Abstract
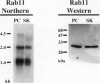
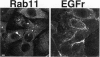
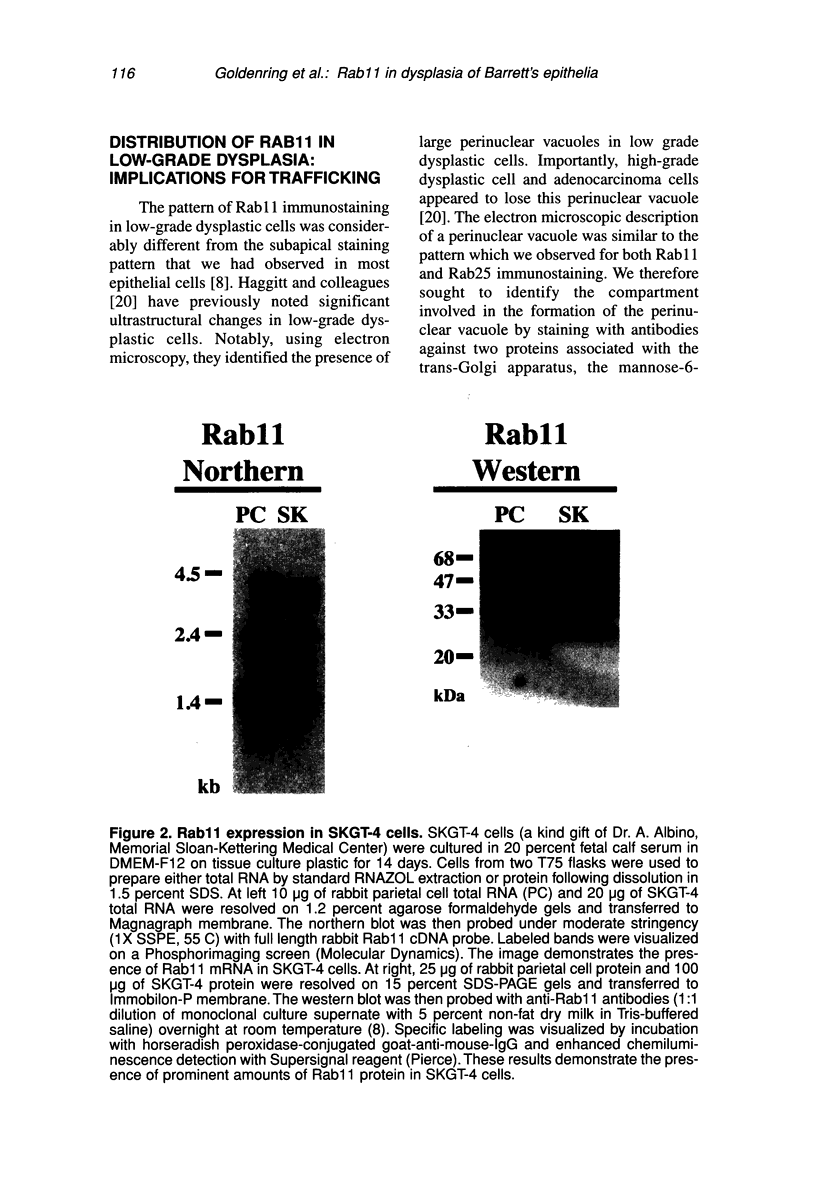
Barrett's esophagus predisposes affected patients to the development of esophageal adenocarcinoma. The development of adenocarcinoma proceeds along a progression through low- and high-grade dysplasia. Surveillance of Barrett's patients requires serial endoscopic investigations and grading mucosal biopsies. Unfortunately, grading of biopsies by conventional hematoxylin and eosin staining is fraught with significant interobserver variations. We have found in both biopsy and resection specimens that immunostaining for the small GTP binding protein Rab11 is increased in low-grade dysplastic cells. This staining is lost in high-grade dysplastic cells. These results suggest that low-grade dysplastic cells undergo an apical trafficking blockade, which is released as cells progress to the less differentiated phenotype of high-grade dysplasia and adenocarcinoma. Examination of the SKGT-4 esophageal adenocarcinoma cell line demonstrated prominent mRNA and protein expression for Rab11. Rab11 immunostaining was present in SKGT-4 cells as a perinuclear nidus of punctate staining along with a more diffuse punctate pattern. Thus, Rab11 expression was present in a esophageal adenocarcinoma cells in culture. Markers of vesicle trafficking may be critical factors for grading of mucosal dysplastic transitions leading to adenocarcinoma.
