Abstract
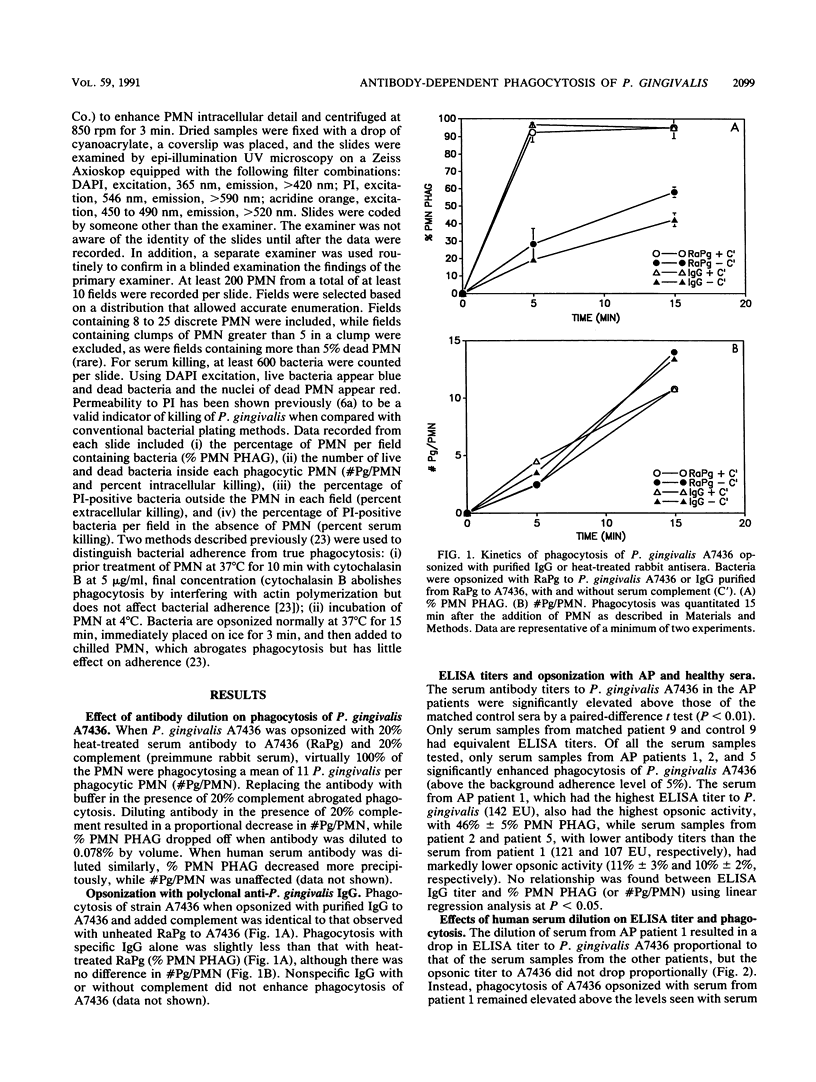
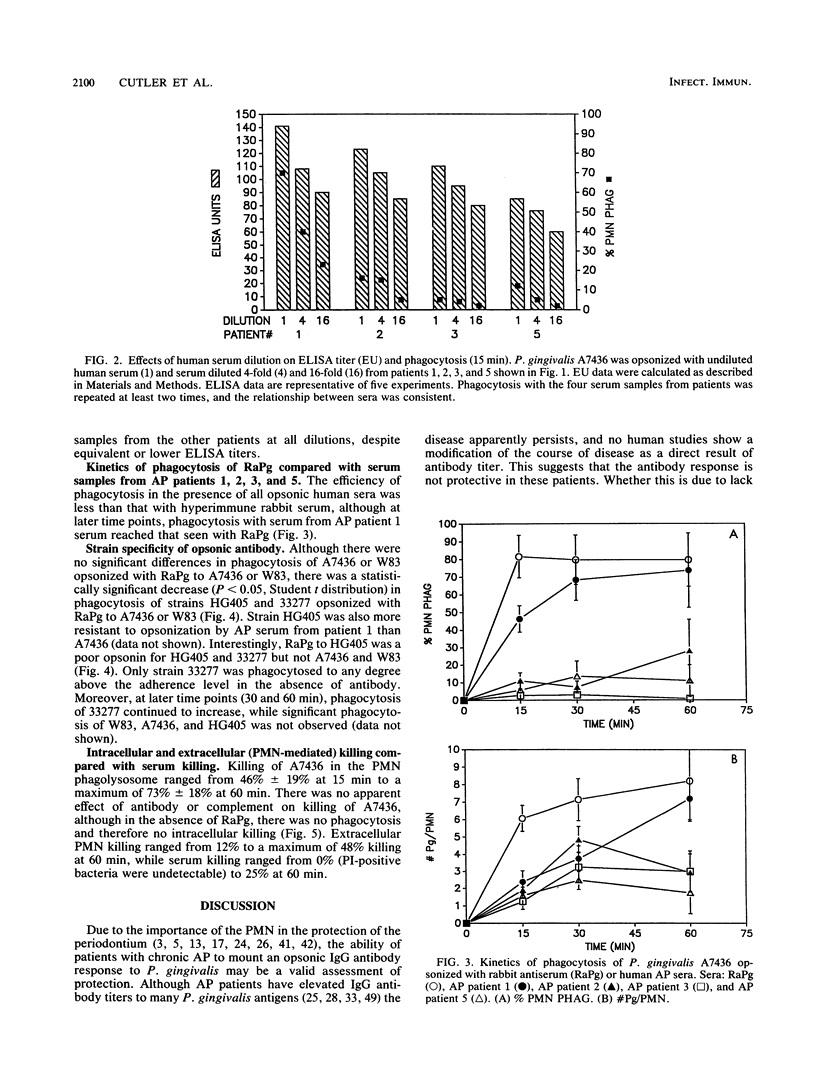
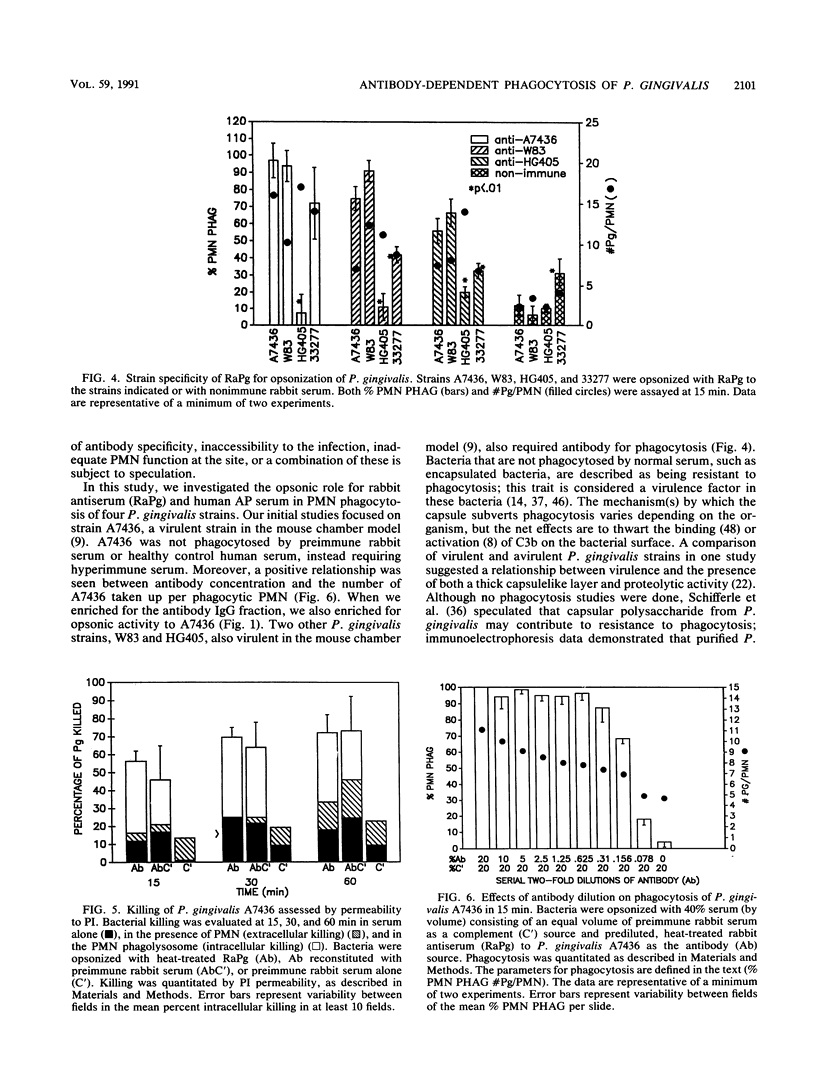
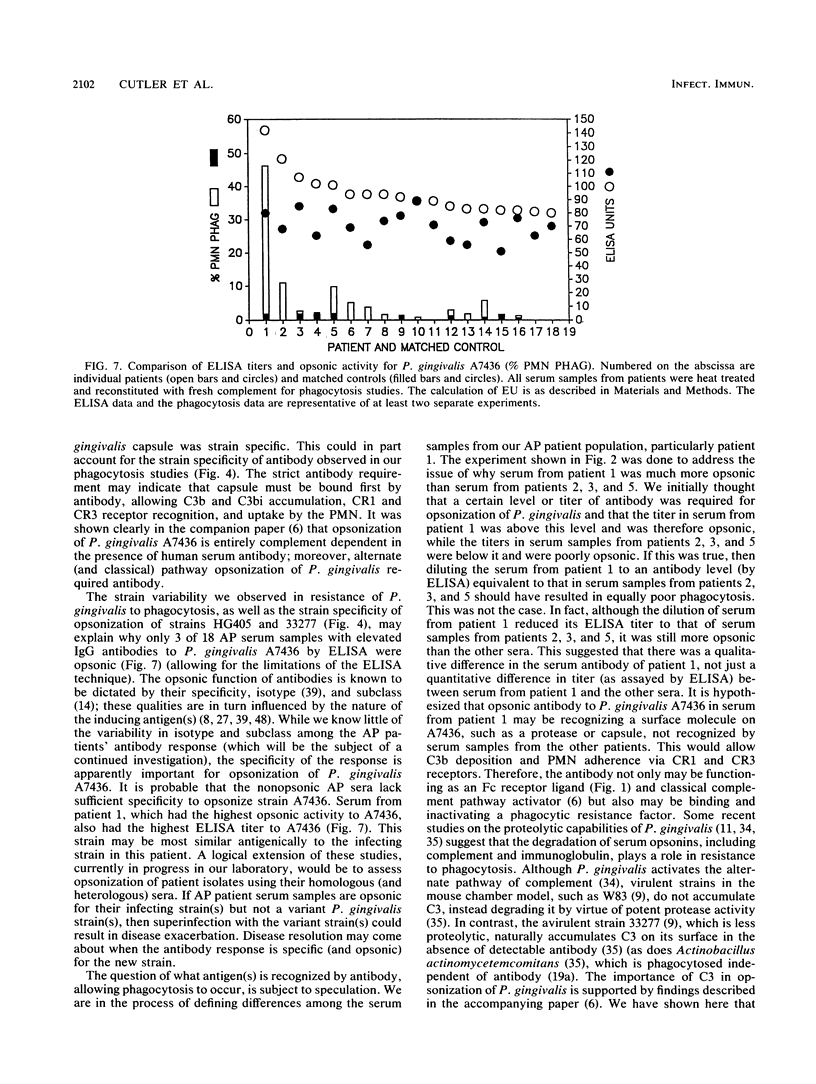
No studies to date clearly define the interactions between Porphyromonas gingivalis and human peripheral blood polymorphonuclear leukocytes (PMN), nor has a protective role for antibody to P. gingivalis been defined. Using a fluorochrome phagocytosis microassay, we investigated PMN phagocytosis and killing of P. gingivalis as a function of P. gingivalis-specific antibody. Sera from a nonimmune rabbit and a healthy human subject were not opsonic for virulent P. gingivalis A7436, W83, and HG405; phagocytosis of these strains (but not 33277) required opsonization with hyperimmune antiserum (RaPg). Diluting RaPg with a constant complement source decreased proportionally the number of P. gingivalis A7436 cells phagocytosed per phagocytic PMN. Enriching for the immunoglobulin G fraction of RAPg A7436 enriched for opsonic activity toward A7436. An opsonic evaluation of 18 serum samples from adult periodontitis patients revealed that only 3 adult periodontitis sera of 17 with elevated immunoglobulin G to P. gingivalis A7436 were opsonic for A7436 and, moreover, that the serum sample with the highest enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay titer was most opsonic (patient 1). However, the opsonic activity of serum from patient 1 was qualitatively and not just quantitatively different from that of the nonopsonic human sera (but was less effective opsonin than RaPg). Strain variability was observed in resistance of P. gingivalis to phagocytosis, and opsonization was strain specific for some, but not all, strains tested. An evaluation of killing of A7436 revealed that serum killing and extracellular killing of P. gingivalis were less effective alone when compared with intracellular PMN killing alone.
