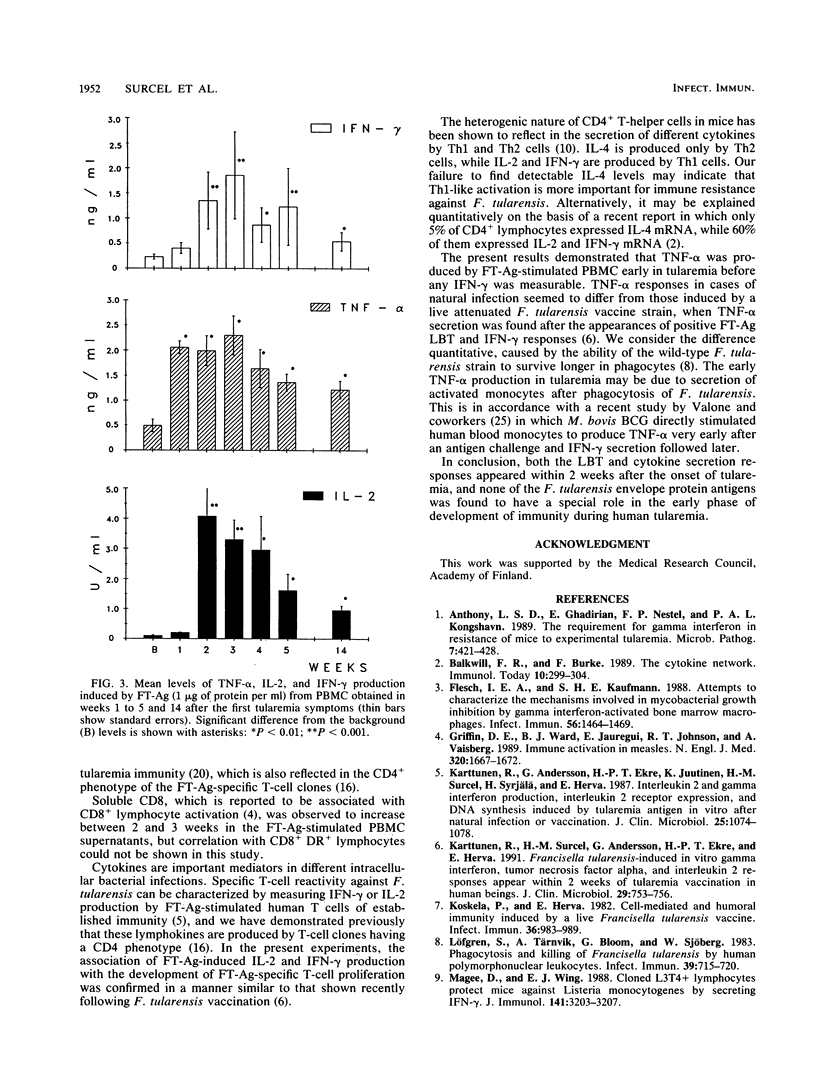
Abstract
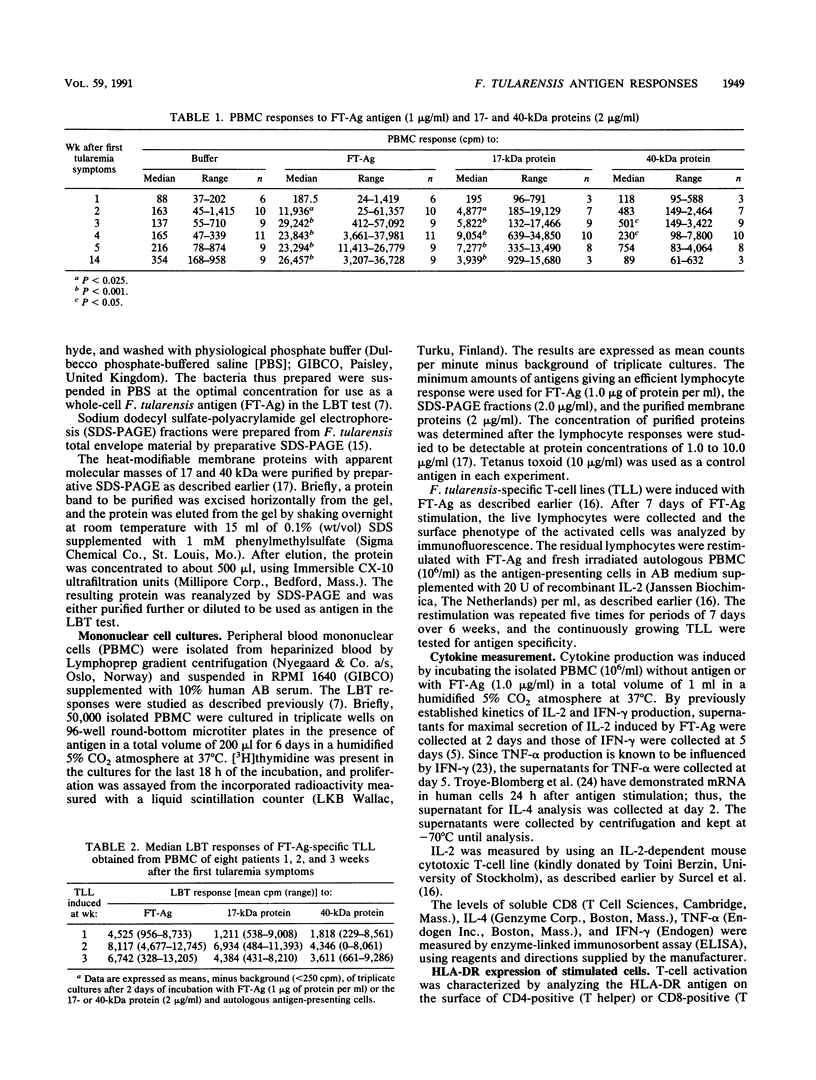
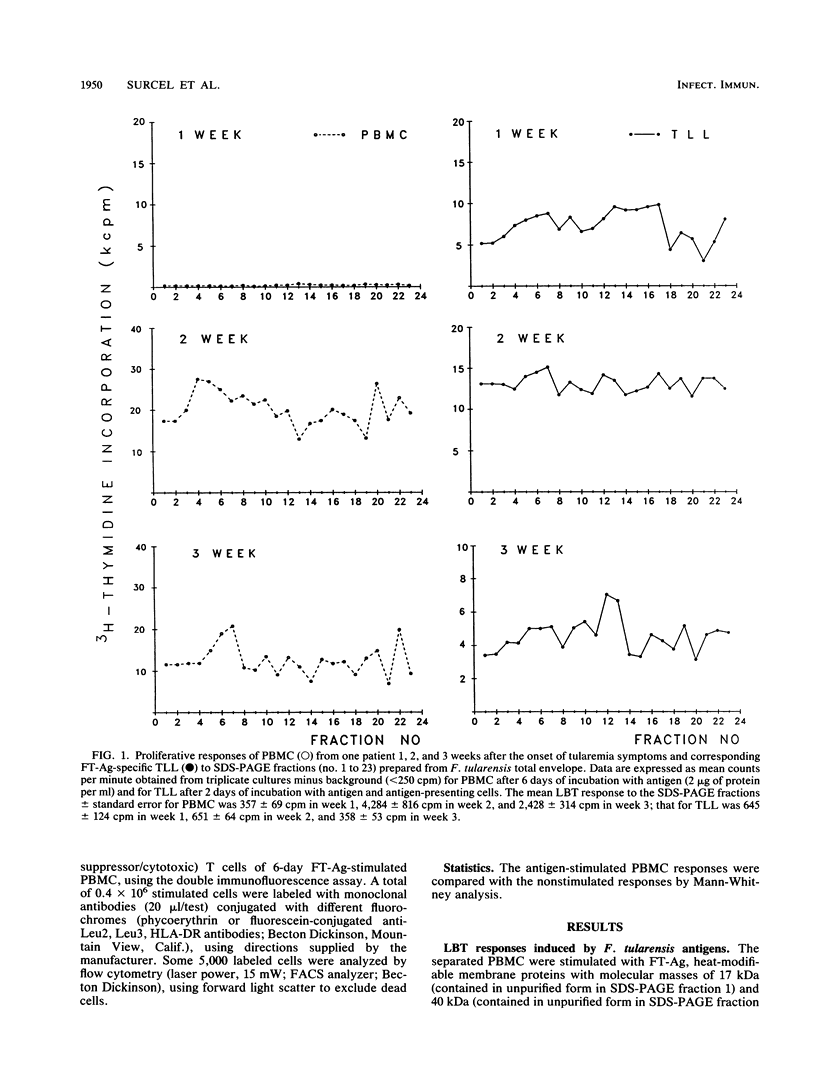
The lymphocyte immune reactivity of 12 tularemia patients to Francisella tularensis antigens prepared from the bacterial cell envelope was examined during a 14-week follow-up study. Lymphocyte blast transformation responses of peripheral blood mononuclear cells (PBMC) to different protein antigens appeared simultaneously 2 weeks after the first symptoms of tularemia, indicating that none of these antigens had any special role at the early phase of immunization. While the lymphocyte blast transformation responses of total lymphocytes to all bacterial antigens were negative in the week 1 samples, continuously growing F. tularensis-specific T-lymphocyte lines were obtained from PBMC at the same time, indicating that an immune response had already occurred. Later, the T-lymphocyte lines and lymphocyte blast transformation responses were similar. Lymphocyte activation among the PBMC was reflected in an increased number of HLA-DR antigen-expressing, CD4-positive T lymphocytes (CD4+ DR+). The mean secretion of soluble CD8 from F. tularemia antigen-stimulated PBMC increased 2 weeks after tularemia onset, but the mean number of CD8+ DR+ T lymphocytes did not vary during the study period and no correlation could be found between the soluble CD8 and number of CD8+ DR+ T lymphocytes. F. tularemia antigen-induced cytokine production was measured from the PBMC supernatants. High levels of tumor necrosis factor alpha were detected from the first week onwards. The highest levels of interleukin-2 and gamma interferon were recorded during the second and third weeks, respectively, after tularemia onset. Interleukin-4 could not be demonstrated in the lymphocyte supernatants.
Full text
PDF

Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Anthony L. S., Ghadirian E., Nestel F. P., Kongshavn P. A. The requirement for gamma interferon in resistance of mice to experimental tularemia. Microb Pathog. 1989 Dec;7(6):421–428. doi: 10.1016/0882-4010(89)90022-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Balkwill F. R., Burke F. The cytokine network. Immunol Today. 