Abstract
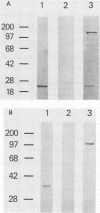
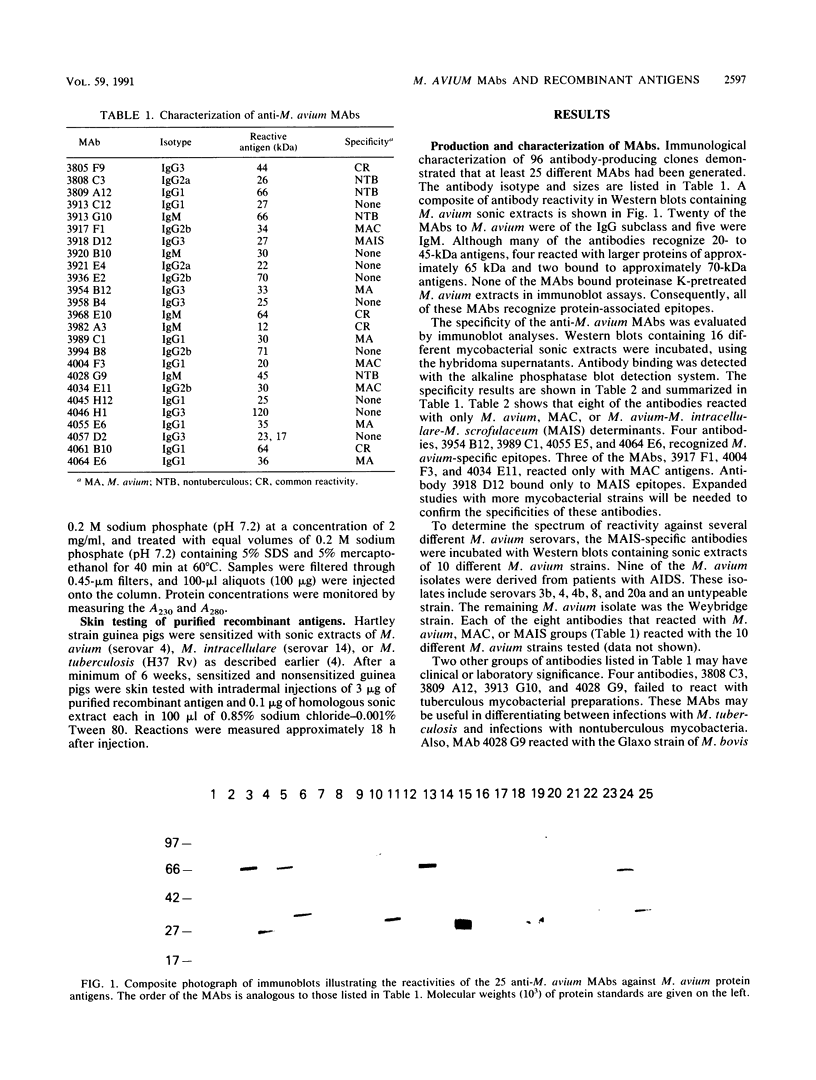
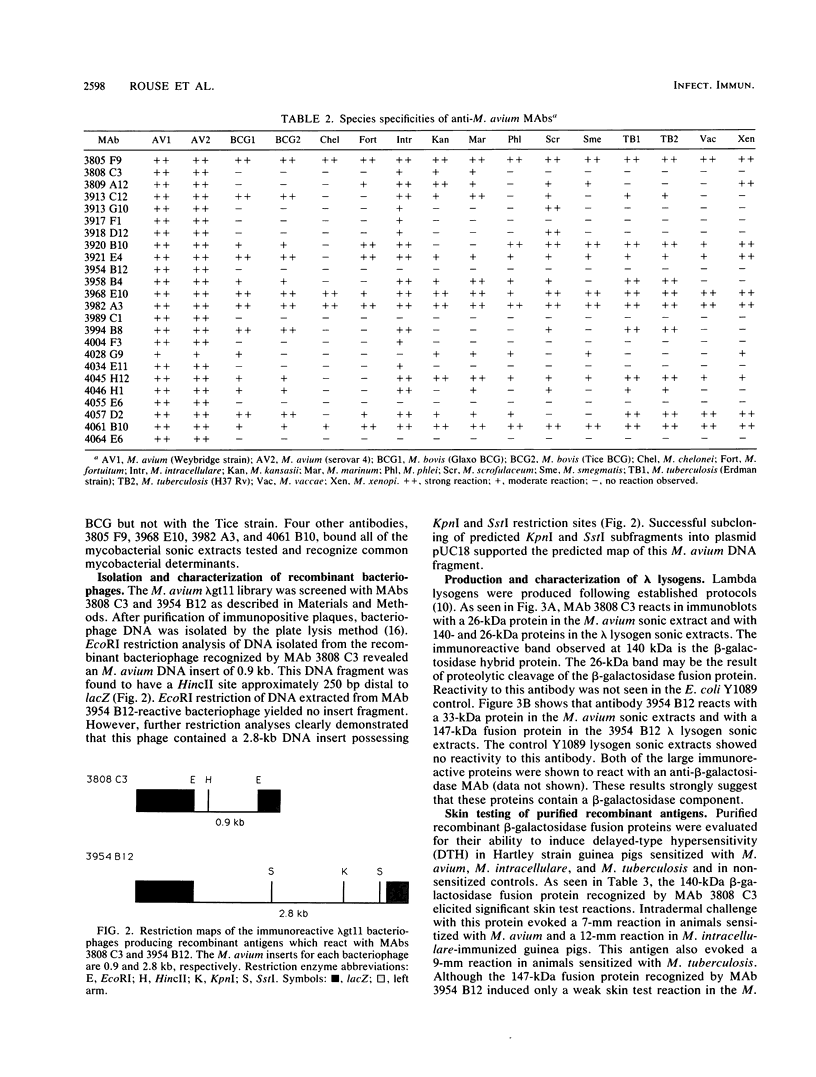
Nontuberculous mycobacteria, particularly Mycobacterium avium, have been isolated from a significant percentage of patients with AIDS. Early detection of M. avium infection is difficult, and treatment regimens are often ineffective. Much needs to be learned about antigens and factors responsible for immunity to and pathogenesis of the disease. Specific antigens and diagnostic procedures for infection need to be developed. To address some of these problems, we have generated 25 different monoclonal antibodies against a serovar 4 strain of M. avium isolated from a patient with AIDS. Protease sensitivity studies have demonstrated that each of these antibodies recognizes a protein-associated epitope. Immunoblot analyses suggest that seven of these monoclonal antibodies react specifically with M. avium and M. intracellular epitopes. Immunoreactive bacteriophages were identified from an M. avium lambda gt11 expression library with two of these monoclonal antibodies (3808 C3 and 3954 B12). Lambda lysogens, generated from the immunoreactive bacteriophages, overproduced beta-galactosidase fusion proteins which were reactive with the two monoclonal antibodies in immunoblot assays. The purified fusion proteins were shown to elicit skin test reactions in sensitized guinea pigs.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Chaparas S. D., Maloney C. J., Hedrick S. R. Specificity of tuberculins and antigens from various species of mycobacteria. Am Rev Respir Dis. 1970 Jan;101(1):74–83. doi: 10.1164/arrd.1970.101.1.74. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chaparas S. D., Vandiviere H. M., Melvin I., Koch G., Becker C. Tuberculin test. Variability with the Mantoux procedure. Am Rev Respir Dis. 1985 Jul;132(1):175–177. doi: 10.1164/arrd.1985.132.1.175. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Collins F. M. AIDS-related mycobacterial disease. Springer Semin Immunopathol. 1988;10(4):375–391. doi: 10.1007/BF02053847. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Collins F. M. Mycobacterial disease, immunosuppression, and acquired immunodeficiency syndrome. Clin Microbiol Rev. 1989 Oct;2(4):360–377. doi: 10.1128/cmr.2.4.360. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Collins F. M. Mycobacterium avium-complex infections and development of the acquired immunodeficiency syndrome: casual opportunist or causal cofactor? Int J Lepr Other Mycobact Dis. 1986 Sep;54(3):458–474. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eisenach K. D., Crawford J. T., Bates J. H. Genetic relatedness among strains of the Mycobacterium tuberculosis complex. Analysis of restriction fragment heterogeneity using cloned DNA probes. Am Rev Respir Dis. 1986 Jun;133(6):1065–1068. doi: 10.1164/arrd.1986.133.6.1065. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hawkins C. C., Gold J. W., Whimbey E., Kiehn T. E., Brannon P., Cammarata R., Brown A. E., Armstrong D. Mycobacterium avium complex infections in patients with the acquired immunodeficiency syndrome. Ann Intern Med. 1986 Aug;105(2):184–188. doi: 10.7326/0003-4819-105-2-184. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ivanyi J., Bothamley G. H., Jackett P. S. Immunodiagnostic assays for tuberculosis and leprosy. Br Med Bull. 1988 Jul;44(3):635–649. doi: 10.1093/oxfordjournals.bmb.a072273. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kadival G. V., Chaparas S. D., Hussong D. Characterization of serologic and cell-mediated reactivity of a 38-kDa antigen isolated from Mycobacterium tuberculosis. J Immunol. 1987 Oct 1;139(7):2447–2451. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kingston A. E., Salgame P. R., Mitchison N. A., Colston M. J. Immunological activity of a 14-kilodalton recombinant protein of Mycobacterium tuberculosis H37Rv. Infect Immun. 1987 Dec;55(12):3149–3154. doi: 10.1128/iai.55.12.3149-3154.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Köhler G., Milstein C. Continuous cultures of fused cells secreting antibody of predefined specificity. Nature. 1975 Aug 7;256(5517):495–497. doi: 10.1038/256495a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Macher A. M., Kovacs J. A., Gill V., Roberts G. D., Ames J., Park C. H., Straus S., Lane H. C., Parrillo J. E., Fauci A. S. Bacteremia due to Mycobacterium avium-intracellulare in the acquired immunodeficiency syndrome. Ann Intern Med. 1983 Dec;99(6):782–785. doi: 10.7326/0003-4819-99-6-782. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morris S. L., Rouse D. A., Hussong D., Chaparas S. D. Isolation and characterization of a recombinant lambda gt11 bacteriophage which expresses an immunoreactive Mycobacterium intracellulare protein in Escherichia coli. Infect Immun. 1988 Dec;56(12):3026–3031. doi: 10.1128/iai.56.12.3026-3031.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Prince D. S., Peterson D. D., Steiner R. M., Gottlieb J. E., Scott R., Israel H. L., Figueroa W. G., Fish J. E. Infection with Mycobacterium avium complex in patients without predisposing conditions. N Engl J Med. 1989 Sep 28;321(13):863–868. doi: 10.1056/NEJM198909283211304. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rouse D. A., Morris S. L., Karpas A. B., Probst P. G., Chaparas S. D. Production, characterization, and species specificity of monoclonal antibodies to Mycobacterium avium complex protein antigens. Infect Immun. 1990 May;58(5):1445–1449. doi: 10.1128/iai.58.5.1445-1449.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Selwyn P. A., Hartel D., Lewis V. A., Schoenbaum E. E., Vermund S. H., Klein R. S., Walker A. T., Friedland G. H. A prospective study of the risk of tuberculosis among intravenous drug users with human immunodeficiency virus infection. N Engl J Med. 1989 Mar 2;320(9):545–550. doi: 10.1056/NEJM198903023200901. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wallace J. M., Hannah J. B. Mycobacterium avium complex infection in patients with the acquired immunodeficiency syndrome. A clinicopathologic study. Chest. 1988 May;93(5):926–932. doi: 10.1378/chest.93.5.926. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wong B., Edwards F. F., Kiehn T. E., Whimbey E., Donnelly H., Bernard E. M., Gold J. W., Armstrong D. Continuous high-grade mycobacterium avium-intracellulare bacteremia in patients with the acquired immune deficiency syndrome. Am J Med. 1985 Jan;78(1):35–40. doi: 10.1016/0002-9343(85)90458-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Worsaae A., Ljungqvist L., Hasløv K., Heron I., Bennedsen J. Allergenic and blastogenic reactivity of three antigens from Mycobacterium tuberculosis in sensitized guinea pigs. Infect Immun. 1987 Dec;55(12):2922–2927. doi: 10.1128/iai.55.12.2922-2927.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Young D., Kent L., Rees A., Lamb J., Ivanyi J. Immunological activity of a 38-kilodalton protein purified from Mycobacterium tuberculosis. Infect Immun. 1986 Oct;54(1):177–183. doi: 10.1128/iai.54.1.177-183.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Young R. A., Davis R. W. Efficient isolation of genes by using antibody probes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1983 Mar;80(5):1194–1198. doi: 10.1073/pnas.80.5.1194. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zakowski P., Fligiel S., Berlin G. W., Johnson L., Jr Disseminated Mycobacterium avium-intracellulare infection in homosexual men dying of acquired immunodeficiency. JAMA. 1982 Dec 10;248(22):2980–2982. doi: 10.1001/jama.1982.03330220024029. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]