Abstract
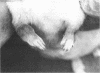
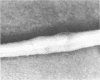
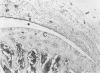
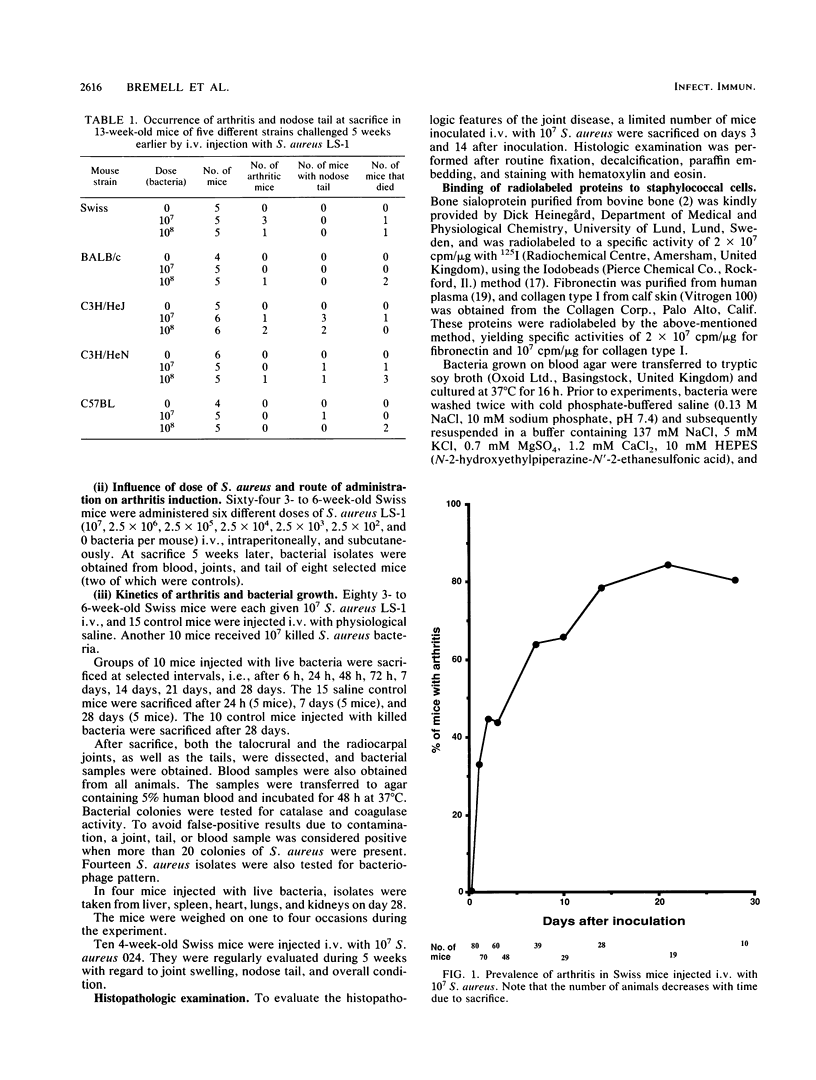
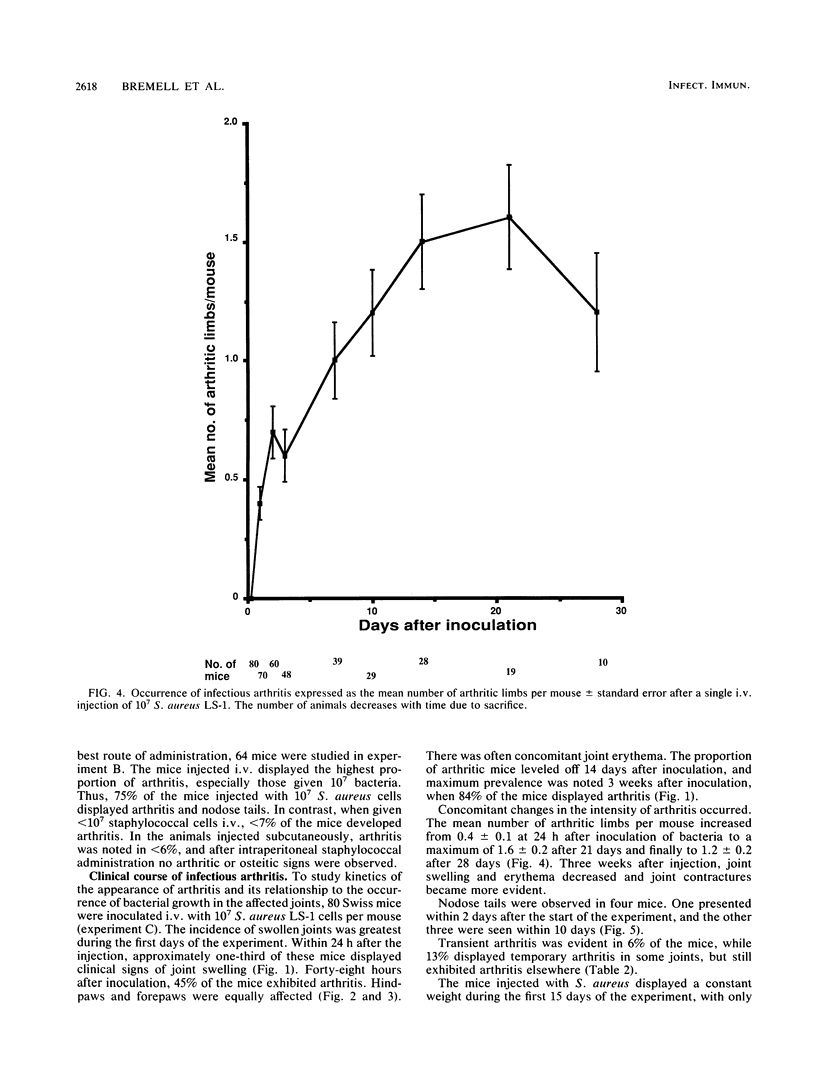
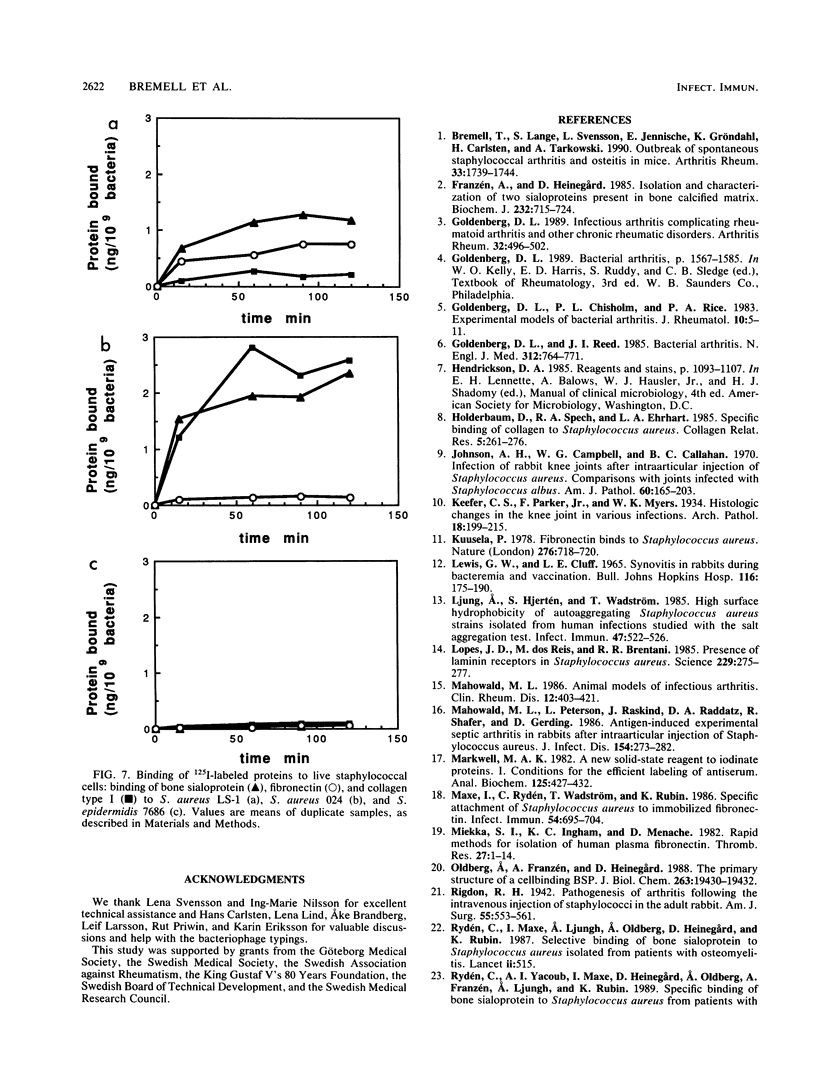
Staphylococcus aureus arthritis is usually caused by bacteremia and is highly destructive. Controlled studies on septic arthritis in humans are difficult to perform, because the time of onset of the infection is unknown. Animal models of bacterial arthritis make it possible to control important variables in experimental studies. We present a mouse model of S. aureus arthritis in which the intravenous administration of 10(7) cells of S. aureus LS-1 induced arthritis or osteitis or both within 3 weeks in 80 to 90% of the mice. Signs of arthritis emerged within the first few days after the injection. An interesting finding was that the S. aureus strain used in this study binds bone sialoprotein, a glycoprotein known to be specifically localized to bone tissue. This new model of S. aureus arthritis enables the study of the kinetics of joint destruction and the host-bacterium relationship as well as therapeutical approaches to septic arthritis and osteomyelitis.