Full text
PDF



Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Armitage G. C., Holt S. C. Interaction of gram-negative periodontal pathogens with retinoic acid-induced and dimethyl sulfoxide-induced HL-60 cells. Oral Microbiol Immunol. 1990 Oct;5(5):248–255. doi: 10.1111/j.1399-302x.1990.tb00421.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Barcellona M. L., Favilla R., von Berger J., Avitabile M., Ragusa N., Masotti L. DNA-4'-6-diamidine-2-phenylindole interactions: a comparative study employing fluorescence and ultraviolet spectroscopy. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1986 Oct;250(1):48–53. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(86)90700-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bjerknes R. Flow cytometric assay for combined measurement of phagocytosis and intracellular killing of Candida albicans. J Immunol Methods. 1984 Aug 3;72(1):229–241. doi: 10.1016/0022-1759(84)90451-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cutler C. W., Kalmar J. R., Arnold R. R. Antibody-dependent alternate pathway of complement activation in opsonophagocytosis of Porphyromonas gingivalis. Infect Immun. 1991 Jun;59(6):2105–2109. doi: 10.1128/iai.59.6.2105-2109.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ebersole J. L., Frey D. E., Taubman M. A., Smith D. J. An ELISA for measuring serum antibodies to Actinobacillus actinomycetemcomitans. J Periodontal Res. 1980 Nov;15(6):621–632. doi: 10.1111/j.1600-0765.1980.tb00321.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Edwards M. S., Nicholson-Weller A., Baker C. J., Kasper D. L. The role of specific antibody in alternative complement pathway-mediated opsonophagocytosis of type III, group B Streptococcus. J Exp Med. 1980 May 1;151(5):1275–1287. doi: 10.1084/jem.151.5.1275. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fanger M. W., Goldstine S. N., Shen L. Cytofluorographic analysis of receptors for IgA on human polymorphonuclear cells and monocytes and the correlation of receptor expression with phagocytosis. Mol Immunol. 1983 Sep;20(9):1019–1027. doi: 10.1016/0161-5890(83)90043-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Genco C. A., Cutler C. W., Kapczynski D., Maloney K., Arnold R. R. A novel mouse model to study the virulence of and host response to Porphyromonas (Bacteroides) gingivalis. Infect Immun. 1991 Apr;59(4):1255–1263. doi: 10.1128/iai.59.4.1255-1263.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Griffin F. M., Jr Roles of macrophage Fc and C3b receptors in phagocytosis of immunologically coated Cryptococcus neoformans. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1981 Jun;78(6):3853–3857. doi: 10.1073/pnas.78.6.3853. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hamilton R. E., Jr, Giansanti J. S. The Chediak-Higashi syndrome. Report of a case and review of the literature. Oral Surg Oral Med Oral Pathol. 1974 May;37(5):754–761. doi: 10.1016/0030-4220(74)90141-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hammarström L., Smith C. I. IgG subclasses in bacterial infections. Monogr Allergy. 1986;19:122–133. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Handley P. S., Tipler L. S. An electron microscope survey of the surface structures and hydrophobicity of oral and non-oral species of the bacterial genus Bacteroides. Arch Oral Biol. 1986;31(5):325–335. doi: 10.1016/0003-9969(86)90047-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hendley J. W., Powell K. R., Rodewald R., Holzgrefe H. H., Lyles R. Demonstration of a capsule on Neisseria gonorrhoeae. N Engl J Med. 1977 Mar 17;296(11):608–611. doi: 10.1056/NEJM197703172961105. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hill H. R., Sauls H. S., Dettloff J. L., Quie P. G. Impaired leukotactic responsiveness in patients with juvenile diabetes mellitus. Clin Immunol Immunopathol. 