Abstract
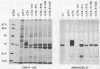
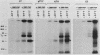
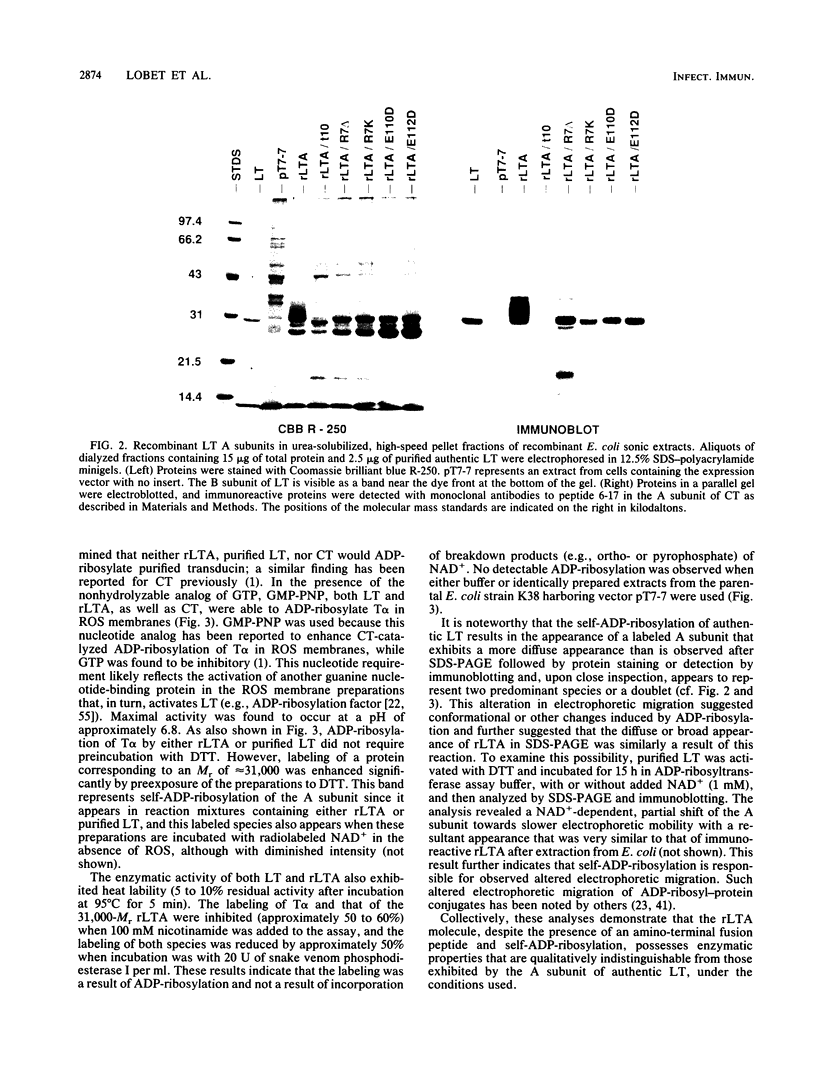
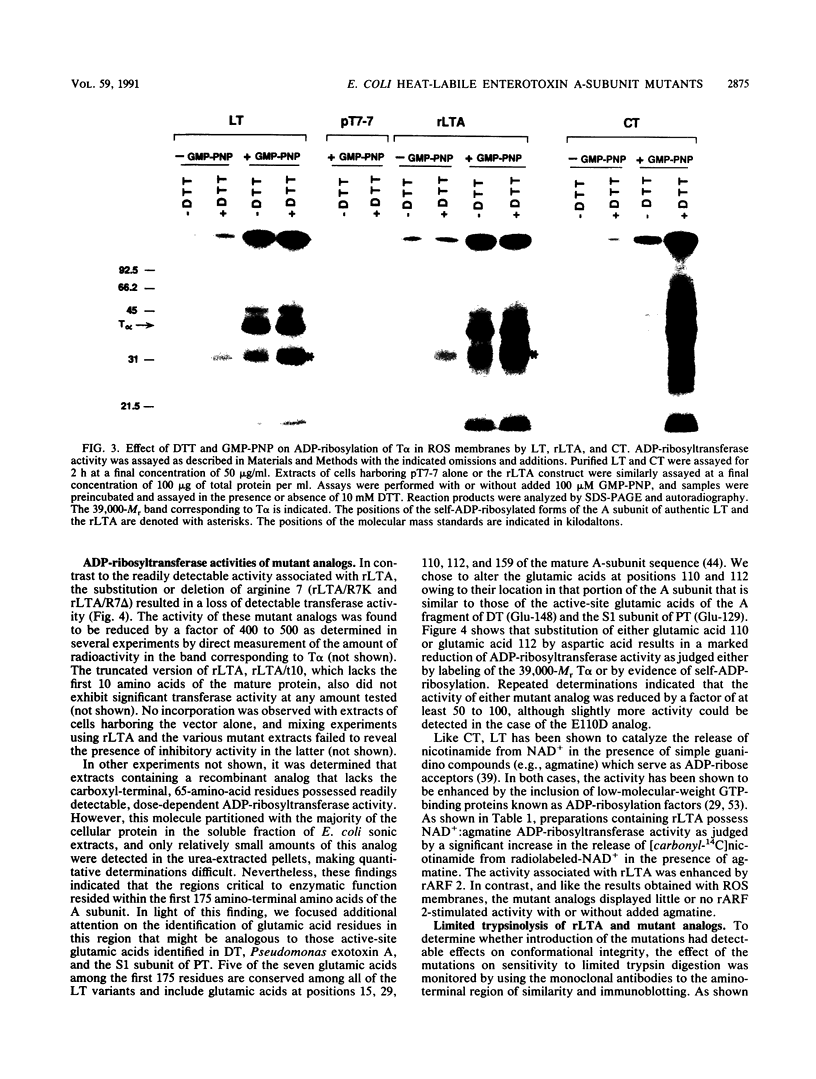
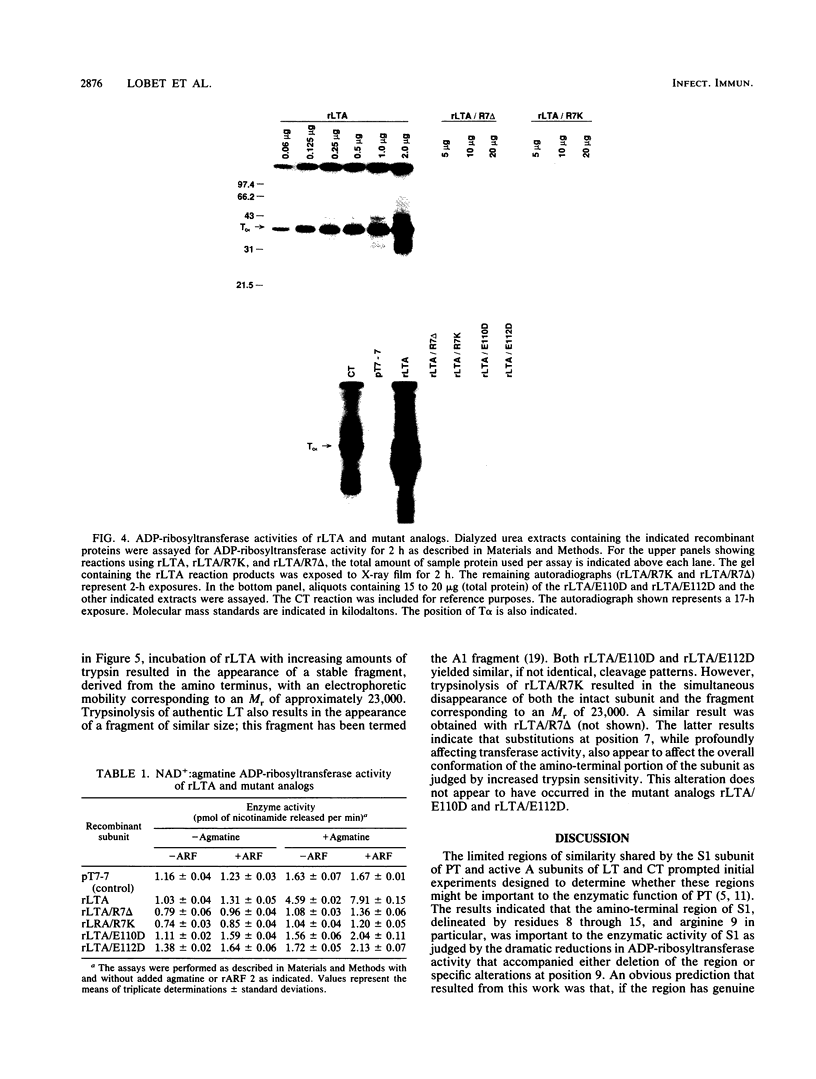
Previous studies of the S1 subunit of pertussis toxin, an NAD(+)-dependent ADP-ribosyltransferase, suggested that a small amino-terminal region of amino acid sequence similarity to the active fragments of both cholera toxin and Escherichia coli heat-labile enterotoxin represents a region containing critical active-site residues that might be involved in the binding of the substrate NAD+. Other studies of two other bacterial toxins possessing ADP-ribosyltransferase activity, diphtheria toxin and Pseudomonas exotoxin A, have revealed the presence of essential glutamic acid residues vicinal to the active site. To help determine the relevance of these observations to activities of the enterotoxins, the A-subunit gene of the E. coli heat-labile enterotoxin was subjected to site-specific mutagenesis in the region encoding the amino-terminal region of similarity to the S1 subunit of pertussis toxin delineated by residues 6 through 17 and at two glutamic acid residues, 110 and 112, that are conserved in the active domains of all of the heat-labile enterotoxin variants and in cholera toxin. Mutant proteins in which arginine 7 was either deleted or replaced with lysine exhibited undetectable levels of ADP-ribosyltransferase activity. However, limited trypsinolysis of the arginine 7 mutants yielded fragmentation kinetics that were different from that yielded by the wild-type recombinant subunit or the authentic A subunit. In contrast, mutant proteins in which glutamic acid residues at either position 110 or 112 were replaced with aspartic acid responded like the wild-type subunit upon limited trypsinolysis, while exhibiting severely depressed, but detectable, ADP-ribosyltransferase activity. The latter results may indicate that either glutamic acid 110 or glutamic acid 112 of the A subunit of heat-labile enterotoxin is analogous to those active-site glutamic acids identified in several other ADP-ribosylating toxins.
Full text
PDF






Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Abood M. E., Hurley J. B., Pappone M. C., Bourne H. R., Stryer L. Functional homology between signal-coupling proteins. Cholera toxin inactivates the GTPase activity of transducin. J Biol Chem. 1982 Sep 25;257(18):10540–10543. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baehr W., Morita E. A., Swanson R. J., Applebury M. L. Characterization of bovine rod outer segment G-protein. J Biol Chem. 1982 Jun 10;257(11):6452–6460. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Barbieri J. T., Cortina G. ADP-ribosyltransferase mutations in the catalytic S-1 subunit of pertussis toxin. Infect Immun. 1988 Aug;56(8):1934–1941. doi: 10.1128/iai.56.8.1934-1941.