Abstract
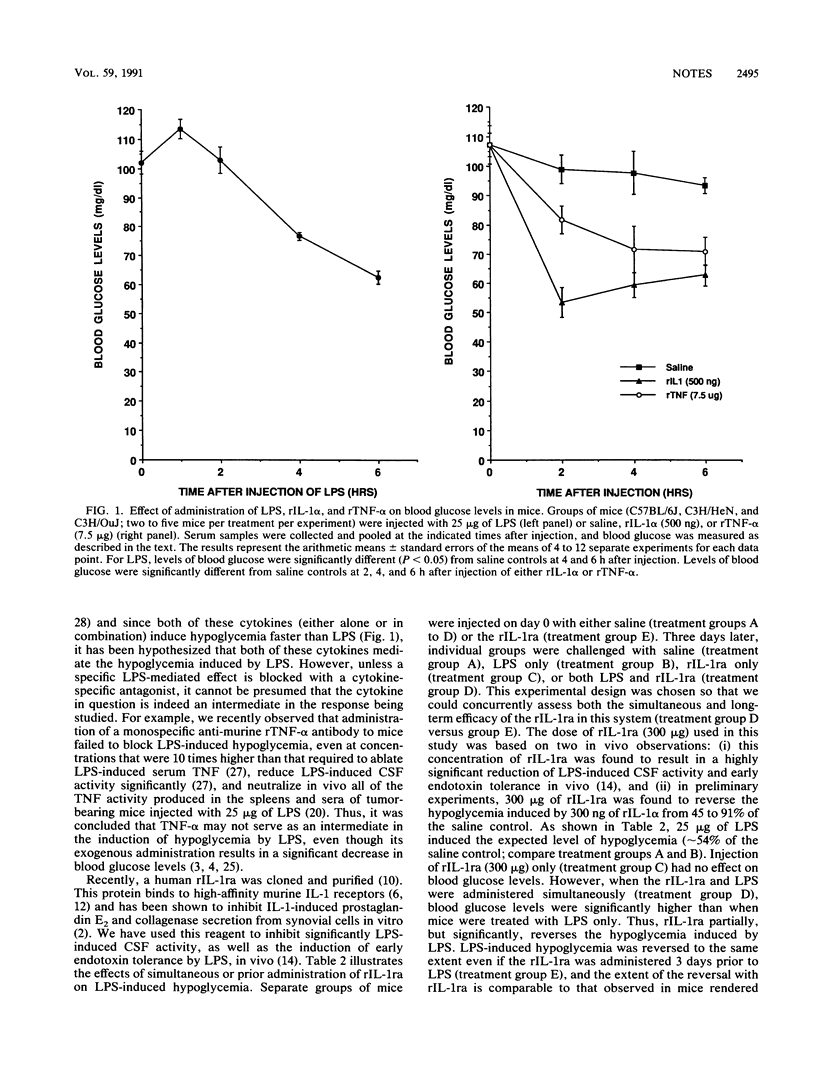
In this study, hypoglycemia induced by injection of lipopolysaccharide (LPS) or the recombinant cytokine interleukin-1 alpha or tumor necrosis factor alpha (administered alone or in combination) was compared. LPS-induced hypoglycemia was reversed significantly by recombinant interleukin-1 receptor antagonist.
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Akira S., Hirano T., Taga T., Kishimoto T. Biology of multifunctional cytokines: IL 6 and related molecules (IL 1 and TNF). FASEB J. 1990 Aug;4(11):2860–2867. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Arend W. P., Welgus H. G., Thompson R. C., Eisenberg S. P. Biological properties of recombinant human monocyte-derived interleukin 1 receptor antagonist. J Clin Invest. 1990 May;85(5):1694–1697. doi: 10.1172/JCI114622. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bagby G. J., Lang C. H., Hargrove D. M., Thompson J. J., Wilson L. A., Spitzer J. J. Glucose kinetics in rats infused with endotoxin-induced monokines or tumor necrosis factor. Circ Shock. 1988 Feb;24(2):111–121. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bauss F., Dröge W., Männel D. N. Tumor necrosis factor mediates endotoxic effects in mice. Infect Immun. 1987 Jul;55(7):1622–1625. doi: 10.1128/iai.55.7.1622-1625.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bird T. A., Davies A., Baldwin S. A., Saklatvala J. Interleukin 1 stimulates hexose transport in fibroblasts by increasing the expression of glucose transporters. J Biol Chem. 1990 Aug 15;265(23):13578–13583. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bomsztyk K., Sims J. E., Stanton T. H., Slack J., McMahan C. J., Valentine M. A., Dower S. K. Evidence for different interleukin 1 receptors in murine B- and T-cell lines. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 Oct;86(20):8034–8038. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.20.8034. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dinarello C. A., Cannon J. G., Wolff S. M., Bernheim H. A., Beutler B., Cerami A., Figari I. S., Palladino M. A., Jr, O'Connor J. V. Tumor necrosis factor (cachectin) is an endogenous pyrogen and induces production of interleukin 1. J Exp Med. 1986 Jun 1;163(6):1433–1450. doi: 10.1084/jem.163.6.1433. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eisenberg S. P., Evans R. J., Arend W. P., Verderber E., Brewer M. T., Hannum C. H., Thompson R. C. Primary structure and functional expression from complementary DNA of a human interleukin-1 receptor antagonist. Nature. 1990 Jan 25;343(6256):341–346. doi: 10.1038/343341a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hannum C. H., Wilcox C. J., Arend W. P., Joslin F. G., Dripps D. J., Heimdal P. L., Armes L. G., Sommer A., Eisenberg S. P., Thompson R. C. Interleukin-1 receptor antagonist activity of a human interleukin-1 inhibitor. Nature. 1990 Jan 25;343(6256):336–340. doi: 10.1038/343336a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Henricson B. E., Benjamin W. R., Vogel S. N. Differential cytokine induction by doses of lipopolysaccharide and monophosphoryl lipid A that result in equivalent early endotoxin tolerance. Infect Immun. 1990 Aug;58(8):2429–2437. doi: 10.1128/iai.58.8.2429-2437.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Henricson B. E., Neta R., Vogel S. N. An interleukin-1 receptor antagonist blocks lipopolysaccharide-induced colony-stimulating factor production and early endotoxin tolerance. Infect Immun. 1991 Mar;59(3):1188–1191. doi: 10.1128/iai.59.3.1188-1191.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hill M. R., Stith R. D., McCallum R. E. Interleukin 1: a regulatory role in glucocorticoid-regulated hepatic metabolism. J Immunol. 