Abstract
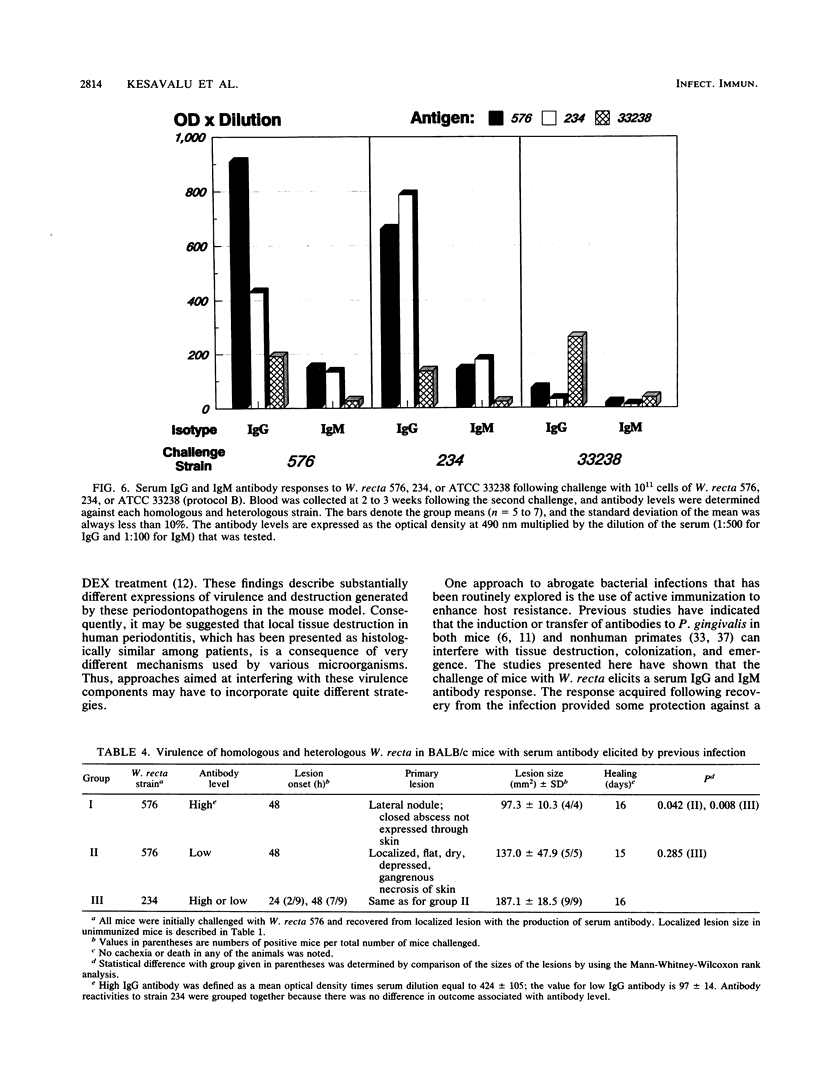
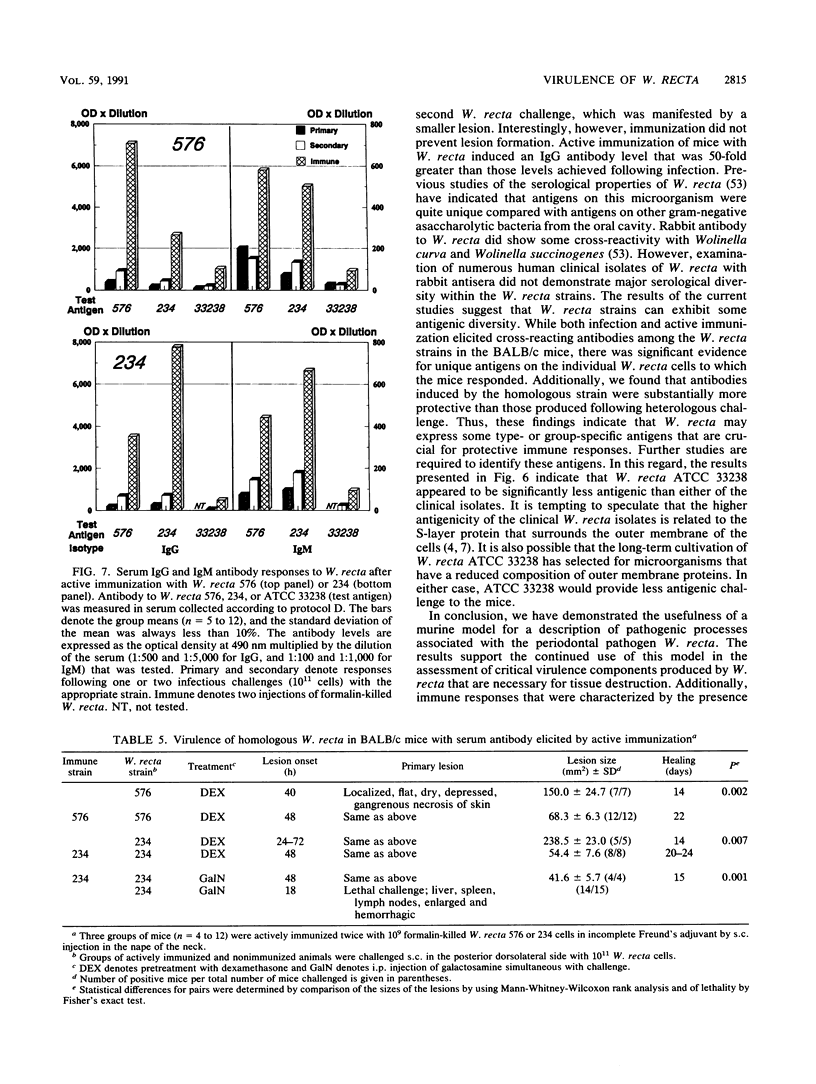
The virulence of Wolinella recta isolates was studied in an experimental animal model by using monoinfection of BALB/c mice. Infection with clinical isolates of W. recta 576 and W. recta 234 induced dry, flat, depressed gangrenous necrotic skin lesions, whereas W. recta ATCC 33238 failed to induce a similar lesion. Histological examination of the skin lesion 72 h postinfection revealed coagulation necrosis of the epidermis, subcutis and cutaneous truncus muscle, with marked exudation of serum proteins and neutrophils. Virulence-modulating agents such as dexamethasone, galactosamine, hydrazine sulfate, and dextran microcarrier beads were used in conjunction with W. recta infection. Dexamethasone, hydrazine sulfate, and dextran beads enhanced the infectivity and pathogenicity of W. recta for lesion formation and tissue destruction compared with what was found in untreated control mice. Galactosamine sensitization enhanced the virulence potential of W. recta to such an extent that a lethal outcome was observed. Laboratory passage of clinical isolates demonstrated a decreased virulence in high-passage strains, which correlated with the minimal virulence observed in the extensively passaged W. recta ATCC 33238. Serum immunoglobulin G (IgG) and IgM responses were detected in the serum of infected animals, and cross-reacting antibody indicated variation in the antigenic makeup of various W. recta strains. Enhanced IgG antibody responses were observed following the secondary challenge. Mice with acquired antibody response to initial infection remained susceptible to lesion formation with subsequent challenge, but the size of the lesion was significantly reduced, indicating partial protection. Serum IgG and IgM antibody levels were significantly increased by active immunization when compared with levels in mice which had recovered from infection. The immunization significantly decreased the lesion size; however, even these high levels of antibody failed to abrogate the lesion induction.
