Abstract
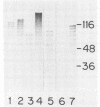
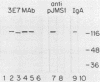
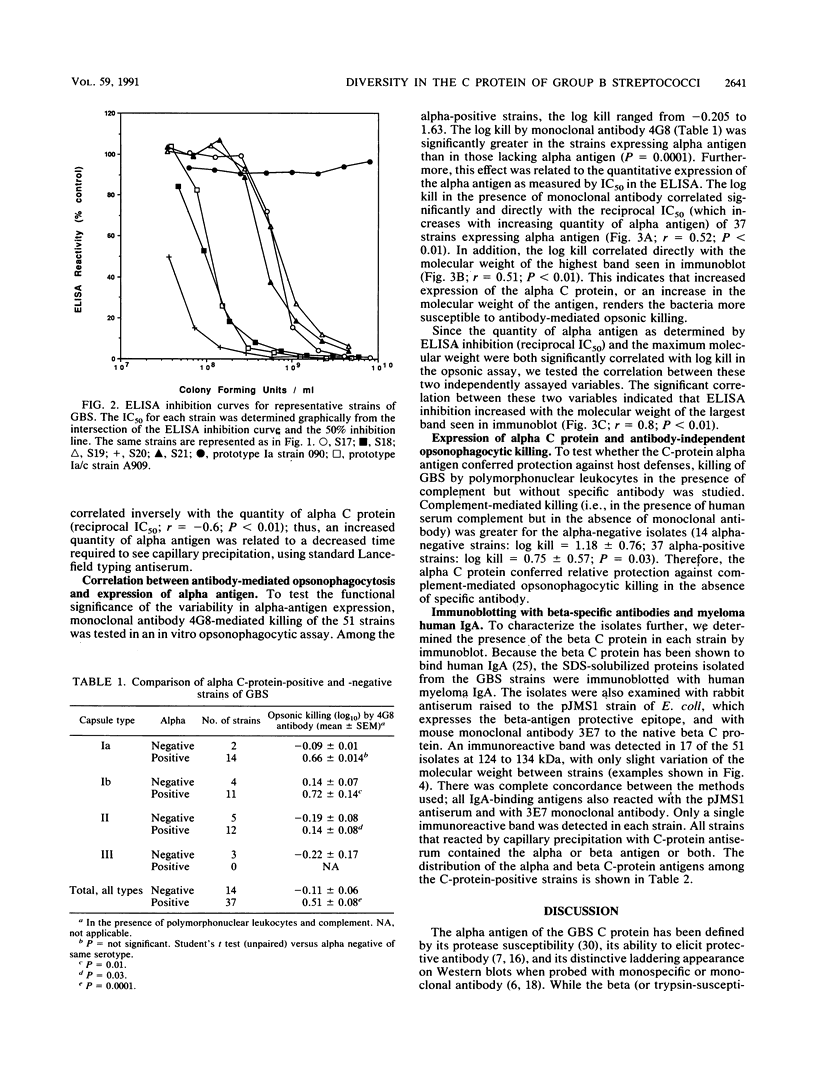
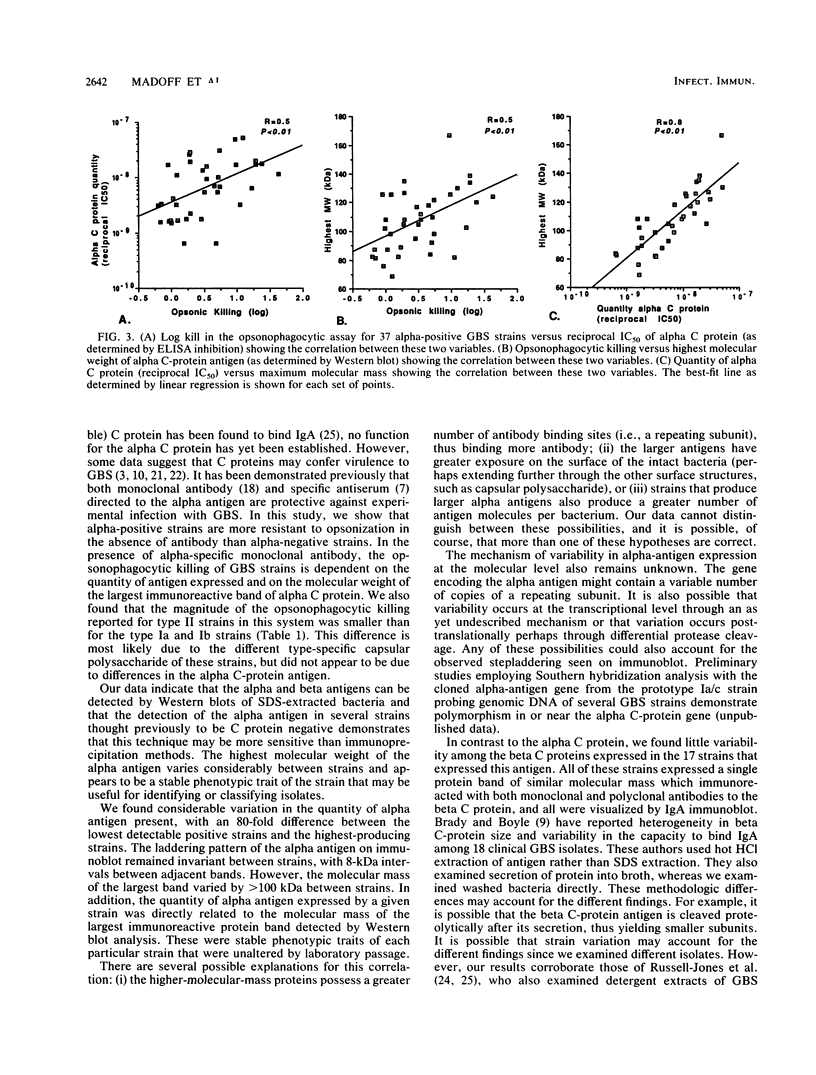
Group B streptococci (GBS) is the leading cause of neonatal sepsis and meningitis. C proteins are an immunologically important group of surface-associated antigens in GBS that remain incompletely characterized. Two C proteins have been designated alpha and beta on the basis of protease susceptibility. We recently used a monoclonal antibody to describe a protective epitope of the GBS alpha (or trypsin-resistant) C protein in the prototype Ia/c GBS strain. In the present study, we examined 51 GBS isolates for expression of C-protein alpha and beta antigens. The alpha antigen, as detected with monoclonal antibody in sodium dodecyl sulfate (SDS) extracts, appears as a heterogeneous series of proteins spaced 8 kDa apart on SDS-polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis, but has a maximum molecular mass that varies among strains from 62.5 to 167 kDa. By immunoblotting with human immunoglobulin A, polyclonal antiserum, or monoclonal antibody, the beta antigen, in contrast, appears as a single protein of molecular mass between 124 and 134 kDa. The amount of alpha antigen expressed by each strain was quantified by enzyme immunoassay inhibition and was found to vary markedly from strain to strain. The susceptibility of strains of GBS to opsonization and killing by human polymorphonuclear leukocytes in the presence of either complement alone or complement with alpha-specific monoclonal antibody was examined. Strains expressing the alpha antigen were less readily killed in the absence of specific antibody than were alpha-negative strains. Killing in the presence of alpha-specific monoclonal antibody was found to correlate directly with the maximum molecular mass of the alpha antigen and with the quantity of antigen on the bacterial cell surface. Isolates of GBS that express the alpha C protein vary widely in the quantity and molecular mass of the alpha antigen produced, and this heterogeneity appears to have biologic importance.
