Abstract
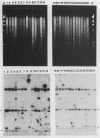
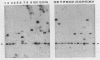
Invasion of intestinal epithelial cells is an essential virulence factor of salmonellae. A group of genes, invABC and invD, that allow Salmonella typhimurium to penetrate cultured epithelial cells have previously been characterized (J. E. Galán and R. Curtiss III, Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 86:6383-6387, 1989). The distribution of these genes among Salmonella isolates belonging to 37 different species or serovars was investigated by Southern and colony blot hybridization analyses. Regions of high sequence similarity to the invABC genes were present in all Salonella isolates examined, while regions of sequence similarity to the invD gene were present in all but one (S. arizonae) of the isolates tested, with little restriction fragment length polymorphism. Sequences similar to these genes were not detected in strains of Escherichia coli, Yersinia spp., or Shigella spp. invA mutants (unable to express the invABC genes) of several Salmonella species or serovars, including S. typhi, were constructed and examined for their ability to penetrate Henle-407 cells. All mutants were deficient for entry into cultured epithelial cells, indicating that the invABC genes were not only present in these strains but also functional.
Full text
PDF




Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Barondess J. J., Beckwith J. A bacterial virulence determinant encoded by lysogenic coliphage lambda. Nature. 1990 Aug 30;346(6287):871–874. doi: 10.1038/346871a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Barrow P. A., Lovell M. A. Invasion of Vero cells by Salmonella species. J Med Microbiol. 1989 Jan;28(1):59–67. doi: 10.1099/00222615-28-1-59. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bernardini M. L., Mounier J., d'Hauteville H., Coquis-Rondon M., Sansonetti P. J. Identification of icsA, a plasmid locus of Shigella flexneri that governs bacterial intra- and intercellular spread through interaction with F-actin. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 May;86(10):3867–3871. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.10.3867. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Birnboim H. C., Doly J. A rapid alkaline extraction procedure for screening recombinant plasmid DNA. Nucleic Acids Res. 1979 Nov 24;7(6):1513–1523. doi: 10.1093/nar/7.6.1513. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bonner T. I., Brenner D. J., Neufeld B. R., Britten R. J. Reduction in the rate of DNA reassociation by sequence divergence. J Mol Biol. 1973 Dec 5;81(2):123–135. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(73)90184-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bölin I., Norlander L., Wolf-Watz H. Temperature-inducible outer membrane protein of Yersinia pseudotuberculosis and Yersinia enterocolitica is associated with the virulence plasmid. Infect Immun. 1982 Aug;37(2):506–512. doi: 10.1128/iai.37.2.506-512.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chikami G. K., Fierer J., Guiney D. G. Plasmid-mediated virulence in Salmonella dublin demonstrated by use of a Tn5-oriT construct. Infect Immun. 1985 Nov;50(2):420–424. doi: 10.1128/iai.50.2.420-424.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clerc P., Sansonetti P. J. Entry of Shigella flexneri into HeLa cells: evidence for directed phagocytosis involving actin polymerization and myosin accumulation. Infect Immun. 1987 Nov;55(11):2681–2688. doi: 10.1128/iai.55.11.2681-2688.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Elsinghorst E. A., Baron L. S., Kopecko D. J. Penetration of human intestinal epithelial cells by Salmonella: molecular cloning and expression of Salmonella typhi invasion determinants in Escherichia coli. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 Jul;86(13):5173–5177. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.13.5173. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fields P. I., Groisman E. A., Heffron F. A Salmonella locus that controls resistance to microbicidal proteins from phagocytic cells. Science. 1989 Feb 24;243(4894 Pt 1):1059–1062. doi: 10.1126/science.2646710. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Finlay B. B., Falkow S. Salmonella as an intracellular parasite. Mol Microbiol. 1989 Dec;3(12):1833–1841. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2958.1989.tb00170.