Full text
PDF






Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Armitage G. C., Holt S. C. Effect of Actinobacillus actinomycetemcomitans, Wolinella recta and Bacteroides gingivalis on the viability of retinoic acid-induced and dimethyl sulfoxide-induced HL-60 cells. Oral Microbiol Immunol. 1990 Oct;5(5):241–247. doi: 10.1111/j.1399-302x.1990.tb00420.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Armitage G. C., Holt S. C. Interaction of gram-negative periodontal pathogens with retinoic acid-induced and dimethyl sulfoxide-induced HL-60 cells. Oral Microbiol Immunol. 1990 Oct;5(5):248–255. doi: 10.1111/j.1399-302x.1990.tb00421.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bertini R., Bianchi M., Erroi A., Villa P., Ghezzi P. Dexamethasone modulation of in vivo effects of endotoxin, tumor necrosis factor, and interleukin-1 on liver cytochrome P-450, plasma fibrinogen, and serum iron. J Leukoc Biol. 1989 Sep;46(3):254–262. doi: 10.1002/jlb.46.3.254. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Borinski R., Holt S. C. Surface characteristics of Wolinella recta ATCC 33238 and human clinical isolates: correlation of structure with function. Infect Immun. 1990 Sep;58(9):2770–2776. doi: 10.1128/iai.58.9.2770-2776.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chen P. B., Neiders M. E., Millar S. J., Reynolds H. S., Zambon J. J. Effect of immunization on experimental Bacteroides gingivalis infection in a murine model. Infect Immun. 1987 Oct;55(10):2534–2537. doi: 10.1128/iai.55.10.2534-2537.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dokland T., Olsen I., Farrants G., Johansen B. V. Three-dimensional structure of the surface layer of Wolinella recta. Oral Microbiol Immunol. 1990 Jun;5(3):162–165. doi: 10.1111/j.1399-302x.1990.tb00415.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dzink J. L., Socransky S. S., Haffajee A. D. The predominant cultivable microbiota of active and inactive lesions of destructive periodontal diseases. J Clin Periodontol. 1988 May;15(5):316–323. doi: 10.1111/j.1600-051x.1988.tb01590.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dzink J. L., Tanner A. C., Haffajee A. D., Socransky S. S. Gram negative species associated with active destructive periodontal lesions. J Clin Periodontol. 1985 Sep;12(8):648–659. doi: 10.1111/j.1600-051x.1985.tb00936.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ebersole J. L., Frey D. E., Taubman M. A., Smith D. J. An ELISA for measuring serum antibodies to Actinobacillus actinomycetemcomitans. J Periodontal Res. 1980 Nov;15(6):621–632. doi: 10.1111/j.1600-0765.1980.tb00321.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ebersole J. L., Taubman M. A., Smith D. J., Frey D. E. Serological classification of Bacteroides from the human oral cavity. J Periodontal Res. 1988 Jan;23(1):22–27. doi: 10.1111/j.1600-0765.1988.tb01022.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ford C. W., Hamel J. C., Stapert D., Yancey R. J. Establishment of an experimental model of a Staphylococcus aureus abscess in mice by use of dextran and gelatin microcarriers. J Med Microbiol. 1989 Apr;28(4):259–266. doi: 10.1099/00222615-28-4-259. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Galanos C., Freudenberg M. A., Reutter W. Galactosamine-induced sensitization to the lethal effects of endotoxin. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Nov;76(11):5939–5943. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.11.5939. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gillespie J., Holt S. C. Growth studies of Wolinella recta, a gram-negative periodontopathogen. Oral Microbiol Immunol. 1987 Sep;2(3):105–111. doi: 10.1111/j.1399-302x.1987.tb00271.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gillespie J., Weintraub S. T., Wong G. G., Holt S. C. Chemical and biological characterization of the lipopolysaccharide of the oral pathogen Wolinella recta ATCC 33238. Infect Immun. 1988 Aug;56(8):2028–2035. doi: 10.1128/iai.56.8.2028-2035.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grenier D., Mayrand D. Selected characteristics of pathogenic and nonpathogenic strains of Bacteroides gingivalis. J Clin Microbiol. 1987 Apr;25(4):738–740. doi: 10.1128/jcm.25.4.738-740.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Haapasalo M. Bacteroides buccae and related taxa in necrotic root canal infections. J Clin Microbiol. 