Abstract
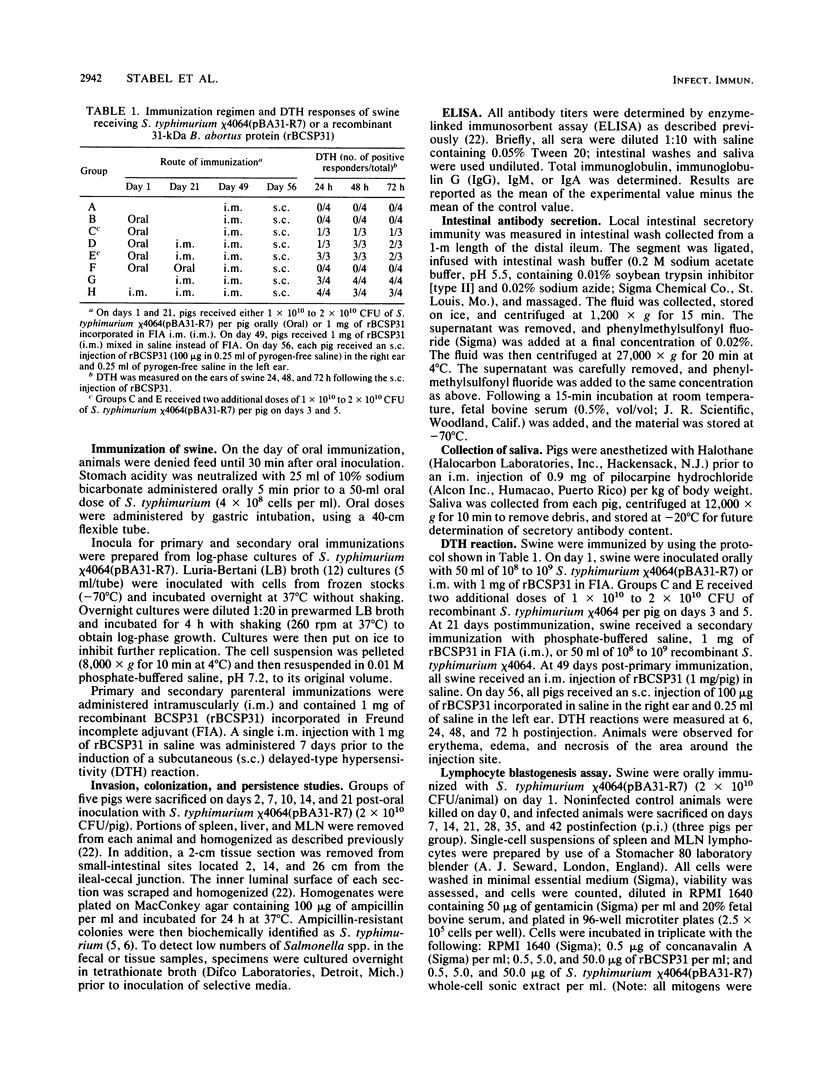
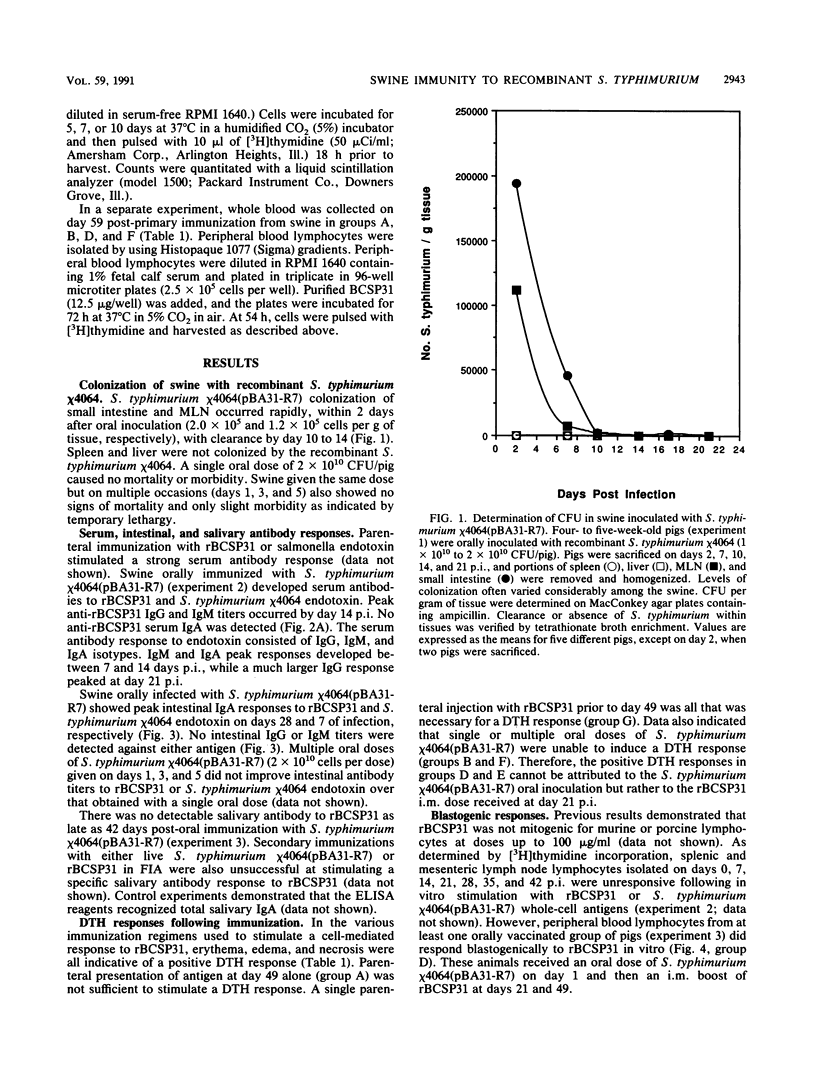
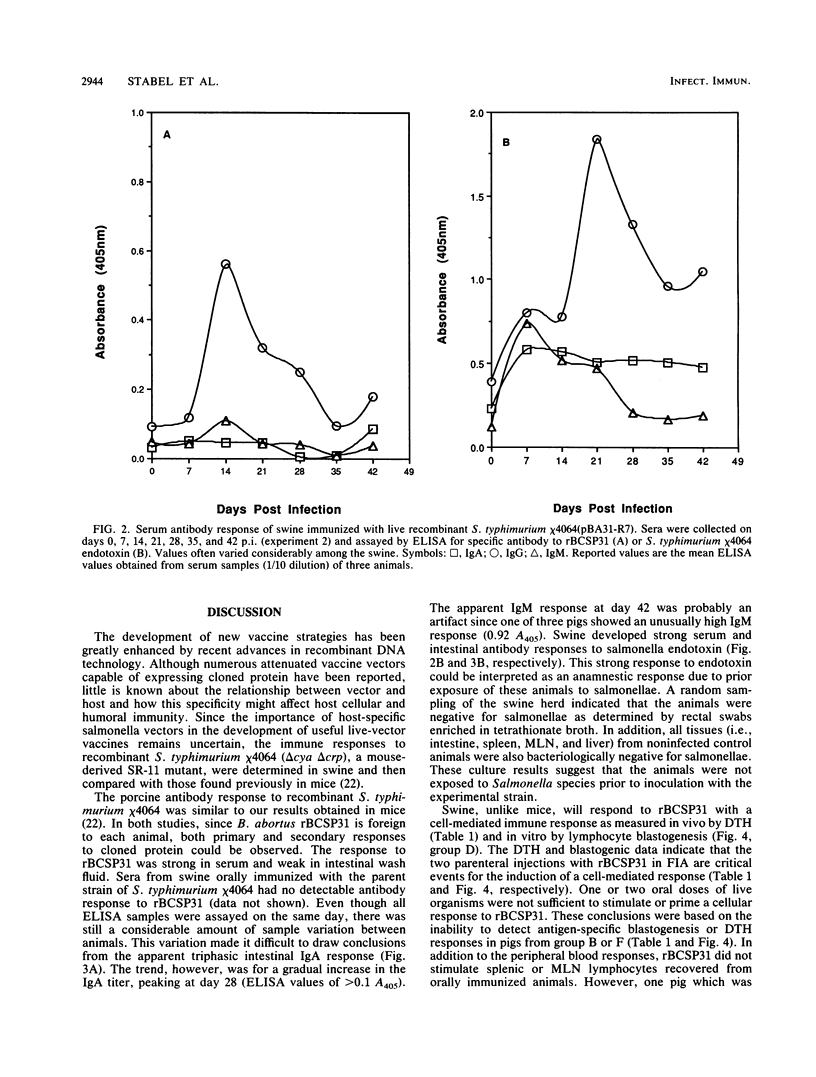
Salmonella typhimurium chi 4064, an attenuated delta cya delta crp mutant of S. typhimurium SR-11, was shown to be avirulent in swine. S. typhimurium chi 4064 was used as a carrier for plasmid pBA31-R7, which codes for the expression of a 31-kDa protein from Brucella abortus (BCSP31). Given orally, S. typhimurium chi 4064(pBA31-R7) colonized the intestine and mesenteric lymph nodes of 5- to 6-week-old crossbred swine. Orally immunized animals developed serum and intestinal antibody responses to the B. abortus 31-kDa protein and to salmonella endotoxin as measured by enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay. Similarly immunized swine did not develop delayed-type hypersensitivity following a subcutaneous injection of recombinant BCSP31. However, swine parenterally immunized with recombinant BCSP31 incorporated in Freund incomplete adjuvant did develop a delayed-type hypersensitivity response to the homologous antigen. The data indicated that oral presentation of antigen to swine in the context of recombinant S. typhimurium effective stimulated mucosal and systemic antibody-mediated immunity but failed to sensitize swine for either an antigen-specific delayed-type hypersensitivity or a blastogenic response to the cloned BCSP31.
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bricker B. J., Tabatabai L. B., Deyoe B. L., Mayfield J. E. Conservation of antigenicity in a 31-kDa Brucella protein. Vet Microbiol. 1988 Dec;18(3-4):313–325. doi: 10.1016/0378-1135(88)90096-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brown A., Hormaeche C. E., Demarco de Hormaeche R., Winther M., Dougan G., Maskell D. J., Stocker B. A. An attenuated aroA Salmonella typhimurium vaccine elicits humoral and cellular immunity to cloned beta-galactosidase in mice. J Infect Dis. 1987 Jan;155(1):86–92. doi: 10.1093/infdis/155.1.86. