Abstract
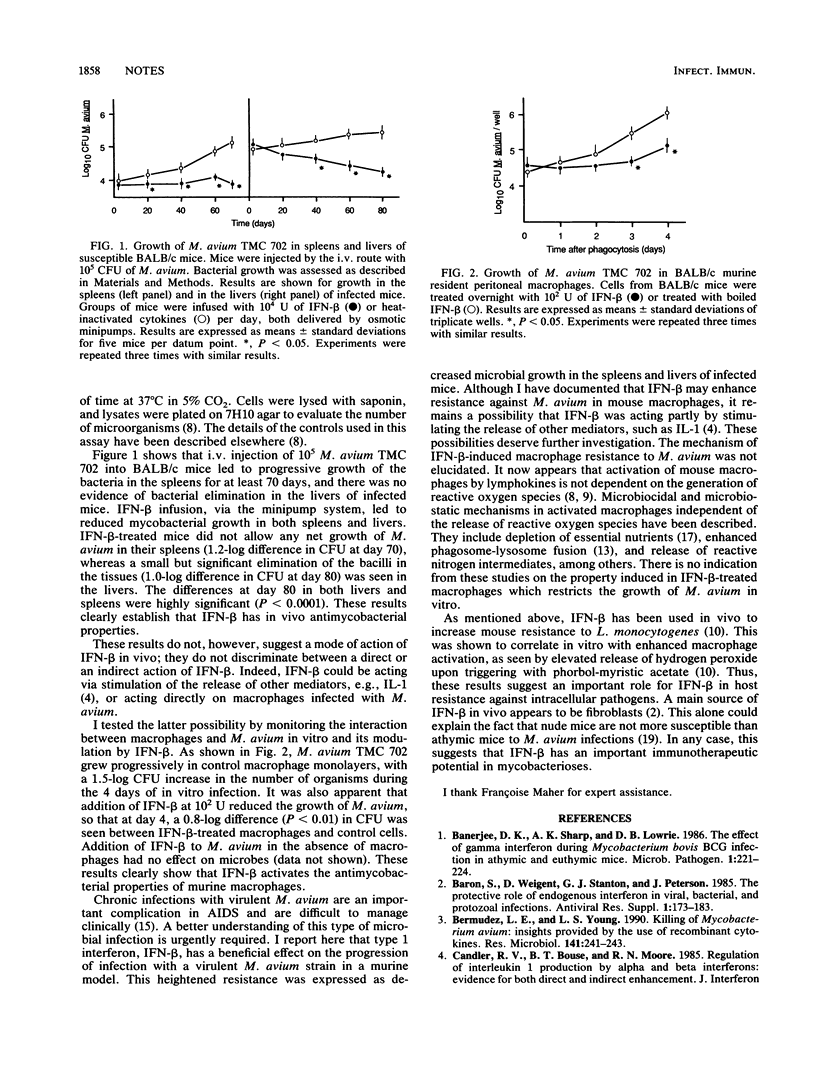
Susceptible BALB/c mice were infected with Mycobacterium avium TMC 702. Groups of mice were then infused with 10(4) U (approximately 400 U/h) of murine beta interferon (IFN-beta) via a minipump system, and the progression of the infection was assessed. Mice infused with IFN-beta showed superior resistance to infection, as determined by reduced bacterial growth in the livers and spleens of infected animals, (1-log reduction in bacterial CFU at 2 months postinfection; P less than 0.001). This was corroborated by the fact that resident peritoneal macrophages treated with IFN-beta in vitro (10(2) U/ml) were more bacteriostatic for M. avium TMC 702 than their untreated counterparts. Overall, these findings suggest an important role for IFN-beta in mycobacterial infections.
