Abstract
The susceptibility of paired mucoid and nonmucoid variants of Pseudomonas aeruginosa isolated from 13 patients with cystic fibrosis (CF) to killing by a 55,000-Da bactericidal protein (BP55) from human polymorphonuclear leukocytes was studied. Mucoid and nonmucoid variants were equally sensitive to killing by BP55 at both pH 5.6 and pH 7.2. Eleven of the isolates were resistant to the bactericidal activity of 10% normal human serum but were as sensitive as the serum-sensitive isolates to BP55. Similarly, the 15 isolates with lipopolysaccharides (LPS) containing O-polysaccharide side chains (smooth LPS) were as sensitive to BP55 as those isolates with rough LPS.P. aeruginosa isolates from patients in poor clinical condition were more likely to have LPS of the smooth type and to be resistant to killing by 10% human serum than the isolates from patients in good clinical condition. We have concluded that the susceptibility of the P. aeruginosa isolates from patients with CF to killing by BP55 does not correlate with mucoid or nonmucoid variations, with the presence or absence of smooth LPS, or with the sensitivity or resistance to killing by normal human serum.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bauernfeind A., Bertele R. M., Harms K., Hörl G., Jungwirth R., Petermüller C., Przyklenk B., Weisslein-Pfister C. Qualitative and quantitative microbiological analysis of sputa of 102 patients with cystic fibrosis. Infection. 1987 Jul-Aug;15(4):270–277. doi: 10.1007/BF01644137. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brasfield D., Hicks G., Soong S., Tiller R. E. The chest roentgenogram in cystic fibrosis: a new scoring system. Pediatrics. 1979 Jan;63(1):24–29. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cryz S. J., Jr, Pitt T. L., Fürer E., Germanier R. Role of lipopolysaccharide in virulence of Pseudomonas aeruginosa. Infect Immun. 1984 May;44(2):508–513. doi: 10.1128/iai.44.2.508-513.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Darveau R. P., Hancock R. E. Procedure for isolation of bacterial lipopolysaccharides from both smooth and rough Pseudomonas aeruginosa and Salmonella typhimurium strains. J Bacteriol. 1983 Aug;155(2):831–838. doi: 10.1128/jb.155.2.831-838.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Farley M. M., Shafer W. M., Spitznagel J. K. Lipopolysaccharide structure determines ionic and hydrophobic binding of a cationic antimicrobial neutrophil granule protein. Infect Immun. 1988 Jun;56(6):1589–1592. doi: 10.1128/iai.56.6.1589-1592.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Godfrey A. J., Hatlelid L., Bryan L. E. Correlation between lipopolysaccharide structure and permeability resistance in beta-lactam-resistant Pseudomonas aeruginosa. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1984 Aug;26(2):181–186. doi: 10.1128/aac.26.2.181. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goldman R. C., Joiner K., Leive L. Serum-resistant mutants of Escherichia coli O111 contain increased lipopolysaccharide, lack an O antigen-containing capsule, and cover more of their lipid A core with O antigen. J Bacteriol. 1984 Sep;159(3):877–882. doi: 10.1128/jb.159.3.877-882.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goldman R. C., Leive L. Heterogeneity of antigenic-side-chain length in lipopolysaccharide from Escherichia coli 0111 and Salmonella typhimurium LT2. Eur J Biochem. 1980;107(1):145–153. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1980.tb04635.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Govan J. R., Harris G. S. Pseudomonas aeruginosa and cystic fibrosis: unusual bacterial adaptation and pathogenesis. Microbiol Sci. 1986 Oct;3(10):302–308. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hancock R. E., Mutharia L. M., Chan L., Darveau R. P., Speert D. P., Pier G. B. Pseudomonas aeruginosa isolates from patients with cystic fibrosis: a class of serum-sensitive, nontypable strains deficient in lipopolysaccharide O side chains. Infect Immun. 1983 Oct;42(1):170–177. doi: 10.1128/iai.42.1.170-177.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hartree E. F. Determination of protein: a modification of the Lowry method that gives a linear photometric response. Anal Biochem. 1972 Aug;48(2):422–427. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(72)90094-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hovde C. J., Gray B. H. Characterization of a protein from normal human polymorphonuclear leukocytes with bactericidal activity against Pseudomonas aeruginosa. Infect Immun. 1986 Oct;54(1):142–148. doi: 10.1128/iai.54.1.142-148.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hovde C. J., Gray B. H. Physiological effects of a bactericidal protein from human polymorphonuclear leukocytes on Pseudomonas aeruginosa. Infect Immun. 1986 Apr;52(1):90–95. doi: 10.1128/iai.52.1.90-95.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Joiner K. A., Grossman N., Schmetz M., Leive L. C3 binds preferentially to long-chain lipopolysaccharide during alternative pathway activation by Salmonella montevideo. J Immunol. 1986 Jan;136(2):710–715. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Katz S., Schöni M. H., Bridges M. A. The calcium hypothesis of cystic fibrosis. Cell Calcium. 