Abstract
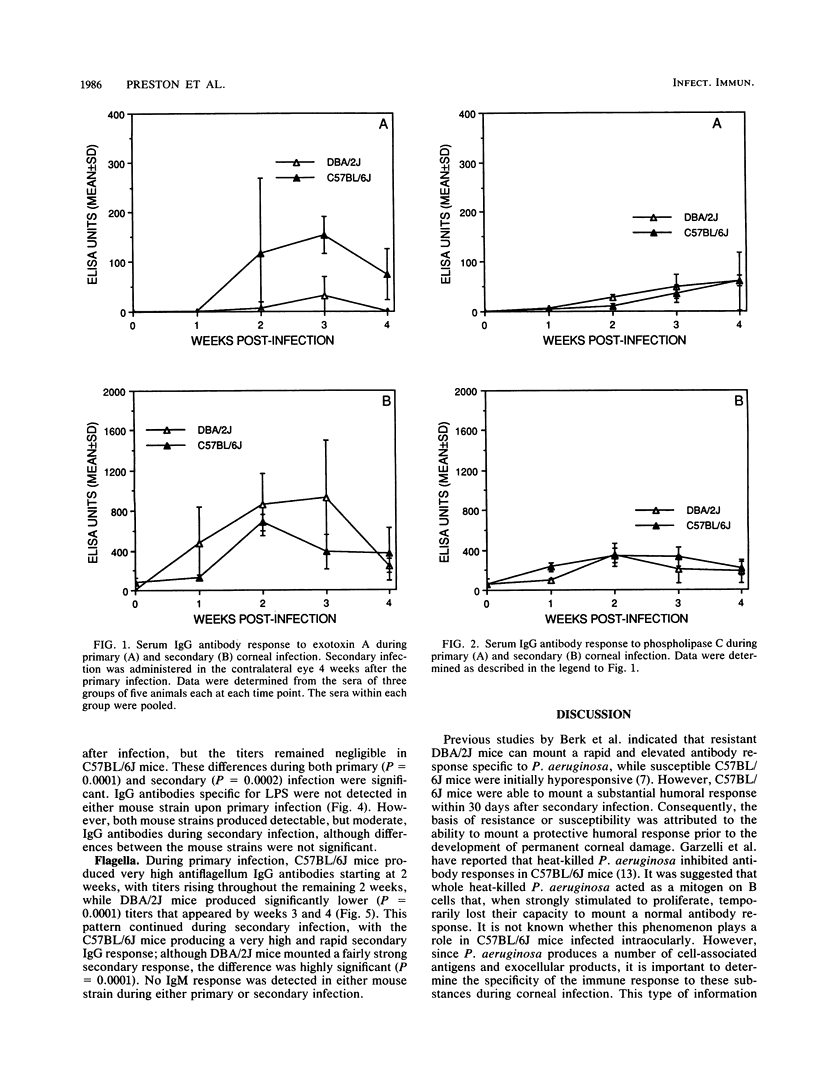
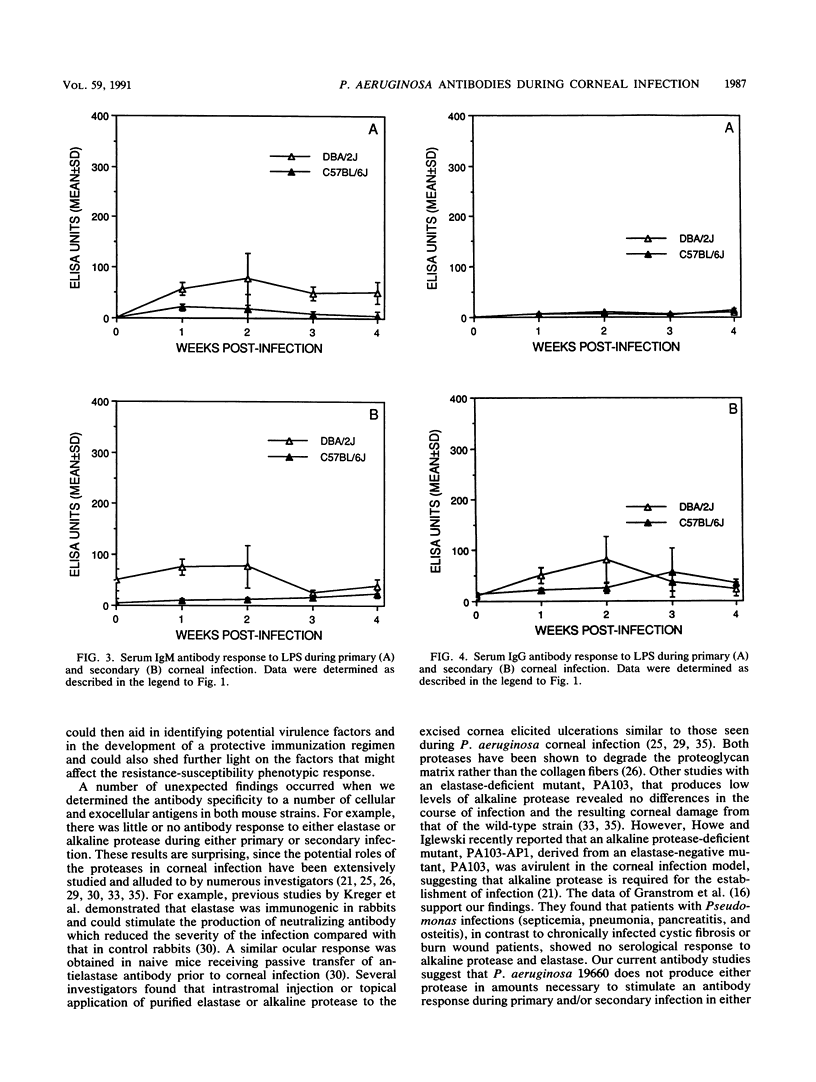
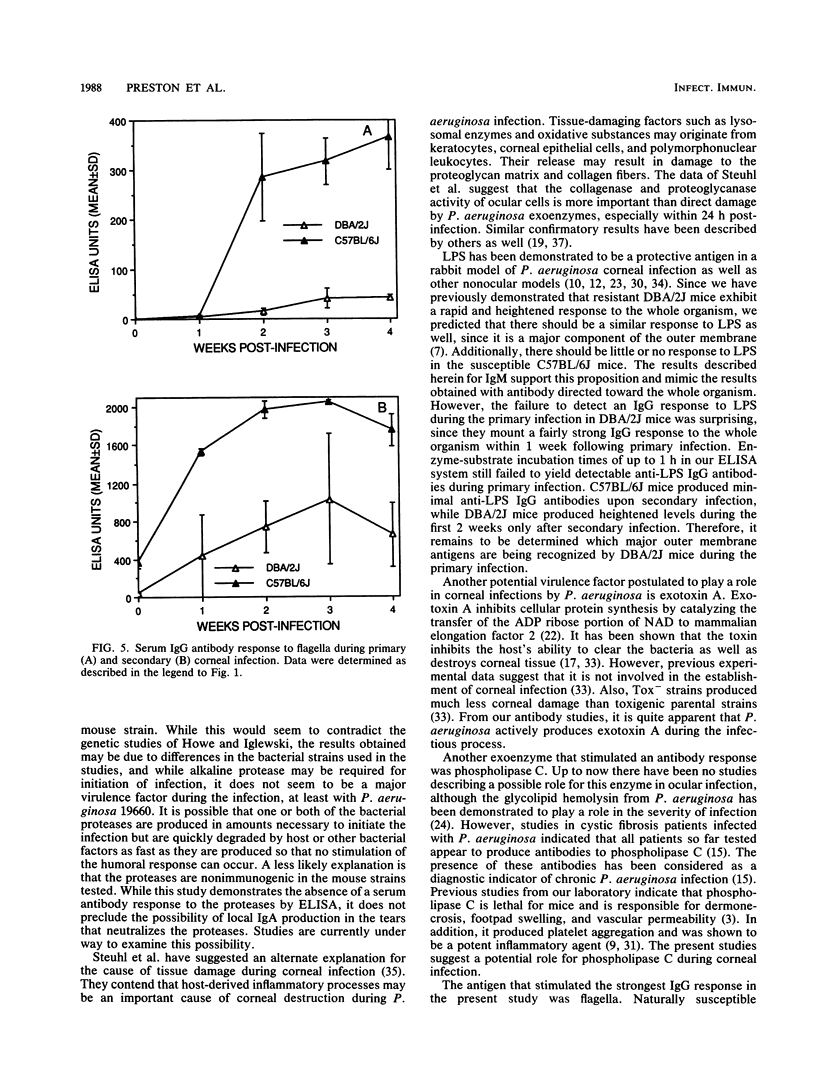
Previous studies in our laboratory have indicated that naturally resistant, inbred DBA/2J mice mount a greater serum antibody response to Pseudomonas aeruginosa 19660 than susceptible C57BL/6J mice. However, the specificity of the antibody produced was not known. The present study examines the specificity and kinetics of the humoral response of these mouse strains to potential virulence factors produced by the organism during both a primary and a secondary corneal infection administered 4 weeks after the primary infection. Serum antibody levels specific for lipopolysaccharide (LPS), exotoxin A, phospholipase C (PLC), alkaline protease, elastase, and flagella were measured by enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay. Little or no antibody to either alkaline protease or elastase was detected during either primary or secondary infection. Immunoglobulin G (IgG) antibodies specific to exotoxin A, PLC, and flagella were detected 2 weeks after primary infection, and a rapid response to these antigens was measured 1 week after secondary infection. During primary infection, detectable LPS-specific antibody was only IgM, while IgG appeared only after secondary infection. The kinetics of the humoral response in susceptible C57BL/6J mice were similar to those in resistant DBA/2J mice, although the magnitude of the response varied according to the antigen tested. These results indicate that LPS, exotoxin A, PLC, and flagella are present or produced in amounts that are immunogenic during corneal infection by P. aeruginosa 19660 in the mouse strains tested.