1986 Aug 1;137(3):858–862. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McIntire F. C., Sievert H. W., Barlow G. H., Finley R. A., Lee A. Y. Chemical, physical, biological properties of a lipopolysaccharide from Escherichia coli K-235. Biochemistry. 1967 Aug;6(8):2363–2372. doi: 10.1021/bi00860a011. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- North R. J., Havell E. A. The antitumor function of tumor necrosis factor (TNF) II. Analysis of the role of endogenous TNF in endotoxin-induced hemorrhagic necrosis and regression of an established sarcoma. J Exp Med. 1988 Mar 1;167(3):1086–1099. doi: 10.1084/jem.167.3.1086. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sacco-Gibson N. A., Filkins J. P. Macrophages, monokines, and the metabolic pathophysiology of septic shock. Prog Clin Biol Res. 1989;286:203–218. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sacco-Gibson N., Filkins J. P. Glucoregulatory effects of interleukin-1: implications to the carbohydrate dyshomeostasis of septic shock. Prog Clin Biol Res. 1988;264:355–360. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Silverstein R., Christoffersen C. A., Morrison D. C. Modulation of endotoxin lethality in mice by hydrazine sulfate. Infect Immun. 1989 Jul;57(7):2072–2078. doi: 10.1128/iai.57.7.2072-2078.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Snyder I. S., Deters M., Ingle J. Effect of endotoxin on pyruvate kinase activity in mouse liver. Infect Immun. 1971 Aug;4(2):138–142. doi: 10.1128/iai.4.2.138-142.1971. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tracey K. J., Beutler B., Lowry S. F., Merryweather J., Wolpe S., Milsark I. W., Hariri R. J., Fahey T. J., 3rd, Zentella A., Albert J. D. Shock and tissue injury induced by recombinant human cachectin. Science. 1986 Oct 24;234(4775):470–474. doi: 10.1126/science.3764421. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vogel S. N., Douches S. D., Kaufman E. N., Neta R. Induction of colony stimulating factor in vivo by recombinant interleukin 1 alpha and recombinant tumor necrosis factor alpha 1. J Immunol. 1987 Apr 1;138(7):2143–2148. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vogel S. N., Havell E. A. Differential inhibition of lipopolysaccharide-induced phenomena by anti-tumor necrosis factor alpha antibody. Infect Immun. 1990 Jul;58(7):2397–2400. doi: 10.1128/iai.58.7.2397-2400.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vogel S. N., Kaufman E. N., Tate M. D., Neta R. Recombinant interleukin-1 alpha and recombinant tumor necrosis factor alpha synergize in vivo to induce early endotoxin tolerance and associated hematopoietic changes. Infect Immun. 1988 Oct;56(10):2650–2657. doi: 10.1128/iai.56.10.2650-2657.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wolfe R. R., Elahi D., Spitzer J. J. Glucose and lactate kinetics after endotoxin administration in dogs. Am J Physiol. 1977 Feb;232(2):E180–E185. doi: 10.1152/ajpendo.1977.232.2.E180. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yelich M. R., Havdala H. S., Filkins J. P. Dexamethasone alters glucose, lactate, and insulin dyshomeostasis during endotoxicosis in the rat. Circ Shock. 1987;22(2):155–171. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- del Rey A., Besedovsky H. Antidiabetic effects of interleukin 1. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 Aug;86(15):5943–5947. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.15.5943. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- del Rey A., Besedovsky H. Interleukin 1 affects glucose homeostasis. Am J Physiol. 1987 Nov;253(5 Pt 2):R794–R798. doi: 10.1152/ajpregu.1987.253.5.R794. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


