Abstract
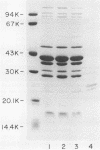
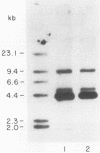
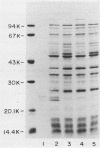
Nontypeable Haemophilus influenzae M37 adheres to human buccal epithelial cells and exhibits mannose-resistant hemagglutination of human erythrocytes. An isogenic variant of this strain which was deficient in hemagglutination was isolated. A protein with an apparent molecular weight of 22,000 was present in the sodium dodecyl sulfate-polyacrylamide gel profile of sarcosyl-insoluble proteins from the hemagglutination-proficient strain but was absent from the profile of the isogenic hemagglutination-deficient variant. A monoclonal antibody which reacts with the hemagglutination-proficient isolate but not with the hemagglutination-deficient isolate has been characterized. This monoclonal antibody was employed in an affinity column for purification of the protein as well as to screen a genomic library for recombinant clones expressing the gene. Several clones which contained overlapping genomic fragments were identified by reaction with the monoclonal antibody. The gene for the 22-kDa protein was subcloned and sequenced. The gene for the type b pilin from H. influenzae type b strain MinnA was also cloned and sequenced. The DNA sequence of the strain MinnA gene was identical to that reported previously for two other type b strains. The DNA sequence of the strain M37 gene is 77% identical to that of the type b pilin gene, and the derived amino acid sequence is 68% identical to that of the type b pilin.
Full text
PDF






Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Apicella M. A., Shero M., Dudas K. C., Stack R. R., Klohs W., LaScolea L. J., Murphy T. F., Mylotte J. M. Fimbriation of Haemophilus species isolated from the respiratory tract of adults. J Infect Dis. 1984 Jul;150(1):40–43. doi: 10.1093/infdis/150.1.40. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bakaletz L. O., Tallan B. M., Hoepf T., DeMaria T. F., Birck H. G., Lim D. J. Frequency of fimbriation of nontypable Haemophilus influenzae and its ability to adhere to chinchilla and human respiratory epithelium. Infect Immun. 1988 Feb;56(2):331–335. doi: 10.1128/iai.56.2.331-335.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Barenkamp S. J., Munson R. S., Jr, Granoff D. M. Subtyping isolates of Haemophilus influenzae type b by outer-membrane protein profiles. J Infect Dis. 1981 May;143(5):668–676. doi: 10.1093/infdis/143.5.668. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Barker J., Gratten M., Riley I., Lehmann D., Montgomery J., Kajoi M., Gratten H., Smith D., Marshall T. F., Alpers M. P. Pneumonia in children in the Eastern Highlands of Papua New Guinea: a bacteriologic study of patients selected by standard clinical criteria. J Infect Dis. 1989 Feb;159(2):348–352. doi: 10.1093/infdis/159.2.348. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Berman S., McIntosh K. Selective primary health care: strategies for control of disease in the developing world. XXI. Acute respiratory infections. Rev Infect Dis. 1985 Sep-Oct;7(5):674–691. doi: 10.1093/clinids/7.5.674. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brinton C. C., Jr, Carter M. J., Derber D. B., Kar S., Kramarik J. A., To A. C., To S. C., Wood S. W. Design and development of pilus vaccines for Haemophilus influenzae diseases. Pediatr Infect Dis J. 1989 Jan;8(1 Suppl):S54–S61. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clark-Curtiss J. E., Jacobs W. R., Docherty M. A., Ritchie L. R., Curtiss R., 3rd Molecular analysis of DNA and construction of genomic libraries of Mycobacterium leprae. J Bacteriol. 1985 Mar;161(3):1093–1102. doi: 10.1128/jb.161.3.1093-1102.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Giebink G. S. The microbiology of otitis media. Pediatr Infect Dis J. 1989 Jan;8(1 Suppl):S18–S20. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gilsdorf J. R., Ferrieri P. Adherence of Haemophilus influenzae to human epithelial cells. Scand J Infect Dis. 1984;16(3):271–278. doi: 10.3109/00365548409070400. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gilsdorf J. R., Marrs C. F., McCrea K. W., Forney L. J. Cloning, expression, and sequence analysis of the Haemophilus influenzae type b strain M43p+ pilin gene. Infect Immun. 1990 Apr;58(4):1065–1072. doi: 10.1128/iai.58.4.1065-1072.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gribskov M., Burgess R. R. Sigma factors from E. coli, B. subtilis, phage SP01, and phage T4 are homologous proteins. Nucleic Acids Res. 1986 Aug 26;14(16):6745–6763. doi: 10.1093/nar/14.16.6745. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Guerina N. G., Langermann S., Clegg H. W., Kessler T. W., Goldman D. A., Gilsdorf J. R. Adherence of piliated Haemophilus influenzae type b to human oropharyngeal cells. J Infect Dis. 1982 Oct;146(4):564–564. doi: 10.1093/infdis/146.4.564. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Guerina N. G., Langermann S., Schoolnik G. K., Kessler T. W., Goldmann D. A. Purification and characterization of Haemophilus influenzae pili, and their structural and serological relatedness to Escherichia coli P and mannose-sensitive pili. J Exp Med. 1985 Jan 1;161(1):145–159. doi: 10.1084/jem.161.1.145. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Helfman D. M., Feramisco J. R., Fiddes J. C., Thomas G. P., Hughes S. H. Identification of clones that encode chicken tropomyosin by direct immunological screening of a cDNA expression library. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1983 Jan;80(1):31–35. doi: 10.1073/pnas.80.1.31. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Himmelreich C. A., Barenkamp S. J., Storch G. A. Comparison of methods for serotyping isolates of Haemophilus influenzae. J Clin Microbiol. 1985 Feb;21(2):158–160. doi: 10.1128/jcm.21.2.158-160.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kar S., To S. C., Brinton C. C., Jr Cloning and expression in Escherichia coli of LKP pilus genes from a nontypeable Haemophilus influenzae strain. Infect Immun. 1990 Apr;58(4):903–908. doi: 10.1128/iai.58.4.903-908.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Karasic R. B., Beste D. J., To S. C., Doyle W. J., Wood S. W., Carter M. J., To A. C., Tanpowpong K., Bluestone C. D., Brinton C. C., Jr Evaluation of pilus vaccines for prevention of experimental otitis media caused by nontypable Haemophilus influenzae. Pediatr Infect Dis J. 1989 Jan;8(1 Suppl):S62–S65. doi: 10.1097/00006454-198901001-00021. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kroll J. S., Moxon E. R. Capsulation and gene copy number at the cap locus of Haemophilus influenzae type b. J Bacteriol. 1988 Feb;170(2):859–864. doi: 10.1128/jb.170.2.859-864.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Langermann S., Wright A. Molecular analysis of the Haemophilus influenzae type b pilin gene. Mol Microbiol. 1990 Feb;4(2):221–230. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2958.1990.tb00589.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Leowski J. Mortality from acute respiratory infections in children under 5 years of age: global estimates. World Health Stat Q. 1986;39(2):138–144. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lugtenberg B., Meijers J., Peters R., van der Hoek P., van Alphen L. Electrophoretic resolution of the "major outer membrane protein" of Escherichia coli K12 into four bands. FEBS Lett. 1975 Oct 15;58(1):254–258. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(75)80272-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mason E. O., Jr, Kaplan S. L., Wiedermann B. L., Norrod E. P., Stenback W. A. Frequency and properties of naturally occurring adherent piliated strains of Haemophilus influenzae type b. Infect Immun. 1985 Jul;49(1):98–103. doi: 10.1128/iai.49.1.98-103.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Matsudaira P. Sequence from picomole quantities of proteins electroblotted onto polyvinylidene difluoride membranes. J Biol Chem. 1987 Jul 25;262(21):10035–10038. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moffatt B. A., Studier F. W. T7 lysozyme inhibits transcription by T7 RNA polymerase. Cell. 1987 Apr 24;49(2):221–227. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(87)90563-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Monto A. S. Acute respiratory infection in children of developing countries: challenge of the 1990s. Rev Infect Dis. 1989 May-Jun;11(3):498–505. doi: 10.1093/clinids/11.3.498. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Munson R. S., Jr, Granoff D. M. Purification and partial characterization of outer membrane proteins P5 and P6 from Haemophilus influenzae type b. Infect Immun. 1985 Sep;49(3):544–549. doi: 10.1128/iai.49.3.544-549.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Munson R. S., Jr, Kabeer M. H., Lenoir A. A., Granoff D. M. Epidemiology and prospects for prevention of disease due to Haemophilus influenzae in developing countries. Rev Infect Dis. 1989 May-Jun;11 (Suppl 3):S588–S597. doi: 10.1093/clinids/11.supplement_3.s588. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Munson R., Jr, Bailey C., Grass S. Diversity of the outer membrane protein P2 gene from major clones of Haemophilus influenzae type b. Mol Microbiol. 1989 Dec;3(12):1797–1803. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2958.1989.tb00165.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Munson R., Jr, Grass S. Purification, cloning, and sequence of outer membrane protein P1 of Haemophilus influenzae type b. Infect Immun. 1988 Sep;56(9):2235–2242. doi: 10.1128/iai.56.9.2235-2242.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Munson R., Jr, Tolan R. W., Jr Molecular cloning, expression, and primary sequence of outer membrane protein P2 of Haemophilus influenzae type b. Infect Immun. 1989 Jan;57(1):88–94. doi: 10.1128/iai.57.1.88-94.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Murphy T. F., Apicella M. A. Nontypable Haemophilus influenzae: a review of clinical aspects, surface antigens, and the human immune response to infection. Rev Infect Dis. 1987 Jan-Feb;9(1):1–15. doi: 10.1093/clinids/9.1.1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Needleman S. B., Wunsch C. D. A general method applicable to the search for similarities in the amino acid sequence of two proteins. J Mol Biol. 1970 Mar;48(3):443–453. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(70)90057-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pichichero M. E., Loeb M., Anderson, Smith D. H. Do pili play a role in pathogenicity of Haemophilus influenzae type B? Lancet. 1982 Oct 30;2(8305):960–962. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(82)90161-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Poustka A., Rackwitz H. R., Frischauf A. M., Hohn B., Lehrach H. Selective isolation of cosmid clones by homologous recombination in Escherichia coli. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 Jul;81(13):4129–4133. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.13.4129. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shann F., Gratten M., Germer S., Linnemann V., Hazlett D., Payne R. Aetiology of pneumonia in children in Goroka Hospital, Papua New Guinea. Lancet. 1984 Sep 8;2(8402):537–541. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(84)90764-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith P. K., Krohn R. I., Hermanson G. T., Mallia A. K., Gartner F. H., Provenzano M. D., Fujimoto E. K., Goeke N. M., Olson B. J., Klenk D. C. Measurement of protein using bicinchoninic acid. Anal Biochem. 1985 Oct;150(1):76–85. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(85)90442-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stirm S., Orskov F., Orskov I., Mansa B. Episome-carried surface antigen K88 of Escherichia coli. II. Isolation and chemical analysis. J Bacteriol. 1967 Feb;93(2):731–739. doi: 10.1128/jb.93.2.731-739.1967. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Studier F. W., Moffatt B. A. Use of bacteriophage T7 RNA polymerase to direct selective high-level expression of cloned genes. J Mol Biol. 1986 May 5;189(1):113–130. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(86)90385-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stull T. L., Mendelman P. M., Haas J. E., Schoenborn M. A., Mack K. D., Smith A. L. Characterization of Haemophilus influenzae type b fimbriae. Infect Immun. 1984 Dec;46(3):787–796. doi: 10.1128/iai.46.3.787-796.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tabor S., Richardson C. C. A bacteriophage T7 RNA polymerase/promoter system for controlled exclusive expression of specific genes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Feb;82(4):1074–1078. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.4.1074. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wald E. R. Haemophilus influenzae as a cause of acute otitis media. Pediatr Infect Dis J. 1989 Jan;8(1 Suppl):S28–S30. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wall R. A., Corrah P. T., Mabey D. C., Greenwood B. M. The etiology of lobar pneumonia in the Gambia. Bull World Health Organ. 1986;64(4):553–558. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weinberg G. A., Ghafoor A., Ishaq Z., Nomani N. K., Kabeer M., Anwar F., Burney M. I., Qureshi A. W., Musser J. M., Selander R. K. Clonal analysis of Hemophilus influenzae isolated from children from Pakistan with lower respiratory tract infections. J Infect Dis. 1989 Oct;160(4):634–643. doi: 10.1093/infdis/160.4.634. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- van Ham S. M., Mooi F. R., Sindhunata M. G., Maris W. R., van Alphen L. Cloning and expression in Escherichia coli of Haemophilus influenzae fimbrial genes establishes adherence to oropharyngeal epithelial cells. EMBO J. 1989 Nov;8(11):3535–3540. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1989.tb08519.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]