1984 Oct;5(5):421–440. doi: 10.1016/0143-4160(84)90021-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kropinski A. M., Jewell B., Kuzio J., Milazzo F., Berry D. Structure and functions of Pseudomonas aeruginosa lipopolysaccharide. Antibiot Chemother (1971) 1985;36:58–73. doi: 10.1159/000410472. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laemmli U. K. Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature. 1970 Aug 15;227(5259):680–685. doi: 10.1038/227680a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marcus H., Austria A., Baker N. R. Adherence of Pseudomonas aeruginosa to tracheal epithelium. Infect Immun. 1989 Apr;57(4):1050–1053. doi: 10.1128/iai.57.4.1050-1053.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morrison D. C., Ulevitch R. J. The effects of bacterial endotoxins on host mediation systems. A review. Am J Pathol. 1978 Nov;93(2):526–618. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ooi C. E., Weiss J., Elsbach P., Frangione B., Mannion B. A 25-kDa NH2-terminal fragment carries all the antibacterial activities of the human neutrophil 60-kDa bactericidal/permeability-increasing protein. J Biol Chem. 1987 Nov 5;262(31):14891–14894. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Palva E. T., Mäkelä P. H. Lipopolysaccharide heterogeneity in Salmonella typhimurium analyzed by sodium dodecyl sulfate polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis. Eur J Biochem. 1980;107(1):137–143. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1980.tb04634.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Penketh A., Pitt T., Roberts D., Hodson M. E., Batten J. C. The relationship of phenotype changes in Pseudomonas aeruginosa to the clinical condition of patients with cystic fibrosis. Am Rev Respir Dis. 1983 May;127(5):605–608. doi: 10.1164/arrd.1983.127.5.605. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pereira H. A., Spitznagel J. K., Winton E. F., Shafer W. M., Martin L. E., Guzman G. S., Pohl J., Scott R. W., Marra M. N., Kinkade J. M., Jr The ontogeny of a 57-Kd cationic antimicrobial protein of human polymorphonuclear leukocytes: localization to a novel granule population. Blood. 1990 Aug 15;76(4):825–834. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rest R. F., Cooney M. H., Spitznagel J. K. Bactericidal activity of specific and azurophil granules from human neutrophils: studies with outer-membrane mutants of Salmonella typhimurium LT-2. Infect Immun. 1978 Jan;19(1):131–137. doi: 10.1128/iai.19.1.131-137.1978. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schiller N. L., Hatch R. A., Joiner K. A. Complement activation and C3 binding by serum-sensitive and serum-resistant strains of Pseudomonas aeruginosa. Infect Immun. 1989 Jun;57(6):1707–1713. doi: 10.1128/iai.57.6.1707-1713.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schiller N. L., Joiner K. A. Interaction of complement with serum-sensitive and serum-resistant strains of Pseudomonas aeruginosa. Infect Immun. 1986 Dec;54(3):689–694. doi: 10.1128/iai.54.3.689-694.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shafer W. M., Casey S. G., Spitznagel J. K. Lipid A and resistance of Salmonella typhimurium to antimicrobial granule proteins of human neutrophil granulocytes. Infect Immun. 1984 Mar;43(3):834–838. doi: 10.1128/iai.43.3.834-838.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thomassen M. J., Demko C. A. Serum bactericidal effect on Pseudomonas aeruginosa isolates from cystic fibrosis patients. Infect Immun. 1981 Aug;33(2):512–518. doi: 10.1128/iai.33.2.512-518.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
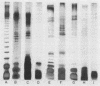
- Tsai C. M., Frasch C. E. A sensitive silver stain for detecting lipopolysaccharides in polyacrylamide gels. Anal Biochem. 1982 Jan 1;119(1):115–119. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(82)90673-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weiss J., Beckerdite-Quagliata S., Elsbach P. Resistance of gram-negative bacteria to purified bactericidal leukocyte proteins: relation to binding and bacterial lipopolysaccharide structure. J Clin Invest. 1980 Mar;65(3):619–628. doi: 10.1172/JCI109707. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weiss J., Elsbach P., Olsson I., Odeberg H. Purification and characterization of a potent bactericidal and membrane active protein from the granules of human polymorphonuclear leukocytes. J Biol Chem. 1978 Apr 25;253(8):2664–2672. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weiss J., Hutzler M., Kao L. Environmental modulation of lipopolysaccharide chain length alters the sensitivity of Escherichia coli to the neutrophil bactericidal/permeability-increasing protein. Infect Immun. 1986 Feb;51(2):594–599. doi: 10.1128/iai.51.2.594-599.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wilkinson S. G. Composition and structure of lipopolysaccharides from Pseudomonas aeruginosa. Rev Infect Dis. 1983 Nov-Dec;5 (Suppl 5):S941–S949. doi: 10.1093/clinids/5.supplement_5.s941. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Young L. S., Armstrong D. Human immunity to Pseudomonas aeruginosa. I. In-vitro interaction of bacteria, polymorphonuclear leukocytes, and serum factors. J Infect Dis. 1972 Sep;126(3):257–276. doi: 10.1093/infdis/126.3.257. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]