1989 Sep;10(9):299–304. doi: 10.1016/0167-5699(89)90085-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Flesch I. E., Kaufmann S. H. Attempts to characterize the mechanisms involved in mycobacterial growth inhibition by gamma-interferon-activated bone marrow macrophages. Infect Immun. 1988 Jun;56(6):1464–1469. doi: 10.1128/iai.56.6.1464-1469.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Griffin D. E., Ward B. J., Jauregui E., Johnson R. T., Vaisberg A. Immune activation in measles. N Engl J Med. 1989 Jun 22;320(25):1667–1672. doi: 10.1056/NEJM198906223202506. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Karttunen R., Andersson G., Ekre H. P., Juutinen K., Surcel H. M., Syrjälä H., Herva E. Interleukin 2 and gamma interferon production, interleukin 2 receptor expression, and DNA synthesis induced by tularemia antigen in vitro after natural infection or vaccination. J Clin Microbiol. 1987 Jun;25(6):1074–1078. doi: 10.1128/jcm.25.6.1074-1078.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Karttunen R., Surcel H. M., Andersson G., Ekre H. P., Herva E. Francisella tularensis-induced in vitro gamma interferon, tumor necrosis factor alpha, and interleukin 2 responses appear within 2 weeks of tularemia vaccination in human beings. J Clin Microbiol. 1991 Apr;29(4):753–756. doi: 10.1128/jcm.29.4.753-756.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Koskela P., Herva E. Cell-mediated and humoral immunity induced by a live Francisella tularensis vaccine. Infect Immun. 1982 Jun;36(3):983–989. doi: 10.1128/iai.36.3.983-989.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Löfgren S., Tärnvik A., Bloom G. D., Sjöberg W. Phagocytosis and killing of Francisella tularensis by human polymorphonuclear leukocytes. Infect Immun. 1983 Feb;39(2):715–720. doi: 10.1128/iai.39.2.715-720.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Magee D. M., Wing E. J. Cloned L3T4+ T lymphocytes protect mice against Listeria monocytogenes by secreting IFN-gamma. J Immunol. 1988 Nov 1;141(9):3203–3207. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mosmann T. R., Coffman R. L. Heterogeneity of cytokine secretion patterns and functions of helper T cells. Adv Immunol. 