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Finlay B. B., Gumbiner B., Falkow S. Penetration of Salmonella through a polarized Madin-Darby canine kidney epithelial cell monolayer. J Cell Biol. 1988 Jul;107(1):221–230. doi: 10.1083/jcb.107.1.221. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Finlay B. B., Starnbach M. N., Francis C. L., Stocker B. A., Chatfield S., Dougan G., Falkow S. Identification and characterization of TnphoA mutants of Salmonella that are unable to pass through a polarized MDCK epithelial cell monolayer. Mol Microbiol. 1988 Nov;2(6):757–766. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2958.1988.tb00087.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Galán J. E., Curtiss R., 3rd Cloning and molecular characterization of genes whose products allow Salmonella typhimurium to penetrate tissue culture cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 Aug;86(16):6383–6387. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.16.6383. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Galán J. E., Curtiss R., 3rd Expression of Salmonella typhimurium genes required for invasion is regulated by changes in DNA supercoiling. Infect Immun. 1990 Jun;58(6):1879–1885. doi: 10.1128/iai.58.6.1879-1885.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Giannella R. A., Washington O., Gemski P., Formal S. B. Invasion of HeLa cells by Salmonella typhimurium: a model for study of invasiveness of Salmonella. J Infect Dis. 1973 Jul;128(1):69–75. doi: 10.1093/infdis/128.1.69. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hoiseth S. K., Stocker B. A. Aromatic-dependent Salmonella typhimurium are non-virulent and effective as live vaccines. Nature. 1981 May 21;291(5812):238–239. doi: 10.1038/291238a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Isberg R. R. Determinants for thermoinducible cell binding and plasmid-encoded cellular penetration detected in the absence of the Yersinia pseudotuberculosis invasin protein. Infect Immun. 1989 Jul;57(7):1998–2005. doi: 10.1128/iai.57.7.1998-2005.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Isberg R. R., Falkow S. A single genetic locus encoded by Yersinia pseudotuberculosis permits invasion of cultured animal cells by Escherichia coli K-12. Nature. 1985 Sep 19;317(6034):262–264. doi: 10.1038/317262a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Isberg R. R., Voorhis D. L., Falkow S. Identification of invasin: a protein that allows enteric bacteria to penetrate cultured mammalian cells. Cell. 1987 Aug 28;50(5):769–778. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(87)90335-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jerse A. E., Yu J., Tall B. D., Kaper J. B. A genetic locus of enteropathogenic Escherichia coli necessary for the production of attaching and effacing lesions on tissue culture cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1990 Oct;87(20):7839–7843. doi: 10.1073/pnas.87.20.7839. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kihlström E., Edebo L. Association of viable and inactivated Salmonella typhimurium 395 MS and MR 10 with HeLa cells. Infect Immun. 1976 Oct;14(4):851–857. doi: 10.1128/iai.14.4.851-857.1976. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kihlström E., Nilsson L. Endocytosis of Salmonella typhimurium 395 MS and MR10 by HeLa cells. Acta Pathol Microbiol Scand B. 1977 Oct;85B(5):322–328. doi: 10.1111/j.1699-0463.1977.tb01982.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kohbata S., Yokoyama H., Yabuuchi E. Cytopathogenic effect of Salmonella typhi GIFU 10007 on M cells of murine ileal Peyer's patches in ligated ileal loops: an ultrastructural study. Microbiol Immunol. 1986;30(12):1225–1237. doi: 10.1111/j.1348-0421.1986.tb03055.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LENNOX E. S. Transduction of linked genetic characters of the host by bacteriophage P1. Virology. 1955 Jul;1(2):190–206. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(55)90016-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Liu S. L., Ezaki T., Miura H., Matsui K., Yabuuchi E. Intact motility as a Salmonella typhi invasion-related factor. Infect Immun. 1988 Aug;56(8):1967–1973. doi: 10.1128/iai.56.8.1967-1973.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Makino S., Sasakawa C., Kamata K., Kurata T., Yoshikawa M. A genetic determinant required for continuous reinfection of adjacent cells on large plasmid in S. flexneri 2a. Cell. 1986 Aug 15;46(4):551–555. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(86)90880-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maurelli A. T., Sansonetti P. J. Genetic determinants of Shigella pathogenicity. Annu Rev Microbiol. 