Full text
PDF





Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Altorki N., Schwartz G. K., Blundell M., Davis B. M., Kelsen D. P., Albino A. P. Characterization of cell lines established from human gastric-esophageal adenocarcinomas. Biologic phenotype and invasion potential. Cancer. 1993 Aug 1;72(3):649–657. doi: 10.1002/1097-0142(19930801)72:3<649::aid-cncr2820720305>3.0.co;2-l. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blount P. L., Galipeau P. C., Sanchez C. A., Neshat K., Levine D. S., Yin J., Suzuki H., Abraham J. M., Meltzer S. J., Reid B. J. 17p allelic losses in diploid cells of patients with Barrett's esophagus who develop aneuploidy. Cancer Res. 1994 May 1;54(9):2292–2295. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blount P. L., Ramel S., Raskind W. H., Haggitt R. C., Sanchez C. A., Dean P. J., Rabinovitch P. S., Reid B. J. 17p allelic deletions and p53 protein overexpression in Barrett's adenocarcinoma. Cancer Res. 1991 Oct 15;51(20):5482–5486. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Calhoun B. C., Goldenring J. R. Two Rab proteins, vesicle-associated membrane protein 2 (VAMP-2) and secretory carrier membrane proteins (SCAMPs), are present on immunoisolated parietal cell tubulovesicles. Biochem J. 1997 Jul 15;325(Pt 2):559–564. doi: 10.1042/bj3250559. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Casson A. G., Manolopoulos B., Troster M., Kerkvliet N., O'Malley F., Inculet R., Finley R., Roth J. A. Clinical implications of p53 gene mutation in the progression of Barrett's epithelium to invasive esophageal cancer. Am J Surg. 1994 Jan;167(1):52–57. doi: 10.1016/0002-9610(94)90053-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fléjou J. F., Potet F., Muzeau F., Le Pelletier F., Fékété F., Hénin D. Overexpression of p53 protein in Barrett's syndrome with malignant transformation. J Clin Pathol. 1993 Apr;46(4):330–333. doi: 10.1136/jcp.46.4.330. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goldenring J. R., Smith J., Vaughan H. D., Cameron P., Hawkins W., Navarre J. Rab11 is an apically located small GTP-binding protein in epithelial tissues. Am J Physiol. 1996 Mar;270(3 Pt 1):G515–G525. doi: 10.1152/ajpgi.1996.270.3.G515. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goldenring J. R., Soroka C. J., Shen K. R., Tang L. H., Rodriguez W., Vaughan H. D., Stoch S. A., Modlin I. M. Enrichment of rab11, a small GTP-binding protein, in gastric parietal cells. Am J Physiol. 1994 Aug;267(2 Pt 1):G187–G194. doi: 10.1152/ajpgi.1994.267.2.G187. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Green E. G., Ramm E., Riley N. M., Spiro D. J., Goldenring J. R., Wessling-Resnick M. Rab11 is associated with transferrin-containing recycling compartments in K562 cells. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1997 Oct 20;239(2):612–616. doi: 10.1006/bbrc.1997.7520. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Haggitt R. C. Barrett's esophagus, dysplasia, and adenocarcinoma. Hum Pathol. 1994 Oct;25(10):982–993. doi: 10.1016/0046-8177(94)90057-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hameeteman W., Tytgat G. N., Houthoff H. J., van den Tweel J. G. Barrett's esophagus: development of dysplasia and adenocarcinoma. Gastroenterology. 1989 May;96(5 Pt 1):1249–1256. doi: 10.1016/s0016-5085(89)80011-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hamelin R., Fléjou J. F., Muzeau F., Potet F., Laurent-Puig P., Fékété F., Thomas G. TP53 gene mutations and p53 protein immunoreactivity in malignant and premalignant Barrett's esophagus. Gastroenterology. 1994 Oct;107(4):1012–1018. doi: 10.1016/0016-5085(94)90225-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hamilton S. R., Smith R. R., Cameron J. L. Prevalence and characteristics of Barrett esophagus in patients with adenocarcinoma of the esophagus or esophagogastric junction. Hum Pathol. 