1989;46:111–147. doi: 10.1016/s0065-2776(08)60652-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nakane A., Minagawa T., Kato K. Endogenous tumor necrosis factor (cachectin) is essential to host resistance against Listeria monocytogenes infection. Infect Immun. 1988 Oct;56(10):2563–2569. doi: 10.1128/iai.56.10.2563-2569.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nash T. W., Libby D. M., Horwitz M. A. IFN-gamma-activated human alveolar macrophages inhibit the intracellular multiplication of Legionella pneumophila. J Immunol. 1988 Jun 1;140(11):3978–3981. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sandström G., Tärnvik A., Wolf-Watz H. Immunospecific T-lymphocyte stimulation by membrane proteins from Francisella tularensis. J Clin Microbiol. 1987 Apr;25(4):641–644. doi: 10.1128/jcm.25.4.641-644.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sjöstedt A., Sandström G., Tärnvik A. Several membrane polypeptides of the live vaccine strain Francisella tularensis LVS stimulate T cells from naturally infected individuals. J Clin Microbiol. 1990 Jan;28(1):43–48. doi: 10.1128/jcm.28.1.43-48.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Surcel H. M. Diversity of Francisella tularensis antigens recognized by human T lymphocytes. Infect Immun. 1990 Aug;58(8):2664–2668. doi: 10.1128/iai.58.8.2664-2668.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Surcel H. M., Ilonen J., Poikonen K., Herva E. Francisella tularensis-specific T-cell clones are human leukocyte antigen class II restricted, secrete interleukin-2 and gamma interferon, and induce immunoglobulin production. Infect Immun. 1989 Sep;57(9):2906–2908. doi: 10.1128/iai.57.9.2906-2908.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Surcel H. M., Sarvas M., Helander I. M., Herva E. Membrane proteins of Francisella tularensis LVS differ in ability to induce proliferation of lymphocytes from tularemia-vaccinated individuals. Microb Pathog. 