Full text
PDF




Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Baker C. J. Group B streptococcal infection in newborns: prevention at last? N Engl J Med. 1986 Jun 26;314(26):1702–1704. doi: 10.1056/NEJM198606263142609. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baker C. J. Immunization to prevent group B streptococcal disease: victories and vexations. J Infect Dis. 1990 May;161(5):917–921. doi: 10.1093/infdis/161.5.917. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baker C. J., Webb B. J., Kasper D. L., Edwards M. S. The role of complement and antibody in opsonophagocytosis of type II group B streptococci. J Infect Dis. 1986 Jul;154(1):47–54. doi: 10.1093/infdis/154.1.47. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baltimore R. S., Kasper D. L., Baker C. J., Goroff D. K. Antigenic specificity of opsonophagocytic antibodies in rabbit anti-sera to group B streptococci. J Immunol. 1977 Feb;118(2):673–678. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bevanger L. Ibc proteins as serotype markers of group B streptococci. Acta Pathol Microbiol Immunol Scand B. 1983 Aug;91(4):231–234. doi: 10.1111/j.1699-0463.1983.tb00038.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bevanger L., Naess A. I. Mouse-protective antibodies against the Ibc proteins of group B streptococci. Acta Pathol Microbiol Immunol Scand B. 1985 Apr;93(2):121–124. doi: 10.1111/j.1699-0463.1985.tb02862.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blake M. S., Johnston K. H., Russell-Jones G. J., Gotschlich E. C. A rapid, sensitive method for detection of alkaline phosphatase-conjugated anti-antibody on Western blots. Anal Biochem. 1984 Jan;136(1):175–179. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(84)90320-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brady L. J., Boyle M. D. Identification of non-immunoglobulin A-Fc-binding forms and low-molecular-weight secreted forms of the group B streptococcal beta antigen. Infect Immun. 1989 May;57(5):1573–1581. doi: 10.1128/iai.57.5.1573-1581.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Johnson D. R., Ferrieri P. Group B streptococcal Ibc protein antigen: distribution of two determinants in wild-type strains of common serotypes. J Clin Microbiol. 1984 Apr;19(4):506–510. doi: 10.1128/jcm.19.4.506-510.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Klegerman M. E., Boyer K. M., Papierniak C. K., Levine L., Gotoff S. P. Type-specific capsular antigen is associated with virulence in late-onset group B Streptococcal type III disease. Infect Immun. 1984 Apr;44(1):124–129. doi: 10.1128/iai.44.1.124-129.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LANCEFIELD R. C. Current knowledge of type-specific M antigens of group A streptococci. J Immunol. 1962 Sep;89:307–313. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laemmli U. K. Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature. 1970 Aug 15;227(5259):680–685. doi: 10.1038/227680a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lancefield R. C., McCarty M., Everly W. N. Multiple mouse-protective antibodies directed against group B streptococci. Special reference to antibodies effective against protein antigens. J Exp Med. 1975 Jul 1;142(1):165–179. doi: 10.1084/jem.142.1.165. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Levy N. J., Nicholson-Weller A., Baker C. J., Kasper D. L. Potentiation of virulence by group B streptococcal polysaccharides. J Infect Dis. 1984 Jun;149(6):851–860. doi: 10.1093/infdis/149.6.851. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Madoff L. C., Michel J. L., Kasper D. L. A monoclonal antibody identifies a protective C-protein alpha-antigen epitope in group B streptococci. Infect Immun. 1991 Jan;59(1):204–210. doi: 10.1128/iai.59.1.204-210.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Michel J. L., Madoff L. C., Kling D. E., Kasper D. L., Ausubel F. M. Cloned alpha and beta C-protein antigens of group B streptococci elicit protective immunity. Infect Immun. 1991 Jun;59(6):2023–2028. doi: 10.1128/iai.59.6.2023-2028.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Payne N. R., Ferrieri P. The relation of the Ibc protein antigen to the opsonization differences between strains of type II group B streptococci. J Infect Dis. 1985 Apr;151(4):672–681. doi: 10.1093/infdis/151.4.672. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Payne N. R., Kim Y. K., Ferrieri P. Effect of differences in antibody and complement requirements on phagocytic uptake and intracellular killing of "c" protein-positive and -negative strains of type II group B streptococci. Infect Immun. 1987 May;55(5):1243–1251. doi: 10.1128/iai.55.5.1243-1251.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Russell-Jones G. J., Gotschlich E. C., Blake M. S. A surface receptor specific for human IgA on group B streptococci possessing the Ibc protein antigen. J Exp Med. 1984 Nov 1;160(5):1467–1475. doi: 10.1084/jem.160.5.1467. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Russell-Jones G. J., Gotschlich E. C. Identification of protein antigens of group B streptococci, with special reference to the Ibc antigens. J Exp Med. 1984 Nov 1;160(5):1476–1484. doi: 10.1084/jem.160.5.1476. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Towbin H., Staehelin T., Gordon J. Electrophoretic transfer of proteins from polyacrylamide gels to nitrocellulose sheets: procedure and some applications. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Sep;76(9):4350–4354. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.9.4350. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Walsh J. A., Hutchins S. Group B streptococcal disease: its importance in the developing world and prospect for prevention with vaccines. Pediatr Infect Dis J. 1989 May;8(5):271–277. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Waltman W. D., McDaniel L. S., Gray B. M., Briles D. E. Variation in the molecular weight of PspA (pneumococcal surface protein A) among Streptococcus pneumoniae. Microb Pathog. 1990 Jan;8(1):61–69. doi: 10.1016/0882-4010(90)90008-e. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wilkinson H. W., Eagon R. G. Type-specific antigens of group B type Ic streptococci. Infect Immun. 1971 Nov;4(5):596–604. doi: 10.1128/iai.4.5.596-604.1971. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]