1986 Dec;24(6):940–944. doi: 10.1128/jcm.24.6.940-944.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Holt S. C., Bramanti T. E. Factors in virulence expression and their role in periodontal disease pathogenesis. Crit Rev Oral Biol Med. 1991;2(2):177–281. doi: 10.1177/10454411910020020301. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Holt S. C., Ebersole J., Felton J., Brunsvold M., Kornman K. S. Implantation of Bacteroides gingivalis in nonhuman primates initiates progression of periodontitis. Science. 1988 Jan 1;239(4835):55–57. doi: 10.1126/science.3336774. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ishiguro E. E., Kay W. W., Ainsworth T., Chamberlain J. B., Austen R. A., Buckley J. T., Trust T. J. Loss of virulence during culture of Aeromonas salmonicida at high temperature. J Bacteriol. 1981 Oct;148(1):333–340. doi: 10.1128/jb.148.1.333-340.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kastelein P., van Steenbergen T. J., Bras J. M., de Graaff J. An experimentally induced phlegmonous abscess by a strain of Bacteroides gingivalis in guinea pigs and mice. Antonie Van Leeuwenhoek. 1981 Mar;47(1):1–9. doi: 10.1007/BF00399062. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Keppler D., Decker K. Studies on the mechanism of galactosamine-1-phosphate and its inhibition of UDP-glucose pyrophosphorylase. Eur J Biochem. 1969 Sep;10(2):219–225. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1969.tb00677.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kornman K. S., Holt S. C., Robertson P. B. The microbiology of ligature-induced periodontitis in the cynomolgus monkey. J Periodontal Res. 1981 Jul;16(4):363–371. doi: 10.1111/j.1600-0765.1981.tb00987.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mandell R. L. A longitudinal microbiological investigation of Actinobacillus actinomycetemcomitans and Eikenella corrodens in juvenile periodontitis. Infect Immun. 1984 Sep;45(3):778–780. doi: 10.1128/iai.45.3.778-780.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marsh P. D., McKee A. S., McDermid A. S., Dowsett A. B. Ultrastructure and enzyme activities of a virulent and an avirulent variant of Bacteroides gingivalis W50. FEMS Microbiol Lett. 1989 May;50(1-2):181–185. doi: 10.1016/0378-1097(89)90482-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mashimo P. A., Yamamoto Y., Slots J., Park B. H., Genco R. J. The periodontal microflora of juvenile diabetics. Culture, immunofluorescence, and serum antibody studies. J Periodontol. 1983 Jul;54(7):420–430. doi: 10.1902/jop.1983.54.7.420. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McArthur W. P., Magnusson I., Marks R. G., Clark W. B. Modulation of colonization by black-pigmented Bacteroides species in squirrel monkeys by immunization with Bacteroides gingivalis. Infect Immun. 1989 Aug;57(8):2313–2317. doi: 10.1128/iai.57.8.2313-2317.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moore W. E., Holdeman L. V., Smibert R. M., Hash D. E., Burmeister J. A., Ranney R. R. Bacteriology of severe periodontitis in young adult humans. Infect Immun. 1982 Dec;38(3):1137–1148. doi: 10.1128/iai.38.3.1137-1148.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Neiders M. E., Chen P. B., Suido H., Reynolds H. S., Zambon J. J., Shlossman M., Genco R. J. Heterogeneity of virulence among strains of Bacteroides gingivalis. J Periodontal Res. 1989 May;24(3):192–198. doi: 10.1111/j.1600-0765.1989.tb02005.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nisengard R., Blann D., Zelonis L., McHenry K., Reynolds H., Zambon J. Effects of immunization with B. macacae on induced periodontitis--preliminary findings. Immunol Invest. 1989 Jan-May;18(1-4):225–237. doi: 10.3109/08820138909112239. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- North R. J. The action of cortisone acetate on cell-mediated immunity to infection. Suppression of host cell proliferation and alteration of cellular composition of infective foci. J Exp Med. 1971 Dec 1;134(6):1485–1500. doi: 10.1084/jem.134.6.1485. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Offenbacher S., Odle B. M., Van Dyke T. E. The use of crevicular fluid prostaglandin E2 levels as a predictor of periodontal attachment loss. J Periodontal Res. 1986 Mar;21(2):101–112. doi: 10.1111/j.1600-0765.1986.tb01443.