1989 Dec;7(6):411–419. doi: 10.1016/0882-4010(89)90021-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Syrjälä H., Herva E., Ilonen J., Saukkonen K., Salminen A. A whole-blood lymphocyte stimulation test for the diagnosis of human tularemia. J Infect Dis. 1984 Dec;150(6):912–915. doi: 10.1093/infdis/150.6.912. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Syrjälä H., Koskela P., Ripatti T., Salminen A., Herva E. Agglutination and ELISA methods in the diagnosis of tularemia in different clinical forms and severities of the disease. J Infect Dis. 1986 Jan;153(1):142–145. doi: 10.1093/infdis/153.1.142. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tracey K. J., Vlassara H., Cerami A. Cachectin/tumour necrosis factor. Lancet. 1989 May 20;1(8647):1122–1126. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(89)92394-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Troye-Blomberg M., Riley E. M., Kabilan L., Holmberg M., Perlmann H., Andersson U., Heusser C. H., Perlmann P. Production by activated human T cells of interleukin 4 but not interferon-gamma is associated with elevated levels of serum antibodies to activating malaria antigens. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1990 Jul;87(14):5484–5488. doi: 10.1073/pnas.87.14.5484. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tärnvik A., Holm S. E. Stimulation of subpopulations of human lymphocytes by a vaccine strain of Francisella tularensis. Infect Immun. 1978 Jun;20(3):698–704. doi: 10.1128/iai.20.3.698-704.1978. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tärnvik A. Nature of protective immunity to Francisella tularensis. Rev Infect Dis. 1989 May-Jun;11(3):440–451. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tärnvik A., Sandström G., Löfgren S. Time of lymphocyte response after onset of tularemia and after tularemia vaccination. J Clin Microbiol. 1979 Dec;10(6):854–860. doi: 10.1128/jcm.10.6.854-860.1979. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Valone S. E., Rich E. A., Wallis R. S., Ellner J. J. Expression of tumor necrosis factor in vitro by human mononuclear phagocytes stimulated with whole Mycobacterium bovis BCG and mycobacterial antigens. Infect Immun. 1988 Dec;56(12):3313–3315. doi: 10.1128/iai.56.12.3313-3315.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