1974 Apr;2(3):395–403. doi: 10.1016/0090-1229(74)90057-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Joiner K. A., Hammer C. H., Brown E. J., Cole R. J., Frank M. M. Studies on the mechanism of bacterial resistance to complement-mediated killing. I. Terminal complement components are deposited and released from Salmonella minnesota S218 without causing bacterial death. J Exp Med. 1982 Mar 1;155(3):797–808. doi: 10.1084/jem.155.3.797. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jones K. H., Senft J. A. An improved method to determine cell viability by simultaneous staining with fluorescein diacetate-propidium iodide. J Histochem Cytochem. 1985 Jan;33(1):77–79. doi: 10.1177/33.1.2578146. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kalmar J. R., Arnold R. R., van Dyke T. E. Direct interaction of Actinobacillus actinomycetemcomitans with normal and defective (LJP) neutrophils. J Periodontal Res. 1987 May;22(3):179–181. doi: 10.1111/j.1600-0765.1987.tb01561.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mackler B. F., Frostad K. B., Robertson P. B., Levy B. M. Immunoglobulin bearing lymphocytes and plasma cells in human periodontal disease. J Periodontal Res. 1977 Jan;12(1):37–45. doi: 10.1111/j.1600-0765.1977.tb00107.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marsh P. D., McKee A. S., McDermid A. S., Dowsett A. B. Ultrastructure and enzyme activities of a virulent and an avirulent variant of Bacteroides gingivalis W50. FEMS Microbiol Lett. 1989 May;50(1-2):181–185. doi: 10.1016/0378-1097(89)90482-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miller M. E., Oski F. A., Harris M. B. Lazy-leucocyte syndrome. A new disorder of neutrophil function. Lancet. 1971 Apr 3;1(7701):665–669. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(71)92679-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mouton C., Hammond P. G., Slots J., Genco R. J. Serum antibodies to oral Bacteroides asaccharolyticus (Bacteroides gingivalis): relationship to age and periondontal disease. Infect Immun. 1981 Jan;31(1):182–192. doi: 10.1128/iai.31.1.182-192.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mowat A., Baum J. Chemotaxis of polymorphonuclear leukocytes from patients with diabetes mellitus. N Engl J Med. 1971 Mar 25;284(12):621–627. doi: 10.1056/NEJM197103252841201. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Müller-Eberhard H. J. Chemistry and reaction mechanisms of complement. Adv Immunol. 1968;8:1–80. doi: 10.1016/s0065-2776(08)60464-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Naito Y., Okuda K., Takazoe I. Detection of specific antibody in adult human periodontitis sera to surface antigens of Bacteroides gingivalis. Infect Immun. 1987 Mar;55(3):832–834. doi: 10.1128/iai.55.3.832-834.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ogawa T., McGhee M. L., Moldoveanu Z., Hamada S., Mestecky J., McGhee J. R., Kiyono H. Bacteroides-specific IgG and IgA subclass antibody-secreting cells isolated from chronically inflamed gingival tissues. Clin Exp Immunol. 1989 Apr;76(1):103–110. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Okuda K., Kato T., Naito Y., Ono M., Kikuchi Y., Takazoe I. Susceptibility of Bacteroides gingivalis to bactericidal activity of human serum. J Dent Res. 1986 Jul;65(7):1024–1027. doi: 10.1177/00220345860650070601. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Parent R., Mouton C., Lamonde L., Bouchard D. Human and animal serotypes of Bacteroides gingivalis defined by crossed immunoelectrophoresis. Infect Immun. 1986 Mar;51(3):909–918. doi: 10.1128/iai.51.3.909-918.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schenck K. IgG, IgA and IgM serum antibodies against lipopolysaccharide from Bacteroides gingivalis in periodontal health and disease. J Periodontal Res. 1985 Jul;20(4):368–377. doi: 10.1111/j.1600-0765.1985.tb00448.