Full text
PDF

Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Banerjee D. K., Sharp A. K., Lowrie D. B. The effect of gamma-interferon during Mycobacterium bovis (BCG) infection in athymic and euthymic mice. Microb Pathog. 1986 Apr;1(2):221–224. doi: 10.1016/0882-4010(86)90024-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baron S., Weigent D., Stanton G. J., Peterson J. The protective role of endogenous interferon in viral, bacterial, and protozoal infections. Antiviral Res. 1985;Suppl 1:173–183. doi: 10.1016/s0166-3542(85)80026-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bermudez L. E., Young L. S. Killing of Mycobacterium avium: insights provided by the use of recombinant cytokines. Res Microbiol. 1990 Feb;141(2):241–243. doi: 10.1016/0923-2508(90)90037-q. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carlin J. M., Borden E. C., Byrne G. I. Interferon-induced indoleamine 2,3-dioxygenase activity inhibits Chlamydia psittaci replication in human macrophages. J Interferon Res. 1989 Jun;9(3):329–337. doi: 10.1089/jir.1989.9.329. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Collins F. M. In vivo vs. in vitro killing of virulent Mycobacterium tuberculosis. Res Microbiol. 1990 Feb;141(2):212–266. doi: 10.1016/0923-2508(90)90033-m. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Denis M., Forget A., Pelletier M., Turcotte R., Skamene E. Control of the Bcg gene of early resistance in mice to infections with BCG substrains and atypical mycobacteria. Clin Exp Immunol. 1986 Mar;63(3):517–525. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Denis M., Gregg E. O. Modulation of Mycobacterium avium growth in murine macrophages: reversal of unresponsiveness to interferon-gamma by indomethacin or interleukin-4. J Leukoc Biol. 1991 Jan;49(1):65–72. doi: 10.1002/jlb.49.1.65. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Flesch I. E., Kaufmann S. H. Attempts to characterize the mechanisms involved in mycobacterial growth inhibition by gamma-interferon-activated bone marrow macrophages. Infect Immun. 1988 Jun;56(6):1464–1469. doi: 10.1128/iai.56.6.1464-1469.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fujiki T., Tanaka A. Antibacterial activity of recombinant murine beta interferon. Infect Immun. 1988 Mar;56(3):548–551. doi: 10.1128/iai.56.3.548-551.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jeevan A., Asherson G. L. Recombinant interleukin-2 limits the replication of Mycobacterium lepraemurium and Mycobacterium bovis BCG in mice. Lymphokine Res. 1988 Summer;7(2):129–140. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kindler V., Sappino A. P., Grau G. E., Piguet P. F., Vassalli P. The inducing role of tumor necrosis factor in the development of bactericidal granulomas during BCG infection. Cell. 1989 Mar 10;56(5):731–740. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(89)90676-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moulder J. W. Comparative biology of intracellular parasitism. Microbiol Rev. 1985 Sep;49(3):298–337. doi: 10.1128/mr.49.3.298-337.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Murray H. W. Interferon-gamma, the activated macrophage, and host defense against microbial challenge. Ann Intern Med. 1988 Apr;108(4):595–608. doi: 10.7326/0003-4819-108-4-595. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- O'Brien R. J., Geiter L. J., Snider D. E., Jr The epidemiology of nontuberculous mycobacterial diseases in the United States. Results from a national survey. Am Rev Respir Dis. 1987 May;135(5):1007–1014. doi: 10.1164/arrd.1987.135.5.1007. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Passwell J. H., Shor R., Shoham J. The enhancing effect of interferon-beta and -gamma on the killing of Leishmania tropica major in human mononuclear phagocytes in vitro. J Immunol. 1986 Apr 15;136(8):3062–3066. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pfefferkorn E. R. Interferon gamma blocks the growth of Toxoplasma gondii in human fibroblasts by inducing the host cells to degrade tryptophan. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 Feb;81(3):908–912. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.3.908. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rook G. A., Steele J., Ainsworth M., Champion B. R. Activation of macrophages to inhibit proliferation of Mycobacterium tuberculosis: comparison of the effects of recombinant gamma-interferon on human monocytes and murine peritoneal macrophages. Immunology. 1986 Nov;59(3):333–338. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Saito H., Tomioka H. The role of macrophages in host defence mechanisms against Mycobacterium avium complex infection induced in mice. Res Microbiol. 1990 Feb;141(2):206–212. doi: 10.1016/0923-2508(90)90032-l. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schmitz J. L., Carlin J. M., Borden E. C., Byrne G. I. Beta interferon inhibits Toxoplasma gondii growth in human monocyte-derived macrophages. Infect Immun. 1989 Oct;57(10):3254–3256. doi: 10.1128/iai.57.10.3254-3256.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Squires K. E., Murphy W. F., Madoff L. C., Murray H. W. Interferon-gamma and Mycobacterium avium-intracellulare infection. J Infect Dis. 1989 Mar;159(3):599–600. doi: 10.1093/infdis/159.3.599. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Toba H., Crawford J. T., Ellner J. J. Pathogenicity of Mycobacterium avium for human monocytes: absence of macrophage-activating factor activity of gamma interferon. Infect Immun. 1989 Jan;57(1):239–244. doi: 10.1128/iai.57.1.239-244.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weigent D. A., Huff T. L., Peterson J. W., Stanton G. J., Baron S. Role of interferon in streptococcal infection in the mouse. Microb Pathog. 1986 Aug;1(4):399–407. doi: 10.1016/0882-4010(86)90071-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