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Barbieri J. T., Mende-Mueller L. M., Rappuoli R., Collier R. J. Photolabeling of Glu-129 of the S-1 subunit of pertussis toxin with NAD. Infect Immun. 1989 Nov;57(11):3549–3554. doi: 10.1128/iai.57.11.3549-3554.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Burnette W. N., Cieplak W., Mar V. L., Kaljot K. T., Sato H., Keith J. M. Pertussis toxin S1 mutant with reduced enzyme activity and a conserved protective epitope. Science. 1988 Oct 7;242(4875):72–74. doi: 10.1126/science.2459776. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Burns D. L., Kenimer J. G., Manclark C. R. Role of the A subunit of pertussis toxin in alteration of Chinese hamster ovary cell morphology. Infect Immun. 1987 Jan;55(1):24–28. doi: 10.1128/iai.55.1.24-28.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carroll S. F., Collier R. J. Active site of Pseudomonas aeruginosa exotoxin A. Glutamic acid 553 is photolabeled by NAD and shows functional homology with glutamic acid 148 of diphtheria toxin. J Biol Chem. 1987 Jun 25;262(18):8707–8711. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carroll S. F., Collier R. J. NAD binding site of diphtheria toxin: identification of a residue within the nicotinamide subsite by photochemical modification with NAD. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 Jun;81(11):3307–3311. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.11.3307. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chen E. Y., Seeburg P. H. Supercoil sequencing: a fast and simple method for sequencing plasmid DNA. DNA. 1985 Apr;4(2):165–170. doi: 10.1089/dna.1985.4.165. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cieplak W., Burnette W. N., Mar V. L., Kaljot K. T., Morris C. F., Chen K. K., Sato H., Keith J. M. Identification of a region in the S1 subunit of pertussis toxin that is required for enzymatic activity and that contributes to the formation of a neutralizing antigenic determinant. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Jul;85(13):4667–4671. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.13.4667. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clements J. D., Finkelstein R. A. Isolation and characterization of homogeneous heat-labile enterotoxins with high specific activity from Escherichia coli cultures. Infect Immun. 1979 Jun;24(3):760–769. doi: 10.1128/iai.24.3.760-769.1979. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dallas W. S., Gill D. M., Falkow S. Cistrons encoding Escherichia coli heat-labile toxin. J Bacteriol. 1979 Sep;139(3):850–858. doi: 10.1128/jb.139.3.850-858.1979. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Douglas C. M., Collier R. J. Exotoxin A of Pseudomonas aeruginosa: substitution of glutamic acid 553 with aspartic acid drastically reduces toxicity and enzymatic activity. J Bacteriol. 1987 Nov;169(11):4967–4971. doi: 10.1128/jb.169.11.4967-4971.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Field M., Rao M. C., Chang E. B. Intestinal electrolyte transport and diarrheal disease (2) N Engl J Med. 1989 Sep 28;321(13):879–883. doi: 10.1056/NEJM198909283211307. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Finkelstein R. A., Burks M. F., Zupan A., Dallas W. S., Jacob C. O., Ludwig D. S. Epitopes of the cholera family of enterotoxins. Rev Infect Dis. 1987 May-Jun;9(3):544–561. doi: 10.1093/clinids/9.3.544. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gill D. M., Clements J. D., Robertson D. C., Finkelstein R. A. Subunit number and arrangement in Escherichia coli heat-labile enterotoxin. Infect Immun. 1981 Sep;33(3):677–682. doi: 10.1128/iai.33.3.677-682.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gill D. M., Meren R. ADP-ribosylation of membrane proteins catalyzed by cholera toxin: basis of the activation of adenylate cyclase. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1978 Jul;75(7):3050–3054. doi: 10.1073/pnas.75.7.3050. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gill D. M., Richardson S. H. Adenosine diphosphate-ribosylation of adenylate cyclase catalyzed by heat-labile enterotoxin of Escherichia coli: comparison with cholera toxin. J Infect Dis. 1980 Jan;141(1):64–70. doi: 10.1093/infdis/141.1.64. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hanahan D. Studies on transformation of Escherichia coli with plasmids. J Mol Biol. 1983 Jun 5;166(4):557–580. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(83)80284-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Harford S., Dykes C. W., Hobden A. N., Read M. J., Halliday I. J. Inactivation of the Escherichia coli heat-labile enterotoxin by in vitro mutagenesis of the A-subunit gene. Eur J Biochem. 1989 Aug 1;183(2):311–316. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1989.tb14930.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kahn R. A., Gilman A. G. Purification of a protein cofactor required for ADP-ribosylation of the stimulatory regulatory component of adenylate cyclase by cholera toxin. J Biol Chem. 1984 May 25;259(10):6228–6234. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kanemoto R. H., Ludden P. W. Effect of ammonia, darkness, and phenazine methosulfate on whole-cell nitrogenase activity and Fe protein modification in Rhodospirillum rubrum. J Bacteriol. 1984 May;158(2):713–720. doi: 10.1128/jb.158.2.713-720.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kaper J. B., Levine M. M. Progress towards a vaccine against enterotoxigenic Escherichia coli. Vaccine. 1988 Apr;6(2):197–199. doi: 10.1016/s0264-410x(88)80028-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Katada T., Ui M. Direct modification of the membrane adenylate cyclase system by islet-activating protein due to ADP-ribosylation of a membrane protein. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1982 May;79(10):3129–3133. doi: 10.1073/pnas.79.10.3129. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kunkel T. A. Rapid and efficient site-specific mutagenesis without phenotypic selection. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Jan;82(2):488–492. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.2.488. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laemmli U. K. Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature. 1970 Aug 15;227(5259):680–685. doi: 10.1038/227680a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lax A. J., Chanter N., Pullinger G. D., Higgins T., Staddon J. M., Rozengurt E. Sequence analysis of the potent mitogenic toxin of Pasteurella multocida. FEBS Lett. 1990 Dec 17;277(1-2):59–64. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(90)80809-w. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lobet Y., Cieplak W., Jr, Smith S. G., Keith J. M. Effects of mutations on enzyme activity and immunoreactivity of the S1 subunit of pertussis toxin. Infect Immun. 1989 Nov;57(11):3660–3662. doi: 10.1128/iai.57.11.3660-3662.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Locht C., Capiau C., Feron C. Identification of amino acid residues essential for the enzymatic activities of pertussis toxin. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 May;86(9):3075–3079. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.9.3075. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Locht C., Cieplak W., Marchitto K. S., Sato H., Keith J. M. Activities of complete and truncated forms of pertussis toxin subunits S1 and S2 synthesized by Escherichia coli. Infect Immun. 1987 Nov;55(11):2546–2553. doi: 10.1128/iai.55.11.2546-2553.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Locht C., Keith J. M. Pertussis toxin gene: nucleotide sequence and genetic organization. Science. 1986 Jun 6;232(4755):1258–1264. doi: 10.1126/science.3704651. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Locht C., Lobet Y., Feron C., Cieplak W., Keith J. M. The role of cysteine 41 in the enzymatic activities of the pertussis toxin S1 subunit as investigated by site-directed mutagenesis. J Biol Chem. 1990 Mar 15;265(8):4552–4559. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Loll P. J., Lattman E. E. Active site mutant Glu-43----Asp in staphylococcal nuclease displays nonlocal structural changes. Biochemistry. 1990 Jul 24;29(29):6866–6873. doi: 10.1021/bi00481a016. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Middlebrook J. L., Dorland R. B. Bacterial toxins: cellular mechanisms of action. Microbiol Rev. 1984 Sep;48(3):199–221. doi: 10.1128/mr.48.3.199-221.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moss J., Osborne J. C., Jr, Fishman P. H., Nakaya S., Robertson D. C. Escherichia coli heat-labile enterotoxin. Ganglioside specificity and ADP-ribosyltransferase activity. J Biol Chem. 1981 Dec 25;256(24):12861–12865. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moss J., Richardson S. H. Activation of adenylate cyclase by heat-labile Escherichia coli enterotoxin. Evidence for ADP-ribosyltransferase activity similar to that of choleragen. J Clin Invest. 1978 Aug;62(2):281–285. doi: 10.1172/JCI109127. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nicosia A., Perugini M., Franzini C., Casagli M. C., Borri M. G., Antoni G., Almoni M., Neri P., Ratti G., Rappuoli R. Cloning and sequencing of the pertussis toxin genes: operon structure and gene duplication. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Jul;83(13):4631–4635. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.13.4631. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Okamoto K., Okamoto K., Miyama A., Tsuji T., Honda T., Miwatani T. Effect of substitution of glycine for arginine at position 146 of the A1 subunit on biological activity of Escherichia coli heat-labile enterotoxin. J Bacteriol. 1988 May;170(5):2208–2211. doi: 10.1128/jb.170.5.2208-2211.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pickett C. L., Twiddy E. M., Coker C., Holmes R. K. Cloning, nucleotide sequence, and hybridization studies of the type IIb heat-labile enterotoxin gene of Escherichia coli. J Bacteriol. 1989 Sep;171(9):4945–4952. doi: 10.1128/jb.171.9.4945-4952.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pierce N. F., Cray W. C., Jr, Sacci J. B., Jr Oral immunization of dogs with purified cholera toxin, crude cholera toxin, or B subunit: evidence for synergistic protection by antitoxic and antibacterial mechanisms. Infect Immun. 1982 Aug;37(2):687–694. doi: 10.1128/iai.37.2.687-694.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pizza M., Bartoloni A., Prugnola A., Silvestri S., Rappuoli R. Subunit S1 of pertussis toxin: mapping of the regions essential for ADP-ribosyltransferase activity. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Oct;85(20):7521–7525. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.20.7521. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pizza M., Covacci A., Bartoloni A., Perugini M., Nencioni L., De Magistris M. T., Villa L., Nucci D., Manetti R., Bugnoli M. Mutants of pertussis toxin suitable for vaccine development. Science. 1989 Oct 27;246(4929):497–500. doi: 10.1126/science.2683073. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Price S. R., Nightingale M., Tsai S. C., Williamson K. C., Adamik R., Chen H. C., Moss J., Vaughan M. Guanine nucleotide-binding proteins that enhance choleragen ADP-ribosyltransferase activity: nucleotide and deduced amino acid sequence of an ADP-ribosylation factor cDNA. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Aug;85(15):5488–5491. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.15.5488. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sanchez J., Uhlin B. E., Grundström T., Holmgren J., Hirst T. R. Immunoactive chimeric ST-LT enterotoxins of Escherichia coli generated by in vitro gene fusion. FEBS Lett. 1986 Nov 24;208(2):194–198. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(86)81016-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sanger F., Nicklen S., Coulson A. R. DNA sequencing with chain-terminating inhibitors. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Dec;74(12):5463–5467. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.12.5463. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith P. K., Krohn R. I., Hermanson G. T., Mallia A. K., Gartner F. H., Provenzano M. D., Fujimoto E. K., Goeke N. M., Olson B. J., Klenk D. C. Measurement of protein using bicinchoninic acid. Anal Biochem. 1985 Oct;150(1):76–85. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(85)90442-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Spicer E. K., Noble J. A. Escherichia coli heat-labile enterotoxin. Nucleotide sequence of the A subunit gene. J Biol Chem. 1982 May 25;257(10):5716–5721. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tabor S., Richardson C. C. A bacteriophage T7 RNA polymerase/promoter system for controlled exclusive expression of specific genes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Feb;82(4):1074–1078. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.4.1074. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Towbin H., Staehelin T., Gordon J. Electrophoretic transfer of proteins from polyacrylamide gels to nitrocellulose sheets: procedure and some applications. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Sep;76(9):4350–4354. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.9.4350. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tsai S. C., Noda M., Adamik R., Chang P. P., Chen H. C., Moss J., Vaughan M. Stimulation of choleragen enzymatic activities by GTP and two soluble proteins purified from bovine brain. J Biol Chem. 1988 Feb 5;263(4):1768–1772. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tsuji T., Inoue T., Miyama A., Okamoto K., Honda T., Miwatani T. A single amino acid substitution in the A subunit of Escherichia coli enterotoxin results in a loss of its toxic activity. J Biol Chem. 1990 Dec 25;265(36):22520–22525. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tweten R. K., Barbieri J. T., Collier R. J. Diphtheria toxin. Effect of substituting aspartic acid for glutamic acid 148 on ADP-ribosyltransferase activity. J Biol Chem. 1985 Sep 5;260(19):10392–10394. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Venkatesan S., Moss B. Donor and acceptor specificities of HeLa cell mRNA guanylyltransferase. J Biol Chem. 1980 Apr 10;255(7):2835–2842. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wozniak D. J., Hsu L. Y., Galloway D. R. His-426 of the Pseudomonas aeruginosa exotoxin A is required for ADP-ribosylation of elongation factor II. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Dec;85(23):8880–8884. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.23.8880. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yamamoto T., Gojobori T., Yokota T. Evolutionary origin of pathogenic determinants in enterotoxigenic Escherichia coli and Vibrio cholerae O1. J Bacteriol. 1987 Mar;169(3):1352–1357. doi: 10.1128/jb.169.3.1352-1357.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]