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schenkein H. A. Failure of Bacteroides gingivalis W83 to accumulate bound C3 following opsonization with serum. J Periodontal Res. 1989 Jan;24(1):20–27. doi: 10.1111/j.1600-0765.1989.tb00853.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schenkein H. A. The effect of periodontal proteolytic Bacteroides species on proteins of the human complement system. J Periodontal Res. 1988 May;23(3):187–192. doi: 10.1111/j.1600-0765.1988.tb01356.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schifferle R. E., Reddy M. S., Zambon J. J., Genco R. J., Levine M. J. Characterization of a polysaccharide antigen from Bacteroides gingivalis. J Immunol. 1989 Nov 1;143(9):3035–3042. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Scribner D. J., Fahrney D. Neutrophil receptors for IgG and complement: their roles in the attachment and ingestion phases of phagocytosis. J Immunol. 1976 Apr;116(4):892–897. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sparham S. J., Huehns E. R. The separation of human globin chains by ion-exchange chromatography on CM-Sepharose CL-6B. Hemoglobin. 1979;3(1):13–20. doi: 10.3109/03630267909069151. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Spiegelberg H. L. Biological activities of immunoglobulins of different classes and subclasses. Adv Immunol. 1974;19(0):259–294. doi: 10.1016/s0065-2776(08)60254-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Spitznagel J. K. Microbial interactions with neutrophils. Rev Infect Dis. 1983 Sep-Oct;5 (Suppl 4):S806–S822. doi: 10.1093/clinids/5.supplement_4.s806. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Van Dyke T. E., Horoszewicz H. U., Cianciola L. J., Genco R. J. Neutrophil chemotaxis dysfunction in human periodontitis. Infect Immun. 1980 Jan;27(1):124–132. doi: 10.1128/iai.27.1.124-132.1980. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Van Steenbergen T. J., Delemarre F. G., Namavar F., De Graaff J. Differences in virulence within the species Bacteroides gingivalis. Antonie Van Leeuwenhoek. 1987;53(4):233–244. doi: 10.1007/BF00393930. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Van Swol R. L., Gross A., Setterstrom J. A., D'Alessandro S. M. Immunoglobulins in periodontal tissues. II. Concentrations of immunoglobulins in granulation tissue from pockets of periodontosis and periodontitis patients. J Periodontol. 1980 Jan;51(1):20–24. doi: 10.1902/jop.1980.51.1.20. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ward H. K., Enders J. F. AN ANALYSIS OF THE OPSONIC AND TROPIC ACTION OF NORMAL AND IMMUNE SERA BASED ON EXPERIMENTS WITH THE PNEUMOCOCCUS. J Exp Med. 1933 Mar 31;57(4):527–547. doi: 10.1084/jem.57.4.527. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wilkinson B. J., Sisson S. P., Kim Y., Peterson P. K. Localization of the third component of complement on the cell wall of encapsulated Staphylococcus aureus M: implications for the mechanism of resistance to phagocytosis. Infect Immun. 1979 Dec;26(3):1159–1163. doi: 10.1128/iai.26.3.1159-1163.1979. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yoshimura F., Sugano T., Kawanami M., Kato H., Suzuki T. Detection of specific antibodies against fimbriae and membrane proteins from the oral anaerobe Bacteroides gingivalis in patients with periodontal diseases. Microbiol Immunol. 1987;31(9):935–941. doi: 10.1111/j.1348-0421.1987.tb03154.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- van Winkelhoff A. J., van Steenbergen T. J., de Graaff J. The role of black-pigmented Bacteroides in human oral infections. J Clin Periodontol. 1988 Mar;15(3):145–155. doi: 10.1111/j.1600-051x.1988.tb01561.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


