Abstract
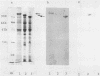
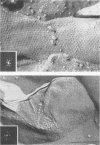
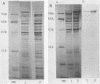
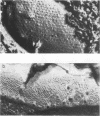
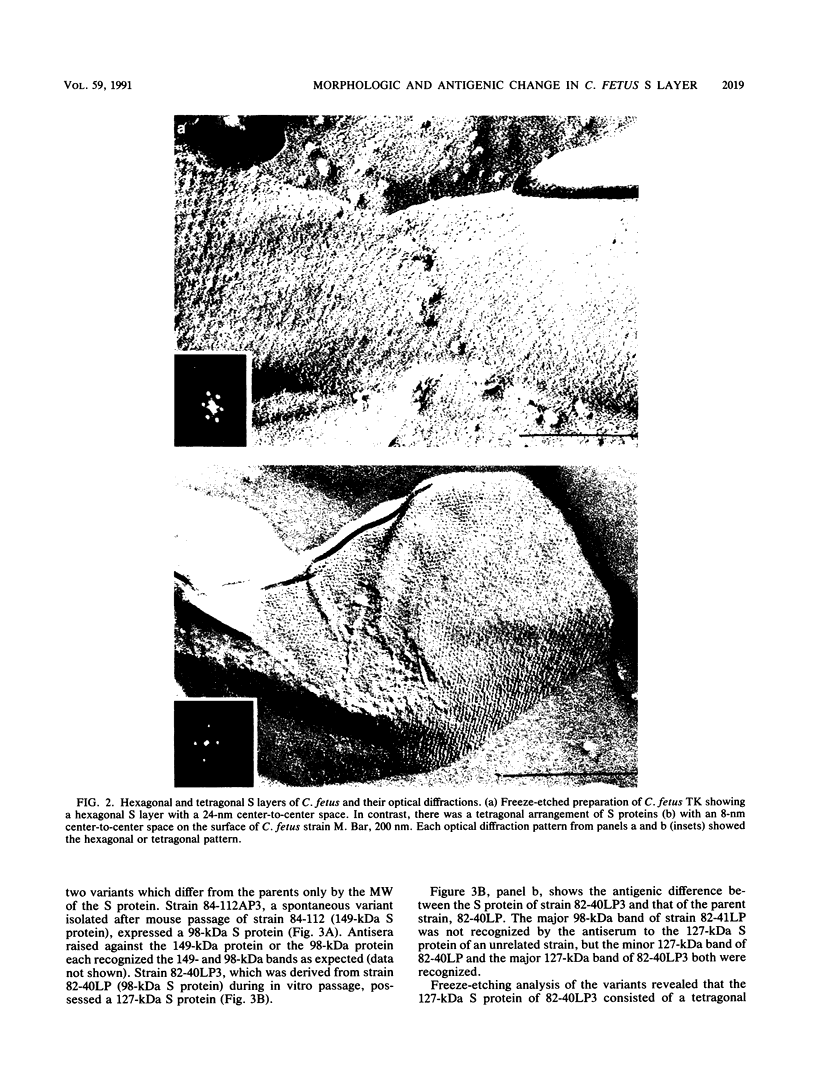
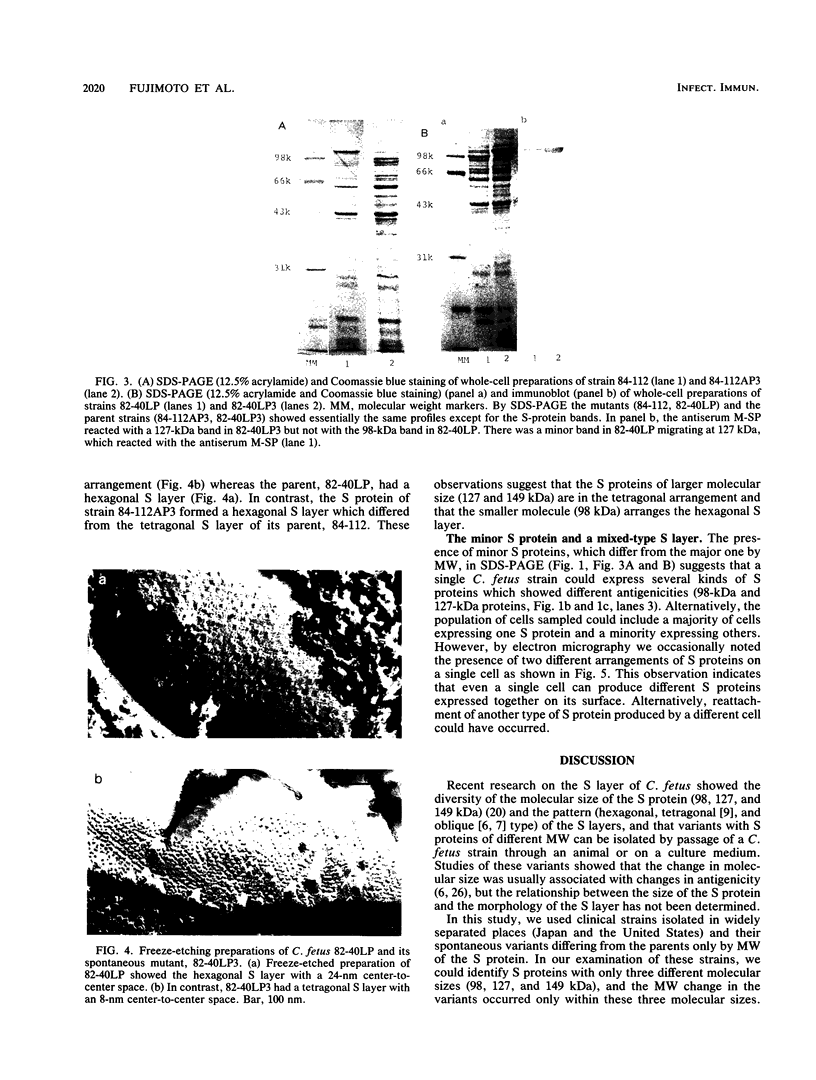
The correlation between the molecular size of the surface layer protein (S protein) and both structure and antigenicity of the Campylobacter fetus surface layer (S layer) was investigated in several clinical strains and their spontaneous variants which produce S proteins of molecular weights (MW) different from those of the parents. Only three molecular sizes of the S proteins were observed (98, 127, and 149 kDa) in the parental and variant strains. Immunologically, the 98-kDa protein and the 149-kDa protein but not the 127-kDa protein were cross-reactive. Freeze-etching analysis showed that the 98-kDa S protein formed a hexagonal arrangement with a 24-nm center-to-center space and that the S proteins with larger MW (127 or 149 kDa) formed tetragonal ones with an 8-nm center-to-center space. Thus, the MW changes of the S proteins seen in the variant strains were associated with both morphological and antigenic changes in S layer. These observations support the hypothesis that the pattern and antigenicity of the C. fetus S layer is determined by the particular type of S protein. Furthermore, the presence of the two different S layer patterns on a single bacterial cell indicates that multiple S proteins can be produced and expressed in a single cell.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Blaser M. J., Gotschlich E. C. Surface array protein of Campylobacter fetus. Cloning and gene structure. J Biol Chem. 1990 Aug 25;265(24):14529–14535. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blaser M. J., Smith P. F., Hopkins J. A., Heinzer I., Bryner J. H., Wang W. L. Pathogenesis of Campylobacter fetus infections: serum resistance associated with high-molecular-weight surface proteins. J Infect Dis. 1987 Apr;155(4):696–706. doi: 10.1093/infdis/155.4.696. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blaser M. J., Smith P. F., Repine J. E., Joiner K. A. Pathogenesis of Campylobacter fetus infections. Failure of encapsulated Campylobacter fetus to bind C3b explains serum and phagocytosis resistance. J Clin Invest. 1988 May;81(5):1434–1444. doi: 10.1172/JCI113474. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cover T. L., Blaser M. J. The pathobiology of Campylobacter infections in humans. Annu Rev Med. 1989;40:269–285. doi: 10.1146/annurev.me.40.020189.001413. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dubreuil J. D., Kostrzynska M., Austin J. W., Trust T. J. Antigenic differences among Campylobacter fetus S-layer proteins. J Bacteriol. 1990 Sep;172(9):5035–5043. doi: 10.1128/jb.172.9.5035-5043.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dubreuil J. D., Logan S. M., Cubbage S., Eidhin D. N., McCubbin W. D., Kay C. M., Beveridge T. J., Ferris F. G., Trust T. J. Structural and biochemical analyses of a surface array protein of Campylobacter fetus. J Bacteriol. 1988 Sep;170(9):4165–4173. doi: 10.1128/jb.170.9.4165-4173.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fogg G. C., Yang L. Y., Wang E., Blaser M. J. Surface array proteins of Campylobacter fetus block lectin-mediated binding to type A lipopolysaccharide. Infect Immun. 1990 Sep;58(9):2738–2744. doi: 10.1128/iai.58.9.2738-2744.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fujimoto S., Umeda A., Takade A., Murata K., Amako K. Hexagonal surface layer of Campylobacter fetus isolated from humans. Infect Immun. 1989 Aug;57(8):2563–2565. doi: 10.1128/iai.57.8.2563-2565.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Howe T. R., LaQuier F. W., Barbour A. G. Organization of genes encoding two outer membrane proteins of the Lyme disease agent Borrelia burgdorferi within a single transcriptional unit. Infect Immun. 1986 Oct;54(1):207–212. doi: 10.1128/iai.54.1.207-212.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ishiguro E. E., Kay W. W., Ainsworth T., Chamberlain J. B., Austen R. A., Buckley J. T., Trust T. J. Loss of virulence during culture of Aeromonas salmonicida at high temperature. J Bacteriol. 1981 Oct;148(1):333–340. doi: 10.1128/jb.148.1.333-340.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laemmli U. K. Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature. 1970 Aug 15;227(5259):680–685. doi: 10.1038/227680a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McCoy E. C., Doyle D., Burda K., Corbeil L. B., Winter A. J. Superficial antigens of Campylobacter (Vibrio) fetus: characterization of antiphagocytic component. Infect Immun. 1975 Mar;11(3):517–525. doi: 10.1128/iai.11.3.517-525.1975. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McCoy E. C., Wiltberger H. A., Winter J. Major outer membrane protein of Campylobacter fetus: physical and immunological characterization. Infect Immun. 1976 Apr;13(4):1258–1265. doi: 10.1128/iai.13.4.1258-1265.1976. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morooka T., Umeda A., Amako K. Motility as an intestinal colonization factor for Campylobacter jejuni. J Gen Microbiol. 1985 Aug;131(8):1973–1980. doi: 10.1099/00221287-131-8-1973. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Myers L. L. Purification and Partial Characterization of a Vibrio fetus Immunogen. Infect Immun. 1971 Apr;3(4):562–566. doi: 10.1128/iai.3.4.562-566.1971. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pei Z., Blaser M. J. Pathogenesis of Campylobacter fetus infections. Role of surface array proteins in virulence in a mouse model. J Clin Invest. 1990 Apr;85(4):1036–1043. doi: 10.1172/JCI114533. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pei Z., Ellison R. T., 3rd, Lewis R. V., Blaser M. J. Purification and characterization of a family of high molecular weight surface-array proteins from Campylobacter fetus. J Biol Chem. 1988 May 5;263(13):6416–6420. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Penner J. L. The genus Campylobacter: a decade of progress. Clin Microbiol Rev. 1988 Apr;1(2):157–172. doi: 10.1128/cmr.1.2.157. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Plasterk R. H., Simon M. I., Barbour A. G. Transposition of structural genes to an expression sequence on a linear plasmid causes antigenic variation in the bacterium Borrelia hermsii. Nature. 1985 Nov 21;318(6043):257–263. doi: 10.1038/318257a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sleytr U. B., Messner P. Crystalline surface layers in procaryotes. J Bacteriol. 1988 Jul;170(7):2891–2897. doi: 10.1128/jb.170.7.2891-2897.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sleytr U. B., Messner P. Crystalline surface layers on bacteria. Annu Rev Microbiol. 1983;37:311–339. doi: 10.1146/annurev.mi.37.100183.001523. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Towbin H., Staehelin T., Gordon J. Electrophoretic transfer of proteins from polyacrylamide gels to nitrocellulose sheets: procedure and some applications. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Sep;76(9):4350–4354. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.9.4350. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Winter A. J., McCoy E. C., Fullmer C. S., Burda K., Bier P. J. Microcapsule of Campylobacter fetus: chemical and physical characterization. Infect Immun. 1978 Dec;22(3):963–971. doi: 10.1128/iai.22.3.963-971.1978. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]