Full text
PDF





Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bremell T., Lange S., Svensson L., Jennische E., Gröndahl K., Carlsten H., Tarkowski A. Outbreak of spontaneous staphylococcal arthritis and osteitis in mice. Arthritis Rheum. 1990 Nov;33(11):1739–1744. doi: 10.1002/art.1780331120. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Franzén A., Heinegård D. Isolation and characterization of two sialoproteins present only in bone calcified matrix. Biochem J. 1985 Dec 15;232(3):715–724. doi: 10.1042/bj2320715. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goldenberg D. L., Chisholm P. L., Rice P. A. Experimental models of bacterial arthritis: a microbiologic and histopathologic characterization of the arthritis after the intraarticular injections of Neisseria gonorrhoeae, Staphylococcus aureus, group A streptococci, and Escherichia coli. J Rheumatol. 1983 Feb;10(1):5–11. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goldenberg D. L. Infectious arthritis complicating rheumatoid arthritis and other chronic rheumatic disorders. Arthritis Rheum. 1989 Apr;32(4):496–502. doi: 10.1002/anr.1780320422. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goldenberg D. L., Reed J. I. Bacterial arthritis. N Engl J Med. 1985 Mar 21;312(12):764–771. doi: 10.1056/NEJM198503213121206. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Holderbaum D., Spech R. A., Ehrhart L. A. Specific binding of collagen to Staphylococcus aureus. Coll Relat Res. 1985 Jun;5(3):261–271. doi: 10.1016/s0174-173x(85)80016-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Johnson A. H., Campbell W. G., Jr, Callahan B. C. Infection of rabbit knee joints after intra-articular injection of Staphylococcus aureus. Comparison with joints injected with Staphylococcus albus. Am J Pathol. 1970 Aug;60(2):165–202. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kuusela P. Fibronectin binds to Staphylococcus aureus. Nature. 1978 Dec 14;276(5689):718–720. doi: 10.1038/276718a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LEWIS G. W., CLUFF L. E. SYNOVITIS IN RABBITS DURING BACTEREMIA AND VACCINATION. Bull Johns Hopkins Hosp. 1965 Mar;116:175–190. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ljungh A., Hjertén S., Wadström T. High surface hydrophobicity of autoaggregating Staphylococcus aureus strains isolated from human infections studied with the salt aggregation test. Infect Immun. 1985 Feb;47(2):522–526. doi: 10.1128/iai.47.2.522-526.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lopes J. D., dos Reis M., Brentani R. R. Presence of laminin receptors in Staphylococcus aureus. Science. 1985 Jul 19;229(4710):275–277. doi: 10.1126/science.3160113. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mahowald M. L. Animal models of infectious arthritis. Clin Rheum Dis. 1986 Aug;12(2):403–421. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mahowald M. L., Peterson L., Raskind J., Raddatz D. A., Shafer R., Gerding D. Antigen-induced experimental septic arthritis in rabbits after intraarticular injection of Staphylococcus aureus. J Infect Dis. 1986 Aug;154(2):273–282. doi: 10.1093/infdis/154.2.273. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Markwell M. A. A new solid-state reagent to iodinate proteins. I. Conditions for the efficient labeling of antiserum. Anal Biochem. 1982 Sep 15;125(2):427–432. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(82)90025-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maxe I., Rydén C., Wadström T., Rubin K. Specific attachment of Staphylococcus aureus to immobilized fibronectin. Infect Immun. 1986 Dec;54(3):695–704. doi: 10.1128/iai.54.3.695-704.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miekka S. I., Ingham K. C., Menache D. Rapid methods for isolation of human plasma fibronectin. Thromb Res. 1982 Jul 1;27(1):1–14. doi: 10.1016/0049-3848(82)90272-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Oldberg A., Franzén A., Heinegård D. The primary structure of a cell-binding bone sialoprotein. J Biol Chem. 1988 Dec 25;263(36):19430–19432. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rydén C., Maxe I., Franzén A., Ljungh A., Heinegård D., Rubin K. Selective binding of bone matrix sialoprotein to Staphylococcus aureus in osteomyelitis. Lancet. 1987 Aug 29;2(8557):515–515. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(87)91830-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schurman D. J., Johnson B. L., Jr, Amstutz H. C. Knee joint infections with Staphylococcus aureus and Micrococcus species. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 1975 Jan;57(1):40–49. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schurman D. J., Mirra J., Ding A., Nagel D. A. Experimental E. coli arthritis in the rabbit. A model of infectious and post-infectious inflammatory synovitis. J Rheumatol. 1977 Summer;4(2):118–128. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tissi L., Marconi P., Mosci P., Merletti L., Cornacchione P., Rosati E., Recchia S., von Hunolstein C., Orefici G. Experimental model of type IV Streptococcus agalactiae (group B streptococcus) infection in mice with early development of septic arthritis. Infect Immun. 1990 Sep;58(9):3093–3100. doi: 10.1128/iai.58.9.3093-3100.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wang Y. Z., Xu J. C., Xue D. M. Experimental study of acute suppurative bone and joint infection. II. Suppurative arthritis. Chin Med J (Engl) 1983 Dec;96(12):907–912. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]