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Onderdonk A. B., Kasper D. L., Cisneros R. L., Bartlett J. G. The capsular polysaccharide of Bacteroides fragilis as a virulence factor: comparison of the pathogenic potential of encapsulated and unencapsulated strains. J Infect Dis. 1977 Jul;136(1):82–89. doi: 10.1093/infdis/136.1.82. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Punsalang A. P., Jr, Sawyer W. D. Role of pili in the virulence of Neisseria gonorrhoeae. Infect Immun. 1973 Aug;8(2):255–263. doi: 10.1128/iai.8.2.255-263.1973. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Saito H., Watanabe T., Horikawa Y. Effects of Lactobacillus casei on Pseudomonas aeruginosa infection in normal and dexamethasone-treated mice. Microbiol Immunol. 1986;30(3):249–259. doi: 10.1111/j.1348-0421.1986.tb00940.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Silverstein R., Christoffersen C. A., Morrison D. C. Modulation of endotoxin lethality in mice by hydrazine sulfate. Infect Immun. 1989 Jul;57(7):2072–2078. doi: 10.1128/iai.57.7.2072-2078.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Slots J., Genco R. J. Black-pigmented Bacteroides species, Capnocytophaga species, and Actinobacillus actinomycetemcomitans in human periodontal disease: virulence factors in colonization, survival, and tissue destruction. J Dent Res. 1984 Mar;63(3):412–421. doi: 10.1177/00220345840630031101. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Slots J., Listgarten M. A. Bacteroides gingivalis, Bacteroides intermedius and Actinobacillus actinomycetemcomitans in human periodontal diseases. J Clin Periodontol. 1988 Feb;15(2):85–93. doi: 10.1111/j.1600-051x.1988.tb00999.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith H. The mounting interest in bacterial and viral pathogenicity. Annu Rev Microbiol. 1989;43:1–22. doi: 10.1146/annurev.mi.43.100189.000245. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Socransky S. S., Haffajee A. D., Dzink J. L., Hillman J. D. Associations between microbial species in subgingival plaque samples. Oral Microbiol Immunol. 1988 Mar;3(1):1–7. doi: 10.1111/j.1399-302x.1988.tb00596.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Syed S. A., Loesche W. J. Survival of human dental plaque flora in various transport media. Appl Microbiol. 1972 Oct;24(4):638–644. doi: 10.1128/am.24.4.638-644.1972. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tanner A. C., Dzink J. L., Ebersole J. L., Socransky S. S. Wolinella recta, campylobacter concisus, bacteroides gracilis, and Eikenella corrodens from periodontal lesions. J Periodontal Res. 1987 Jul;22(4):327–330. doi: 10.1111/j.1600-0765.1987.tb01593.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tanner A. C., Haffer C., Bratthall G. T., Visconti R. A., Socransky S. S. A study of the bacteria associated with advancing periodontitis in man. J Clin Periodontol. 1979 Oct;6(5):278–307. doi: 10.1111/j.1600-051x.1979.tb01931.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Van Dyke T. E., Dowell V. R., Jr, Offenbacher S., Snyder W., Hersh T. Potential role of microorganisms isolated from periodontal lesions in the pathogenesis of inflammatory bowel disease. Infect Immun. 1986 Sep;53(3):671–677. doi: 10.1128/iai.53.3.671-677.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ward M. E., Watt P. J., Glynn A. A. Gonococci in urethral exudates possess a virulence factor lost on subculture. Nature. 1970 Jul 25;227(5256):382–384. doi: 10.1038/227382a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wyss C. Campylobacter-Wolinella group organisms are the only oral bacteria that form arylsulfatase-active colonies on a synthetic indicator medium. Infect Immun. 1989 May;57(5):1380–1383. doi: 10.1128/iai.57.5.1380-1383.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zambon J. J., Christersson L. A., Slots J. Actinobacillus actinomycetemcomitans in human periodontal disease. Prevalence in patient groups and distribution of biotypes and serotypes within families. J Periodontol. 1983 Dec;54(12):707–711. doi: 10.1902/jop.1983.54.12.707. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- van Steenbergen T. J., Kastelein P., Touw J. J., de Graaff J. Virulence of black-pigmented Bacteroides strains from periodontal pockets and other sites in experimentally induced skin lesions in mice. J Periodontal Res. 1982 Jan;17(1):41–49. doi: 10.1111/j.1600-0765.1982.tb01129.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]