Abstract
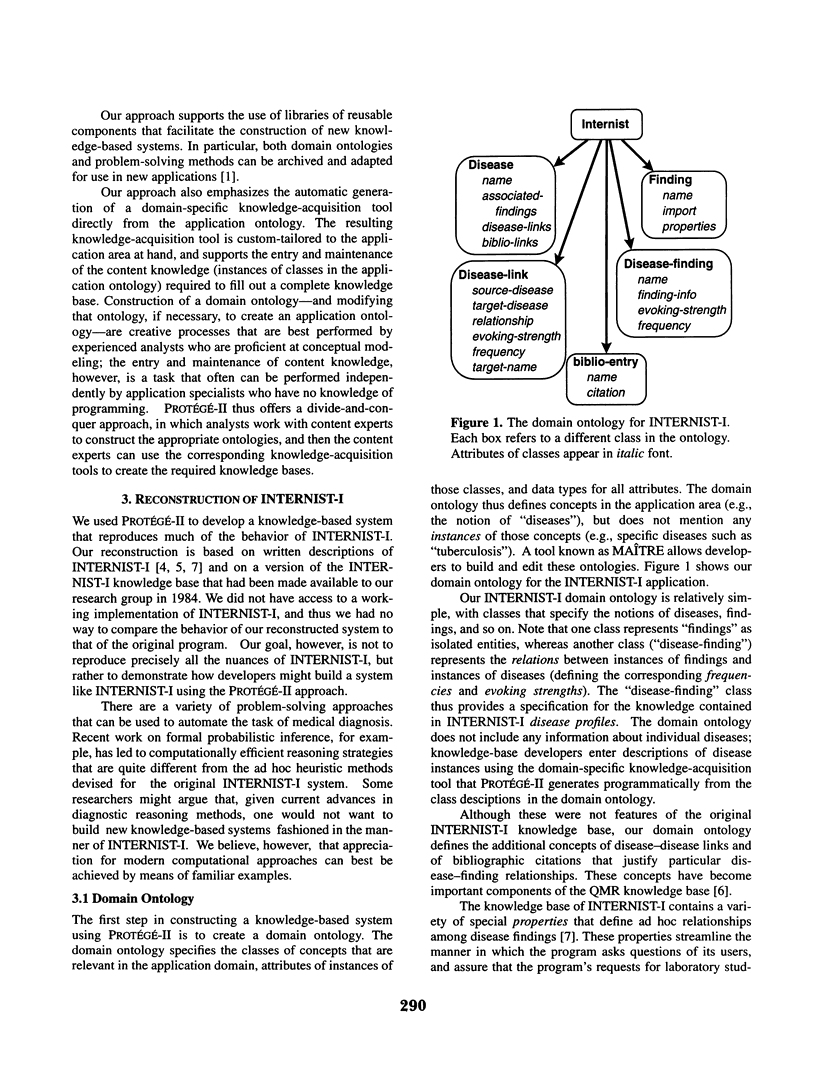
PROTEGE-II is a methodology and a suite of tools that allow developers to build and maintain knowledge-based systems in a principled manner. We used PROTEGE-II to reconstruct the well-known INTERNIST-I system, demonstrating the role of a domain ontology (a framework for specification of a model of an application area), a reusable problem-solving method, and declarative mapping relations in creating a new, working program. PROTEGE-II generates automatically a domain-specific knowledge-acquisition tool, which, in the case of the INTERNIST-I reconstruction, has much of the functionality of the QMR-KAT knowledge-acquisition tool. This study provides a means to understand better both the PROTEGE-II methodology and the models that underlie INTERNIST-I.
Full text
PDF
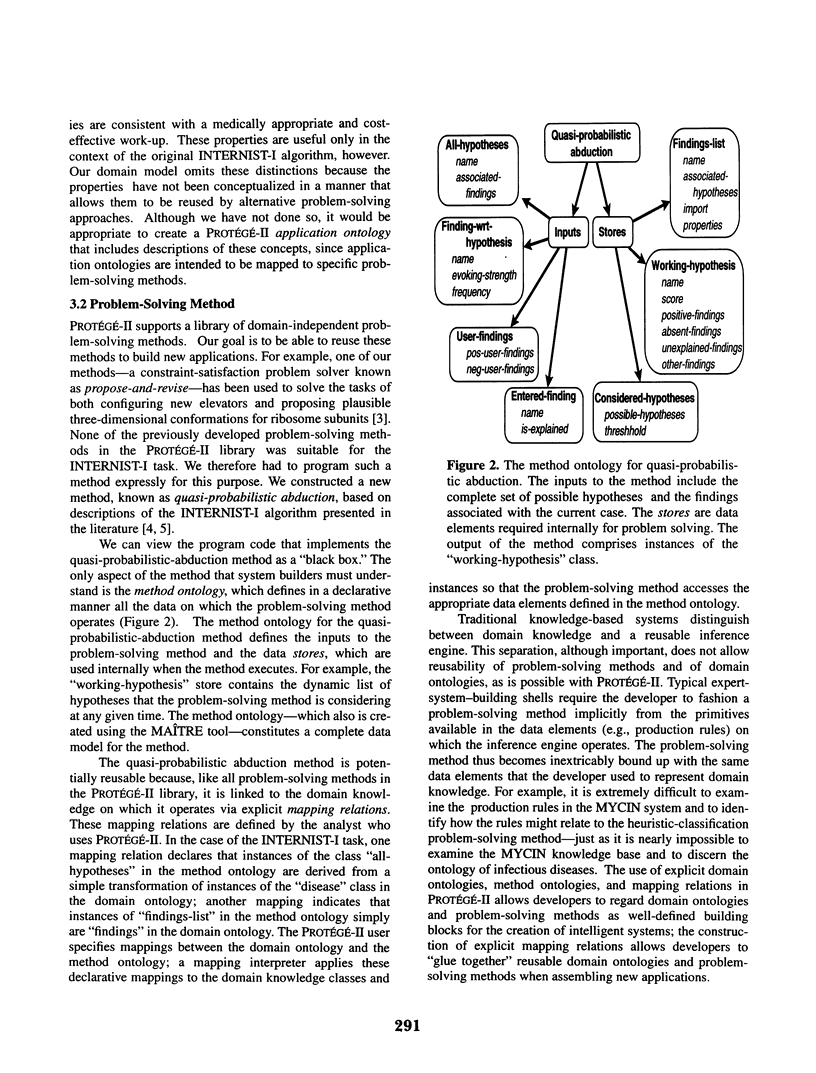


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Masarie F. E., Jr, Miller R. A., Myers J. D. INTERNIST-I properties: representing common sense and good medical practice in a computerized medical knowledge base. Comput Biomed Res. 1985 Oct;18(5):458–479. doi: 10.1016/0010-4809(85)90022-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miller R. A., McNeil M. A., Challinor S. M., Masarie F. E., Jr, Myers J. D. The INTERNIST-1/QUICK MEDICAL REFERENCE project--status report. West J Med. 1986 Dec;145(6):816–822. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miller R. A., Pople H. E., Jr, Myers J. D. Internist-1, an experimental computer-based diagnostic consultant for general internal medicine. N Engl J Med. 1982 Aug 19;307(8):468–476. doi: 10.1056/NEJM198208193070803. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Musen M. A. Dimensions of knowledge sharing and reuse. Comput Biomed Res. 1992 Oct;25(5):435–467. doi: 10.1016/0010-4809(92)90003-s. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