Full text
PDF



Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Anderson T. R., Montie T. C. Flagellar antibody stimulated opsonophagocytosis of Pseudomonas aeruginosa associated with response to either a- or b-type flagellar antigen. Can J Microbiol. 1989 Sep;35(9):890–894. doi: 10.1139/m89-148. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Beisel K. W., Hazlett L. D., Berk R. S. Dominant susceptibility effect on the murine corneal response to Pseudomonas aeruginosa. Proc Soc Exp Biol Med. 1983 Apr;172(4):488–491. doi: 10.3181/00379727-172-41592. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Berk R. S., Brown D., Coutinho I., Meyers D. In vivo studies with two phospholipase C fractions from Pseudomonas aeruginosa. Infect Immun. 1987 Jul;55(7):1728–1730. doi: 10.1128/iai.55.7.1728-1730.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Berk R. S., Hazlett L. D., Beisel K. W. Genetic studies on resistant and susceptibility genes controlling the mouse cornea to infection with Pseudomonas aeruginosa. Antibiot Chemother (1971) 1987;39:83–91. doi: 10.1159/000414336. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Berk R. S., Hazlett L. D. Further studies on the genetic control of murine corneal response to Pseudomonas aeruginosa. Rev Infect Dis. 1983 Nov-Dec;5 (Suppl 5):S936–S940. doi: 10.1093/clinids/5.supplement_5.s936. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Berk R. S., Leon M. A., Hazlett L. D. Genetic control of the murine corneal response to Pseudomonas aeruginosa. Infect Immun. 1979 Dec;26(3):1221–1223. doi: 10.1128/iai.26.3.1221-1223.1979. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Berk R. S., Montgomery I. N., Hazlett L. D. Serum antibody and ocular responses to murine corneal infection caused by Pseudomonas aeruginosa. Infect Immun. 1988 Dec;56(12):3076–3080. doi: 10.1128/iai.56.12.3076-3080.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chusid M. J., Davis S. D. Experimental bacterial keratitis in neutropenic guinea pigs: polymorphonuclear leukocytes in corneal host defense. Infect Immun. 1979 Jun;24(3):948–952. doi: 10.1128/iai.24.3.948-952.1979. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Coutinho I. R., Berk R. S., Mammen E. Platelet aggregation by a phospholipase C from Pseudomonas aeruginosa. Thromb Res. 1988 Sep 1;51(5):495–505. doi: 10.1016/0049-3848(88)90115-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Crowder J. G., Fisher M. W., White A. Type-specific immunity in pseudomonas diseases. J Lab Clin Med. 1972 Jan;79(1):47–54. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cryz S. J., Jr, Fürer E., Germanier R. Protection against Pseudomonas aeruginosa infection in a murine burn wound sepsis model by passive transfer of antitoxin A, antielastase, and antilipopolysaccharide. Infect Immun. 1983 Mar;39(3):1072–1079. doi: 10.1128/iai.39.3.1072-1079.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Drake D., Montie T. C. Protection against Pseudomonas aeruginosa infection by passive transfer of anti-flagellar serum. Can J Microbiol. 1987 Sep;33(9):755–763. doi: 10.1139/m87-130. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Garzelli C., Colizzi V., Campa M., Bozzi L., Falcone G. Depression of the antibody response in Pseudomonas aeruginosa-injected mice. Infect Immun. 1979 Apr;24(1):32–38. doi: 10.1128/iai.24.1.32-38.1979. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gerke J. R., Magliocco M. V. Experimental Pseudomonas aeruginosa Infection of the Mouse Cornea. Infect Immun. 1971 Feb;3(2):209–216. doi: 10.1128/iai.3.2.209-216.1971. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Granström M., Ericsson A., Strandvik B., Wretlind B., Pavlovskis O. R., Berka R., Vasil M. L. Relation between antibody response to Pseudomonas aeruginosa exoproteins and colonization/infection in patients with cystic fibrosis. Acta Paediatr Scand. 1984 Nov;73(6):772–777. doi: 10.1111/j.1651-2227.1984.tb17774.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Granström M., Wretlind B., Markman B., Pavlovskis O. R., Vasil M. L. Enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay for detection of antibodies to Pseudomonas aeruginosa exoproteins. Eur J Clin Microbiol. 1985 Apr;4(2):197–200. doi: 10.1007/BF02013597. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hazlett L. D., Berk R. S., Iglewski B. H. Microscopic characterization of ocular damage produced by Pseudomonas aeruginosa toxin A. Infect Immun. 1981 Dec;34(3):1025–1035. doi: 10.1128/iai.34.3.1025-1035.