Abstract
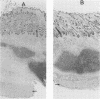
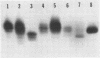
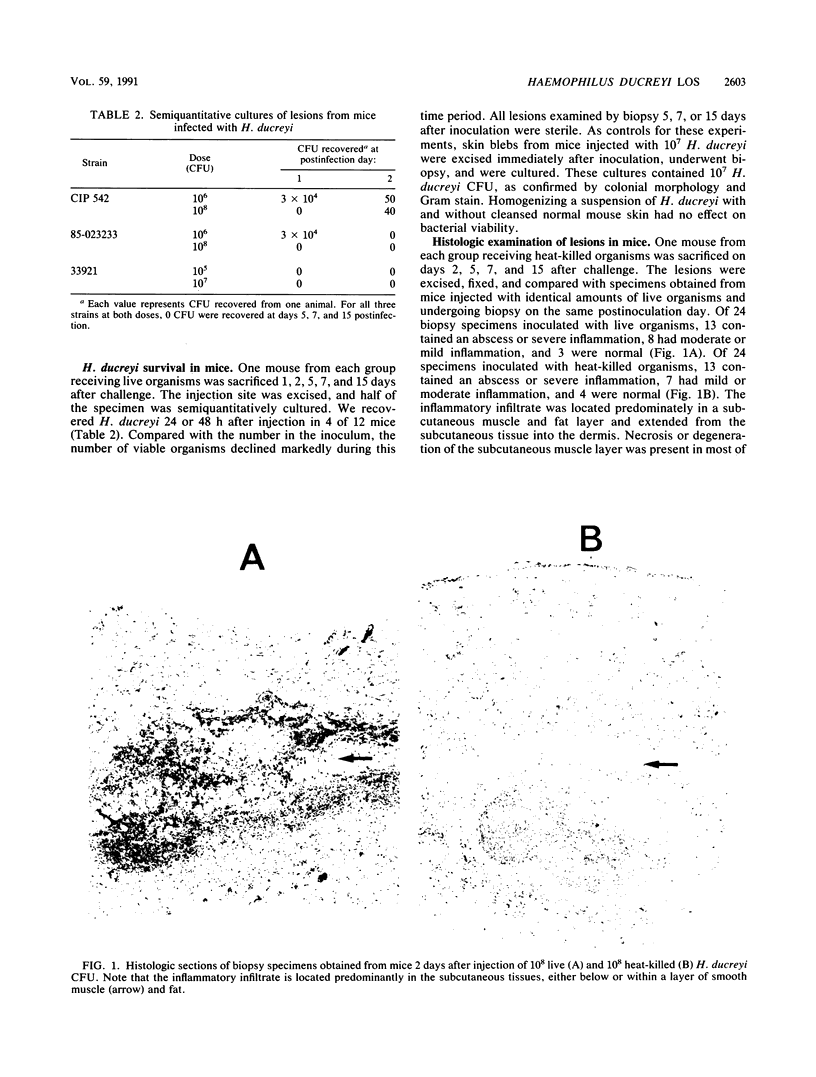
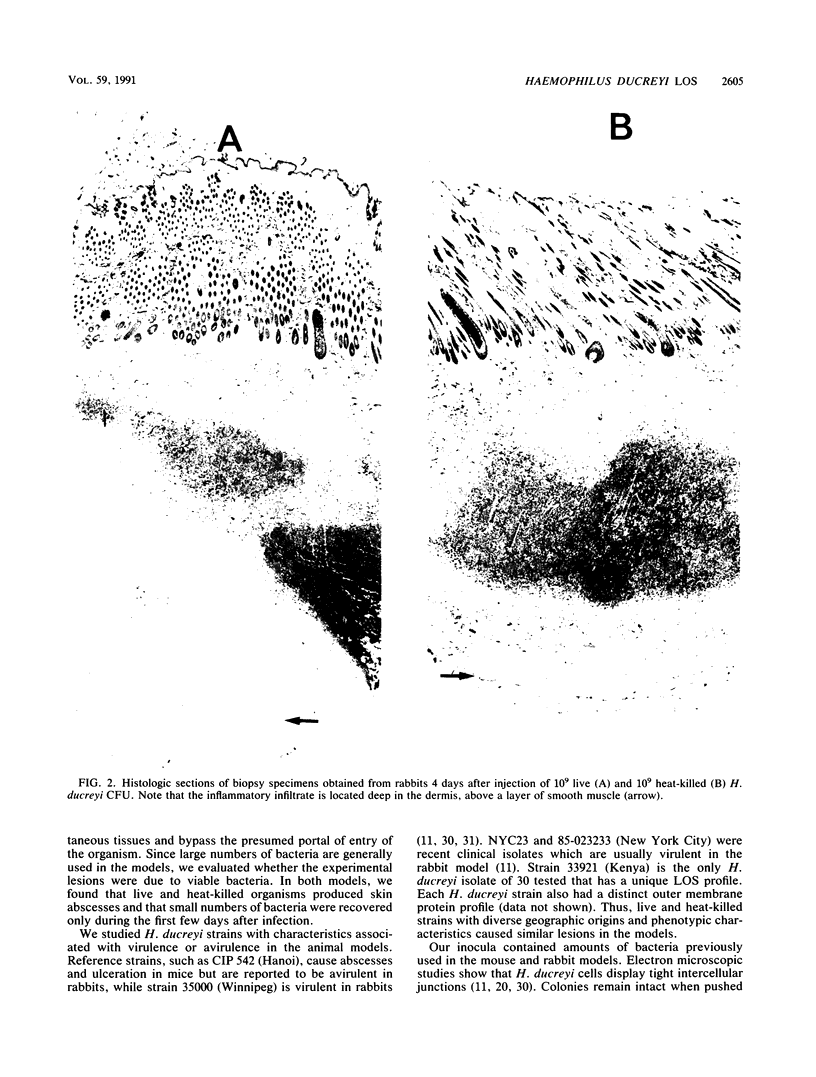
The mouse and rabbit intradermal injection models have been used to define factors that may be important in Haemophilus ducreyi pathogenesis. We used H. ducreyi strains with diverse geographic origins and phenotypic characteristics to evaluate the experimental models. Injection of live and heat-killed bacteria caused skin abscesses in both models. Semiquantitative cultures of skin injected with live bacteria showed that H. ducreyi failed to replicate in animal tissue. These data suggested that the experimental lesions were caused by a heat-stable substance such as lipooligosaccharide (LOS). In mice, injection of H. ducreyi and Haemophilus influenzae LOS and Escherichia coli lipopolysaccharide caused mild to moderate inflammation. In rabbits, injection of H. ducreyi LOS caused intradermal abscesses that were histologically similar to those caused by live and heat-killed bacteria. H. ducreyi and Neisseria gonorrhoeae LOS caused significantly larger lesions than equivalent amounts of H. influenzae LOS and E. coli lipopolysaccharide in the rabbit model. We conclude that the intradermal injection models are not valid models to study the growth of H. ducreyi in vivo. However, these data indicate that H. ducreyi LOS may play an important role in the pathogenesis of chancroid and that the rabbit model should be useful in studying H. ducreyi LOS toxicity at the cellular level.
Full text
PDF




Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Apicella M. A., Mandrell R. E., Shero M., Wilson M. E., Griffiss J. M., Brooks G. F., Lammel C., Breen J. F., Rice P. A. Modification by sialic acid of Neisseria gonorrhoeae lipooligosaccharide epitope expression in human urethral exudates: an immunoelectron microscopic analysis. J Infect Dis. 1990 Aug;162(2):506–512. doi: 10.1093/infdis/162.2.506. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Berczi I., Bertók L., Bereznai T. Comparative studies on the toxicity of Escherichia coli lipopolysaccharide endotoxin in various animal species. Can J Microbiol. 1966 Oct;12(5):1070–1071. doi: 10.1139/m66-143. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Berkley S. F., Widy-Wirski R., Okware S. I., Downing R., Linnan M. J., White K. E., Sempala S. Risk factors associated with HIV infection in Uganda. J Infect Dis. 1989 Jul;160(1):22–30. doi: 10.1093/infdis/160.1.22. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Campagnari A. A., Spinola S. M., Lesse A. J., Kwaik Y. A., Mandrell R. E., Apicella M. A. Lipooligosaccharide epitopes shared among gram-negative non-enteric mucosal pathogens. Microb Pathog. 1990 May;8(5):353–362. doi: 10.1016/0882-4010(90)90094-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- D'Costa L. J., Bowmer I., Nsanze H., Dylewski J., Fransen L., Plummer F. A., Piot P., Ronald A. R. Advances in the diagnosis and management of chancroid. Sex Transm Dis. 1986 Jul-Sep;13(3 Suppl):189–191. doi: 10.1097/00007435-198607000-00019. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Freinkel A. L. Histological aspects of sexually transmitted genital lesions. Histopathology. 1987 Aug;11(8):819–831. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2559.1987.tb01885.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gregg C. R., Melly M. A., Hellerqvist C. G., Coniglio J. G., McGee Z. A. Toxic activity of purified lipopolysaccharide of Neisseria gonorrhoeae for human fallopian tube mucosa. J Infect Dis. 1981 Mar;143(3):432–439. doi: 10.1093/infdis/143.3.432. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hammond G. W., Lian C. J., Wilt J. C., Ronald A. R. Antimicrobial susceptibility of Haemophilus ducreyi. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1978 Apr;13(4):608–612. doi: 10.1128/aac.13.4.608. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Holmberg S. D., Horsburgh C. R., Jr, Ward J. W., Jaffe H. W. Biologic factors in the sexual transmission of human immunodeficiency virus. J Infect Dis. 1989 Jul;160(1):116–125. doi: 10.1093/infdis/160.1.116. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Inzana T. J. Electrophoretic heterogeneity and interstrain variation of the lipopolysaccharide of Haemophilus influenzae. J Infect Dis. 1983 Sep;148(3):492–499. doi: 10.1093/infdis/148.3.492. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- KAPLAN W., DEACON W. E., OLANSKY S., ALBRITTON D. C. V.D.R.L. chancroid studies. III. Use of Ducrey skin test vaccines on rabbits. J Invest Dermatol. 1956 May;26(5):415–419. doi: 10.1038/jid.1956.53. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kreiss J. K., Coombs R., Plummer F., Holmes K. K., Nikora B., Cameron W., Ngugi E., Ndinya Achola J. O., Corey L. Isolation of human immunodeficiency virus from genital ulcers in Nairobi prostitutes. J Infect Dis. 1989 Sep;160(3):380–384. doi: 10.1093/infdis/160.3.380. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kreiss J. K., Koech D., Plummer F. A., Holmes K. K., Lightfoote M., Piot P., Ronald A. R., Ndinya-Achola J. O., D'Costa L. J., Roberts P. AIDS virus infection in Nairobi prostitutes. Spread of the epidemic to East Africa. N Engl J Med. 1986 Feb 13;314(7):414–418. doi: 10.1056/NEJM198602133140704. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laemmli U. K. Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature. 1970 Aug 15;227(5259):680–685. doi: 10.1038/227680a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mandrell R. E., Griffiss J. M., Macher B. A. Lipooligosaccharides (LOS) of Neisseria gonorrhoeae and Neisseria meningitidis have components that are immunochemically similar to precursors of human blood group antigens. Carbohydrate sequence specificity of the mouse monoclonal antibodies that recognize crossreacting antigens on LOS and human erythrocytes. J Exp Med. 1988 Jul 1;168(1):107–126. doi: 10.1084/jem.168.1.107. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morse S. A. Chancroid and Haemophilus ducreyi. Clin Microbiol Rev. 1989 Apr;2(2):137–157. doi: 10.1128/cmr.2.2.137. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mustafa M. M., Ramilo O., Syrogiannopoulos G. A., Olsen K. D., McCracken G. H., Jr, Hansen E. J. Induction of meningeal inflammation by outer membrane vesicles of Haemophilus influenzae type b. J Infect Dis. 1989 May;159(5):917–922. doi: 10.1093/infdis/159.5.917. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Odumeru J. A., Wiseman G. M., Ronald A. R. Relationship between lipopolysaccharide composition and virulence of Haemophilus ducreyi. J Med Microbiol. 1987 Mar;23(2):155–162. doi: 10.1099/00222615-23-2-155. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Odumeru J. A., Wiseman G. M., Ronald A. R. Virulence factors of Haemophilus ducreyi. Infect Immun. 1984 Feb;43(2):607–611. doi: 10.1128/iai.43.2.607-611.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schalla W. O., Sanders L. L., Schmid G. P., Tam M. R., Morse S. A. Use of dot-immunobinding and immunofluorescence assays to investigate clinically suspected cases of chancroid. J Infect Dis. 1986 May;153(5):879–887. doi: 10.1093/infdis/153.5.879. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schmid G. P., Sanders L. L., Jr, Blount J. H., Alexander E. R. Chancroid in the United States. Reestablishment of an old disease. JAMA. 1987 Dec 11;258(22):3265–3268. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sheldon W. H., Heyman A. Studies on Chancroid: I. Observations on the Histology with an Evaluation of Biopsy as a Diagnostic Procedure. Am J Pathol. 1946 Mar;22(2):415–425. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Simonsen J. N., Cameron D. W., Gakinya M. N., Ndinya-Achola J. O., D'Costa L. J., Karasira P., Cheang M., Ronald A. R., Piot P., Plummer F. A. Human immunodeficiency virus infection among men with sexually transmitted diseases. Experience from a center in Africa. N Engl J Med. 1988 Aug 4;319(5):274–278. doi: 10.1056/NEJM198808043190504. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stamm W. E., Handsfield H. H., Rompalo A. M., Ashley R. L., Roberts P. L., Corey L. The association between genital ulcer disease and acquisition of HIV infection in homosexual men. JAMA. 1988 Sep 9;260(10):1429–1433. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tsai C. M., Frasch C. E. A sensitive silver stain for detecting lipopolysaccharides in polyacrylamide gels. Anal Biochem. 1982 Jan 1;119(1):115–119. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(82)90673-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
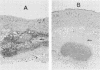
- Tuffrey M., Alexander F., Ballard R. C., Taylor-Robinson D. Characterization of skin lesions in mice following intradermal inoculation of Haemophilus ducreyi. J Exp Pathol (Oxford) 1990 Apr;71(2):233–244. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]