplasma hyorhinis. Infect Immun. 1989 Jan;57(1):245–254. doi: 10.1128/iai.57.1.245-254.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bøe O., Iversen O. E., Mehl A. Septicemia due to Mycoplasma hominis. Scand J Infect Dis. 1983;15(1):87–90. doi: 10.3109/inf.1983.15.issue-1.14. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cassell G. H., Watson H. L., Blalock D. K., Horowitz S. A., Duffy L. B. Protein antigens of genital mycoplasmas. Rev Infect Dis. 1988 Jul-Aug;10 (Suppl 2):S391–S398. doi: 10.1093/cid/10.supplement_2.s391. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chandler D. K., Razin S., Stephens E. B., Harasawa R., Barile M. F. Genomic and phenotypic analyses of Mycoplasma pneumoniae strains. Infect Immun. 1982 Nov;38(2):604–609. doi: 10.1128/iai.38.2.604-609.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Christiansen C., Frydenberg J., Christiansen G., Andersen H., Hedegaard L. Analysis of the mycoplasma genome by recombinant DNA technology. Isr J Med Sci. 1984 Sep;20(9):781–784. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Christiansen G., Andersen H., Birkelund S., Freundt E. A. Genomic and gene variation in Mycoplasma hominis strains. Isr J Med Sci. 1987 Jun;23(6):595–602. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cunningham T. M., Walker E. M., Miller J. N., Lovett M. A. Selective release of the Treponema pallidum outer membrane and associated polypeptides with Triton X-114. J Bacteriol. 1988 Dec;170(12):5789–5796. doi: 10.1128/jb.170.12.5789-5796.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dan M., Robertson J. Mycoplasma hominis septicemia after heart surgery. Am J Med. 1988 May;84(5):976–977. doi: 10.1016/0002-9343(88)90085-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fanger B. O. Adaptation of the Bradford protein assay to membrane-bound proteins by solubilizing in glucopyranoside detergents. Anal Biochem. 1987 Apr;162(1):11–17. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(87)90004-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Feldner J., Bredt W., Razin S. Adherence of Mycoplasma pneumoniae to glass surfaces. Infect Immun. 1979 Oct;26(1):70–75. doi: 10.1128/iai.26.1.70-75.1979. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Freundt E. A. A collaborative assay of mycoplasma reference antisera. J Biol Stand. 1983 Jul;11(3):227–240. doi: 10.1016/s0092-1157(83)80010-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Freundt E. A. Mycoplasma hominis: historical outline and taxonomy. Sex Transm Dis. 1983 Oct-Dec;10(4 Suppl):226–229. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Geary S. J., Gabridge M. G. Characterization of a human lung fibroblast receptor site for Mycoplasma pneumoniae. Isr J Med Sci. 1987 May;23(5):462–468. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hollingdale M. R., Manchee R. J. The role of mycoplasma membrane proteins in the adsorption of animal cells to Mycoplasma hominis colonies. J Gen Microbiol. 1972 Apr;70(2):391–393. doi: 10.1099/00221287-70-2-391. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hu P. C., Cole R. M., Huang Y. S., Graham J. A., Gardner D. E., Collier A. M., Clyde W. A., Jr Mycoplasma pneumoniae infection: role of a surface protein in the attachment organelle. Science. 1982 Apr 16;216(4543):313–315. doi: 10.1126/science.6801766. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Izumikawa K., Chandler D. K., Grabowski M. W., Barile M. F. Attachment of Mycoplasma hominis to human cell cultures. Isr J Med Sci. 1987 Jun;23(6):603–607. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kenimer J. G., Kim K. J., Probst P. G., Manclark C. R., Burstyn D. G., Cowell J. L. Monoclonal antibodies to pertussis toxin: utilization as probes of toxin function. Hybridoma. 1989 Feb;8(1):37–51. doi: 10.1089/hyb.1989.8.37. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Krause D. C., Leith D. K., Wilson R. M., Baseman J. B. Identification of Mycoplasma pneumoniae proteins associated with hemadsorption and virulence. Infect Immun. 1982 Mar;35(3):809–817. doi: 10.1128/iai.35.3.809-817.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Krivan H. C., Olson L. D., Barile M. F., Ginsburg V., Roberts D. D. Adhesion of Mycoplasma pneumoniae to sulfated glycolipids and inhibition by dextran sulfate. J Biol Chem. 1989 Jun 5;264(16):9283–9288. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Köhler G., Milstein C. Continuous cultures of fused cells secreting antibody of predefined specificity. Nature. 1975 Aug 7;256(5517):495–497. doi: 10.1038/256495a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laemmli U. K. Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature. 1970 Aug 15;227(5259):680–685. doi: 10.1038/227680a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lin J. S., Alpert S., Radnay K. M. Combined type-specific antisera in the identification of Mycoplasma hominis. J Infect Dis. 1975 Jun;131(6):727–730. doi: 10.1093/infdis/131.6.727. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lin J. S. An antigenic analysis for membranes of Mycoplasma hominis by cross-absorption. J Gen Microbiol. 1980 Jan;116(1):187–193. doi: 10.1099/00221287-116-1-187. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lin J. S., Kass E. H. Serological reactions of Mycoplasma hominis: differences among mycoplasmacidal, metabolic inhibition, and growth agglutination tests. Infect Immun. 1974 Sep;10(3):535–540. doi: 10.1128/iai.10.3.535-540.1974. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lin J. S., Kendrick M. I., Kass E. H. Serologic typing of human genital T-mycoplasmas by a complement-dependent mycoplasmacidal test. J Infect Dis. 1972 Dec;126(6):658–663. doi: 10.1093/infdis/126.6.658. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Loomes L. M., Uemura K., Feizi T. Interaction of Mycoplasma pneumoniae with erythrocyte glycolipids of I and i antigen types. Infect Immun. 1985 Jan;47(1):15–20. doi: 10.1128/iai.47.1.15-20.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roberts D. D., Olson L. D., Barile M. F., Ginsburg V., Krivan H. C. Sialic acid-dependent adhesion of Mycoplasma pneumoniae to purified glycoproteins. J Biol Chem. 1989 Jun 5;264(16):9289–9293. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rosengarten R., Wise K. S. Phenotypic switching in mycoplasmas: phase variation of diverse surface lipoproteins. Science. 1990 Jan 19;247(4940):315–318. doi: 10.1126/science.1688663. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rouse D. A., Morris S. L., Karpas A. B., Probst P. G., Chaparas S. D. Production, characterization, and species specificity of monoclonal antibodies to Mycobacterium avium complex protein antigens. Infect Immun. 1990 May;58(5):1445–1449. doi: 10.1128/iai.58.5.1445-1449.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sneller M., Wellborne F., Barile M. F., Plotz P. Prosthetic joint infection with Mycoplasma hominis. J Infect Dis. 1986 Jan;153(1):174–175. doi: 10.1093/infdis/153.1.174. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- TAYLOR-ROBINSON D., LUDWIG W. M., PURCELL R. H., MUFSON M. A., CHANOCK R. M. SIGNIFICANCE OF ANTIBODY TO MYCOPLASMA HOMINIS TYPE 1 AS MEASURED BY INDIRECT HEMAGGLUTINATION. Proc Soc Exp Biol Med. 1965 Apr;118:1073–1083. doi: 10.3181/00379727-118-30049. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Taylor-Robinson D., Thomas B. J., Furr P. M., Keat A. C. The association of Mycoplasma hominis with arthritis. Sex Transm Dis. 1983 Oct-Dec;10(4 Suppl):341–344. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Waites K. B., Rudd P. T., Crouse D. T., Canupp K. C., Nelson K. G., Ramsey C., Cassell G. H. Chronic Ureaplasma urealyticum and Mycoplasma hominis infections of central nervous system in preterm infants. Lancet. 1988 Jan 2;1(8575-6):17–21. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(88)91002-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Washburn L. R., Ramsay J. R., Roberts L. K. Characterization of the metabolism inhibition antigen of Mycoplasma arthritidis. Infect Immun. 1985 Aug;49(2):357–364. doi: 10.1128/iai.49.2.357-364.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Watson H. L., McDaniel L. S., Blalock D. K., Fallon M. T., Cassell G. H. Heterogeneity among strains and a high rate of variation within strains of a major surface antigen of Mycoplasma pulmonis. Infect Immun. 1988 May;56(5):1358–1363. doi: 10.1128/iai.56.5.1358-1363.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wilson M. E., Dietze C. Mycoplasma hominis surgical wound infection: a case report and discussion. Surgery. 1988 Feb;103(2):257–260. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]