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Holder I. A., Naglich J. G. Experimental studies of the pathogenesis of infections due to Pseudomonas aeruginosa: immunization using divalent flagella preparations. J Trauma. 1986 Feb;26(2):118–122. doi: 10.1097/00005373-198602000-00003. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Howe T. R., Iglewski B. H. Isolation and characterization of alkaline protease-deficient mutants of Pseudomonas aeruginosa in vitro and in a mouse eye model. Infect Immun. 1984 Mar;43(3):1058–1063. doi: 10.1128/iai.43.3.1058-1063.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Iglewski B. H., Liu P. V., Kabat D. Mechanism of action of Pseudomonas aeruginosa exotoxin Aiadenosine diphosphate-ribosylation of mammalian elongation factor 2 in vitro and in vivo. Infect Immun. 1977 Jan;15(1):138–144. doi: 10.1128/iai.15.1.138-144.1977. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Johnson M. K., Allen J. H. The role of hemolysin in corneal infections with Pseudomonas aeruginosa. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci. 1978 May;17(5):480–483. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kawaharajo K., Abe C., Homma J. Y., Kawano M., Goto E. Corneal ulcers caused by protease and elastase from Pseudomonas aeruginosa. Jpn J Exp Med. 1974 Oct;44(5):435–442. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kessler E., Kennah H. E., Brown S. I. Pseudomonas protease. Purification, partial characterization, and its effect on collagen, proteoglycan, and rabbit corneas. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci. 1977 Jun;16(6):488–497. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kessler E., Mondino B. J., Brown S. I. The corneal response to Pseudomonas aeruginosa: histopathological and enzymatic characterization. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci. 1977 Feb;16(2):116–125. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kreger A. S., Gray L. D. Purification of Pseudomonas aeruginosa proteases and microscopic characterization of pseudomonal protease-induced rabbit corneal damage. Infect Immun. 1978 Feb;19(2):630–648. doi: 10.1128/iai.19.2.630-648.1978. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kreger A. S., Lyerly D. M., Hazlett L. D., Berk R. S. Immunization against experimental Pseudomonas aeruginosa and Serratia marcescens keratitis. Vaccination with lipopolysaccharide endotoxins and proteases. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci. 1986 Jun;27(6):932–939. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kreger A. S. Pathogenesis of Pseudomonas aeruginosa ocular diseases. Rev Infect Dis. 1983 Nov-Dec;5 (Suppl 5):S931–S935. doi: 10.1093/clinids/5.supplement_5.s931. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Meyers D. J., Berk R. S. Characterization of phospholipase C from Pseudomonas aeruginosa as a potent inflammatory agent. Infect Immun. 1990 Mar;58(3):659–666. doi: 10.1128/iai.58.3.659-666.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Montie T. C., Anderson T. R. Enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay for detection of Pseudomonas aeruginosa H (flagellar) antigen. Eur J Clin Microbiol Infect Dis. 1988 Apr;7(2):256–260. doi: 10.1007/BF01963097. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ohman D. E., Burns R. P., Iglewski B. H. Corneal infections in mice with toxin A and elastase mutants of Pseudomonas aeruginosa. J Infect Dis. 1980 Oct;142(4):547–555. doi: 10.1093/infdis/142.4.547. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Steuhl K. P., Döring G., Henni A., Thiel H. J., Botzenhart K. Relevance of host-derived and bacterial factors in Pseudomonas aeruginosa corneal infections. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci. 1987 Sep;28(9):1559–1568. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stoll B. J., Pollack M., Young L. S., Koles N., Gascon R., Pier G. B. Functionally active monoclonal antibody that recognizes an epitope on the O side chain of Pseudomonas aeruginosa immunotype-1 lipopolysaccharide. Infect Immun. 1986 Sep;53(3):656–662. doi: 10.1128/iai.53.3.656-662.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Twining S. S., Lohr K. M., Moulder J. E. The immune system in experimental Pseudomonas keratitis. Model and early effects. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci. 1986 Apr;27(4):507–515. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Van Horn D. L., Davis S. D., Hyndiuk R. A., Pederson H. J. Experimental Pseudomonas keratitis in the rabbit: bacteriologic, clinical, and microscopic observations. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci. 1981 Feb;20(2):213–221. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