1988;42:127–150. doi: 10.1146/annurev.mi.42.100188.001015. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miller S. I., Kukral A. M., Mekalanos J. J. A two-component regulatory system (phoP phoQ) controls Salmonella typhimurium virulence. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 Jul;86(13):5054–5058. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.13.5054. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miller V. L., Falkow S. Evidence for two genetic loci in Yersinia enterocolitica that can promote invasion of epithelial cells. Infect Immun. 1988 May;56(5):1242–1248. doi: 10.1128/iai.56.5.1242-1248.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miller V. L., Farmer J. J., 3rd, Hill W. E., Falkow S. The ail locus is found uniquely in Yersinia enterocolitica serotypes commonly associated with disease. Infect Immun. 1989 Jan;57(1):121–131. doi: 10.1128/iai.57.1.121-131.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miller V. L., Finlay B. B., Falkow S. Factors essential for the penetration of mammalian cells by Yersinia. Curr Top Microbiol Immunol. 1988;138:15–39. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moulder J. W. Comparative biology of intracellular parasitism. Microbiol Rev. 1985 Sep;49(3):298–337. doi: 10.1128/mr.49.3.298-337.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mounier J., Ryter A., Coquis-Rondon M., Sansonetti P. J. Intracellular and cell-to-cell spread of Listeria monocytogenes involves interaction with F-actin in the enterocytelike cell line Caco-2. Infect Immun. 1990 Apr;58(4):1048–1058. doi: 10.1128/iai.58.4.1048-1058.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mroczenski-Wildey M. J., Di Fabio J. L., Cabello F. C. Invasion and lysis of HeLa cell monolayers by Salmonella typhi: the role of lipopolysaccharide. Microb Pathog. 1989 Feb;6(2):143–152. doi: 10.1016/0882-4010(89)90017-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pierson D. E., Falkow S. Nonpathogenic isolates of Yersinia enterocolitica do not contain functional inv-homologous sequences. Infect Immun. 1990 Apr;58(4):1059–1064. doi: 10.1128/iai.58.4.1059-1064.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Portnoy D. A., Moseley S. L., Falkow S. Characterization of plasmids and plasmid-associated determinants of Yersinia enterocolitica pathogenesis. Infect Immun. 1981 Feb;31(2):775–782. doi: 10.1128/iai.31.2.775-782.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pulkkinen W. S., Miller S. I. A Salmonella typhimurium virulence protein is similar to a Yersinia enterocolitica invasion protein and a bacteriophage lambda outer membrane protein. J Bacteriol. 1991 Jan;173(1):86–93. doi: 10.1128/jb.173.1.86-93.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sansonetti P. J., Ryter A., Clerc P., Maurelli A. T., Mounier J. Multiplication of Shigella flexneri within HeLa cells: lysis of the phagocytic vacuole and plasmid-mediated contact hemolysis. Infect Immun. 1986 Feb;51(2):461–469. doi: 10.1128/iai.51.2.461-469.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Small P. L., Isberg R. R., Falkow S. Comparison of the ability of enteroinvasive Escherichia coli, Salmonella typhimurium, Yersinia pseudotuberculosis, and Yersinia enterocolitica to enter and replicate within HEp-2 cells. Infect Immun. 1987 Jul;55(7):1674–1679. doi: 10.1128/iai.55.7.1674-1679.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Southern E. M. Detection of specific sequences among DNA fragments separated by gel electrophoresis. J Mol Biol. 1975 Nov 5;98(3):503–517. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(75)80083-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stoorvogel J., van Bussel M. J., Tommassen J., van de Klundert J. A. Molecular characterization of an Enterobacter cloacae outer membrane protein (OmpX). J Bacteriol. 1991 Jan;173(1):156–160. doi: 10.1128/jb.173.1.156-160.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Takeuchi A. Electron microscope studies of experimental Salmonella infection. I. Penetration into the intestinal epithelium by Salmonella typhimurium. Am J Pathol. 1967 Jan;50(1):109–136. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tilney L. G., Portnoy D. A. Actin filaments and the growth, movement, and spread of the intracellular bacterial parasite, Listeria monocytogenes. J Cell Biol. 1989 Oct;109(4 Pt 1):1597–1608. doi: 10.1083/jcb.109.4.1597. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]