1988 Aug;19(8):942–948. doi: 10.1016/s0046-8177(88)80010-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hardwick R. H., Shepherd N. A., Moorghen M., Newcomb P. V., Alderson D. Adenocarcinoma arising in Barrett's oesophagus: evidence for the participation of p53 dysfunction in the dysplasia/carcinoma sequence. Gut. 1994 Jun;35(6):764–768. doi: 10.1136/gut.35.6.764. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Iftikhar S. Y., James P. D., Steele R. J., Hardcastle J. D., Atkinson M. Length of Barrett's oesophagus: an important factor in the development of dysplasia and adenocarcinoma. Gut. 1992 Sep;33(9):1155–1158. doi: 10.1136/gut.33.9.1155. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Isolauri J., Laippala P. Prevalence of symptoms suggestive of gastro-oesophageal reflux disease in an adult population. Ann Med. 1995 Feb;27(1):67–70. doi: 10.3109/07853899509031939. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jones D. R., Davidson A. G., Summers C. L., Murray G. F., Quinlan D. C. Potential application of p53 as an intermediate biomarker in Barrett's esophagus. Ann Thorac Surg. 1994 Mar;57(3):598–603. doi: 10.1016/0003-4975(94)90551-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Krishnadath K. K., Tilanus H. W., van Blankenstein M., Bosman F. T., Mulder A. H. Accumulation of p53 protein in normal, dysplastic, and neoplastic Barrett's oesophagus. J Pathol. 1995 Feb;175(2):175–180. doi: 10.1002/path.1711750204. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Levine D. S., Reid B. J., Haggitt R. C., Rubin C. E., Rabinovitch P. S. Correlation of ultrastructural aberrations with dysplasia and flow cytometric abnormalities in Barrett's epithelium. Gastroenterology. 1989 Feb;96(2 Pt 1):355–367. doi: 10.1016/s0016-5085(89)91559-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Levine D. S., Rubin C. E., Reid B. J., Haggitt R. C. Specialized metaplastic columnar epithelium in Barrett's esophagus. A comparative transmission electron microscopic study. Lab Invest. 1989 Mar;60(3):418–432. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Meltzer S. J., Yin J., Manin B., Rhyu M. G., Cottrell J., Hudson E., Redd J. L., Krasna M. J., Abraham J. M., Reid B. J. Microsatellite instability occurs frequently and in both diploid and aneuploid cell populations of Barrett's-associated esophageal adenocarcinomas. Cancer Res. 1994 Jul 1;54(13):3379–3382. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miros M., Kerlin P., Walker N. Only patients with dysplasia progress to adenocarcinoma in Barrett's oesophagus. Gut. 1991 Dec;32(12):1441–1446. doi: 10.1136/gut.32.12.1441. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moskaluk C. A., Heitmiller R., Zahurak M., Schwab D., Sidransky D., Hamilton S. R. p53 and p21(WAF1/CIP1/SDI1) gene products in Barrett esophagus and adenocarcinoma of the esophagus and esophagogastric junction. Hum Pathol. 1996 Nov;27(11):1211–1220. doi: 10.1016/s0046-8177(96)90317-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Neshat K., Sanchez C. A., Galipeau P. C., Blount P. L., Levine D. S., Joslyn G., Reid B. J. p53 mutations in Barrett's adenocarcinoma and high-grade dysplasia. Gastroenterology. 1994 Jun;106(6):1589–1595. doi: 10.1016/0016-5085(94)90415-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nishimaki T., Hölscher A. H., Schüler M., Bollschweiler E., Becker K., Siewert J. R. Histopathologic characteristics of early adenocarcinoma in Barrett's esophagus. Cancer. 1991 Oct 15;68(8):1731–1736. doi: 10.1002/1097-0142(19911015)68:8<1731::aid-cncr2820680814>3.0.co;2-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ovaska J., Miettinen M., Kivilaakso E. Adenocarcinoma arising in Barrett's esophagus. Dig Dis Sci. 1989 Sep;34(9):1336–1339. doi: 10.1007/BF01538065. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Provenzale D., Kemp J. A., Arora S., Wong J. B. A guide for surveillance of patients with Barrett's esophagus. Am J Gastroenterol. 1994 May;89(5):670–680. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ray G. S., Lee J. R., Nwokeji K., Mills L. R., Goldenring J. R. Increased immunoreactivity for Rab11, a small GTP-binding protein, in low-grade dysplastic Barrett's epithelia. Lab Invest. 1997 Nov;77(5):503–511. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reid B. J. Barrett's esophagus and esophageal adenocarcinoma. Gastroenterol Clin North Am. 1991 Dec;20(4):817–834. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reid B. J., Blount P. L., Rubin C. E., Levine D. S., Haggitt R. C., Rabinovitch P. S. Flow-cytometric and histological progression to malignancy in Barrett's esophagus: prospective endoscopic surveillance of a cohort. Gastroenterology. 1992 Apr;102(4 Pt 1):1212–1219. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reid B. J., Haggitt R. C., Rubin C. E., Rabinovitch P. S. Barrett's esophagus. Correlation between flow cytometry and histology in detection of patients at risk for adenocarcinoma. Gastroenterology. 1987 Jul;93(1):1–11. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reid B. J., Haggitt R. C., Rubin C. E., Roth G., Surawicz C. M., Van Belle G., Lewin K., Weinstein W. M., Antonioli D. A., Goldman H. Observer variation in the diagnosis of dysplasia in Barrett's esophagus. Hum Pathol. 1988 Feb;19(2):166–178. doi: 10.1016/s0046-8177(88)80344-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rice T. W., Goldblum J. R., Falk G. W., Tubbs R. R., Kirby T. J., Casey G. p53 immunoreactivity in Barrett's metaplasia, dysplasia, and carcinoma. J Thorac Cardiovasc Surg. 1994 Dec;108(6):1132–1137. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Riddell R. H., Goldman H., Ransohoff D. F., Appelman H. D., Fenoglio C. M., Haggitt R. C., Ahren C., Correa P., Hamilton S. R., Morson B. C. Dysplasia in inflammatory bowel disease: standardized classification with provisional clinical applications. Hum Pathol. 1983 Nov;14(11):931–968. doi: 10.1016/s0046-8177(83)80175-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Robertson C. S., Mayberry J. F., Nicholson D. A., James P. D., Atkinson M. Value of endoscopic surveillance in the detection of neoplastic change in Barrett's oesophagus. Br J Surg. 1988 Aug;75(8):760–763. doi: 10.1002/bjs.1800750813. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Räihä I. J., Impivaara O., Seppälä M., Sourander L. B. Prevalence and characteristics of symptomatic gastroesophageal reflux disease in the elderly. J Am Geriatr Soc. 1992 Dec;40(12):1209–1211. doi: 10.1111/j.1532-5415.1992.tb03643.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sorsdahl K., Casson A. G., Troster M., Van Meyel D., Inculet R., Chambers A. F. p53 and ras gene expression in human esophageal cancer and Barrett's epithelium: a prospective study. Cancer Detect Prev. 1994;18(3):179–185. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Spechler S. J., Goyal R. K. Barrett's esophagus. N Engl J Med. 1986 Aug 7;315(6):362–371. doi: 10.1056/NEJM198608073150605. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Starnes V. A., Adkins R. B., Ballinger J. F., Sawyers J. L. Barrett's esophagus. A surgical entity. Arch Surg. 1984 May;119(5):563–567. doi: 10.1001/archsurg.1984.01390170059012. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thompson J. J., Zinsser K. R., Enterline H. T. Barrett's metaplasia and adenocarcinoma of the esophagus and gastroesophageal junction. Hum Pathol. 1983 Jan;14(1):42–61. doi: 10.1016/s0046-8177(83)80045-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ullrich O., Reinsch S., Urbé S., Zerial M., Parton R. G. Rab11 regulates recycling through the pericentriolar recycling endosome. J Cell Biol. 1996 Nov;135(4):913–924. doi: 10.1083/jcb.135.4.913. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Younes M., Lebovitz R. M., Lechago L. V., Lechago J. p53 protein accumulation in Barrett's metaplasia, dysplasia, and carcinoma: a follow-up study. Gastroenterology. 1993 Dec;105(6):1637–1642. doi: 10.1016/0016-5085(93)91058-p. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]