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carter P. B., Collins F. M. The route of enteric infection in normal mice. J Exp Med. 1974 May 1;139(5):1189–1203. doi: 10.1084/jem.139.5.1189. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clements J. D., Lyon F. L., Lowe K. L., Farrand A. L., el-Morshidy S. Oral immunization of mice with attenuated Salmonella enteritidis containing a recombinant plasmid which codes for production of the B subunit of heat-labile Escherichia coli enterotoxin. Infect Immun. 1986 Sep;53(3):685–692. doi: 10.1128/iai.53.3.685-692.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Curtiss R., 3rd, Kelly S. M. Salmonella typhimurium deletion mutants lacking adenylate cyclase and cyclic AMP receptor protein are avirulent and immunogenic. Infect Immun. 1987 Dec;55(12):3035–3043. doi: 10.1128/iai.55.12.3035-3043.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dougan G., Smith L., Heffron F. Live bacterial vaccines and their application as carriers for foreign antigens. Adv Vet Sci Comp Med. 1989;33:271–300. doi: 10.1016/b978-0-12-039233-9.50012-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Harrington R., Jr, Hulse D. C., Blackburn B. O. Salmonella isolated from swine suspected fo having hog cholera. Am J Vet Res. 1971 Aug;32(8):1297–1299. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- James S. P., Fiocchi C., Graeff A. S., Strober W. Phenotypic analysis of lamina propria lymphocytes. Predominance of helper-inducer and cytolytic T-cell phenotypes and deficiency of suppressor-inducer phenotypes in Crohn's disease and control patients. Gastroenterology. 1986 Dec;91(6):1483–1489. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- James S. P., Kwan W. C., Sneller M. C. T cells in inductive and effector compartments of the intestinal mucosal immune system of nonhuman primates differ in lymphokine mRNA expression, lymphokine utilization, and regulatory function. J Immunol. 1990 Feb 15;144(4):1251–1256. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Koster F. T., McGregor D. D., Mackaness G. B. The mediator of cellular immunity. II. Migration of immunologically committed lymphocytes into inflammatory exudates. J Exp Med. 1971 Feb 1;133(2):400–409. doi: 10.1084/jem.133.2.400. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maskell D. J., Sweeney K. J., O'Callaghan D., Hormaeche C. E., Liew F. Y., Dougan G. Salmonella typhimurium aroA mutants as carriers of the Escherichia coli heat-labile enterotoxin B subunit to the murine secretory and systemic immune systems. Microb Pathog. 1987 Mar;2(3):211–221. doi: 10.1016/0882-4010(87)90022-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mayfield J. E., Bricker B. J., Godfrey H., Crosby R. M., Knight D. J., Halling S. M., Balinsky D., Tabatabai L. B. The cloning, expression, and nucleotide sequence of a gene coding for an immunogenic Brucella abortus protein. Gene. 1988;63(1):1–9. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(88)90540-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Michalek S. M., Kiyono H., Wannemuehler M. J., Mosteller L. M., McGhee J. R. Lipopolysaccharide (LPS) regulation of the immune response: LPS influence on oral tolerance induction. J Immunol. 1982 May;128(5):1992–1998. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morehouse L. G. Salmonellosis in swine and its control. J Am Vet Med Assoc. 1972 Feb 15;160(4):593–601. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morrison D. C., Leive L. Fractions of lipopolysaccharide from Escherichia coli O111:B4 prepared by two extraction procedures. J Biol Chem. 1975 Apr 25;250(8):2911–2919. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Poirier T. P., Kehoe M. A., Beachey E. H. Protective immunity evoked by oral administration of attenuated aroA Salmonella typhimurium expressing cloned streptococcal M protein. J Exp Med. 1988 Jul 1;168(1):25–32. doi: 10.1084/jem.168.1.25. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reed W. M., Olander H. J., Thacker H. L. Studies on the pathogenesis of Salmonella typhimurium and Salmonella choleraesuis var kunzendorf infection in weanling pigs. Am J Vet Res. 1986 Jan;47(1):75–83. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schaible U. E., Kramer M. D., Justus C. W., Museteanu C., Simon M. M. Demonstration of antigen-specific T cells and histopathological alterations in mice experimentally inoculated with Borrelia burgdorferi. Infect Immun. 1989 Jan;57(1):41–47. doi: 10.1128/iai.57.1.41-47.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stabel T. J., Mayfield J. E., Tabatabai L. B., Wannemuehler M. J. Oral immunization of mice with attenuated Salmonella typhimurium containing a recombinant plasmid which codes for production of a 31-kilodalton protein of Brucella abortus. Infect Immun. 1990 Jul;58(7):2048–2055. doi: 10.1128/iai.58.7.2048-2055.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wood R. L., Pospischil A., Rose R. Distribution of persistent Salmonella typhimurium infection in internal organs of swine. Am J Vet Res. 1989 Jul;50(7):1015–1021. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zeitz M., Greene W. C., Peffer N. J., James S. P. Lymphocytes isolated from the intestinal lamina propria of normal nonhuman primates have increased expression of genes associated with T-cell activation. Gastroenterology. 1988 Mar;94(3):647–655. doi: 10.1016/0016-5085(88)90235-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zeitz M., Quinn T. C., Graeff A. S., James S. P. Mucosal T cells provide helper function but do not proliferate when stimulated by specific antigen in lymphogranuloma venereum proctitis in nonhuman primates. Gastroenterology. 1988 Feb;94(2):353–366. doi: 10.1016/0016-5085(88)90422-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



