Abstract
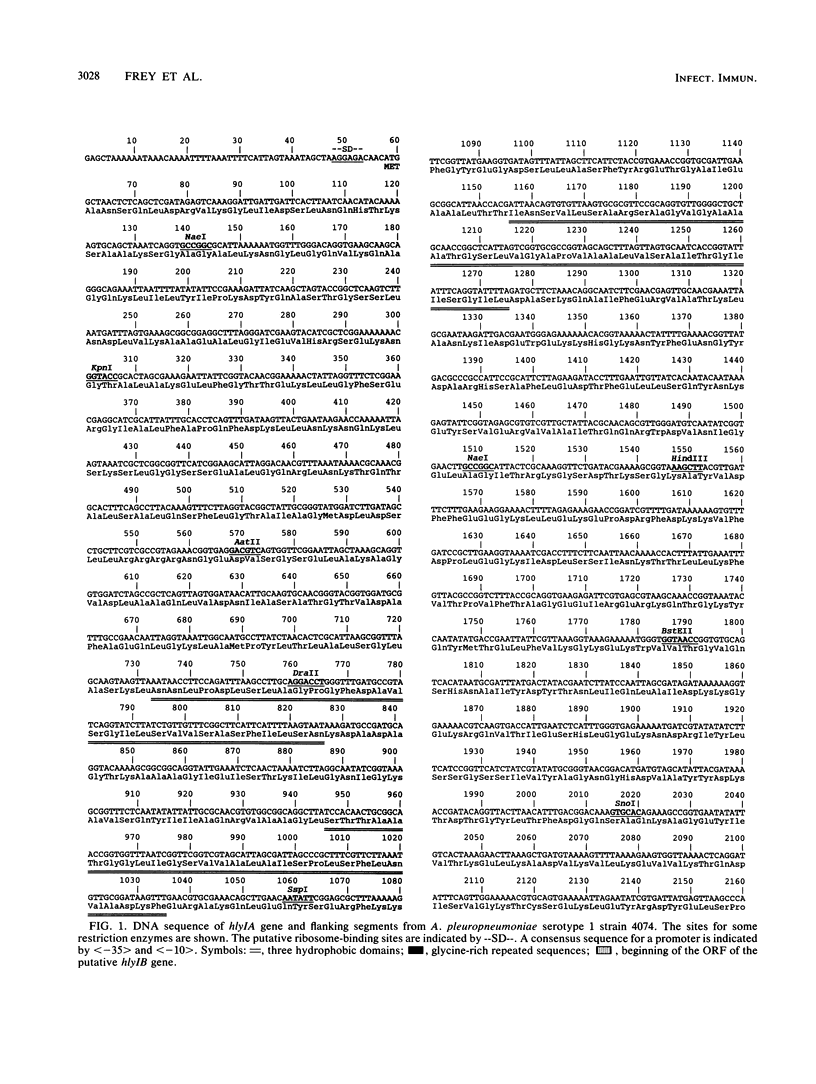
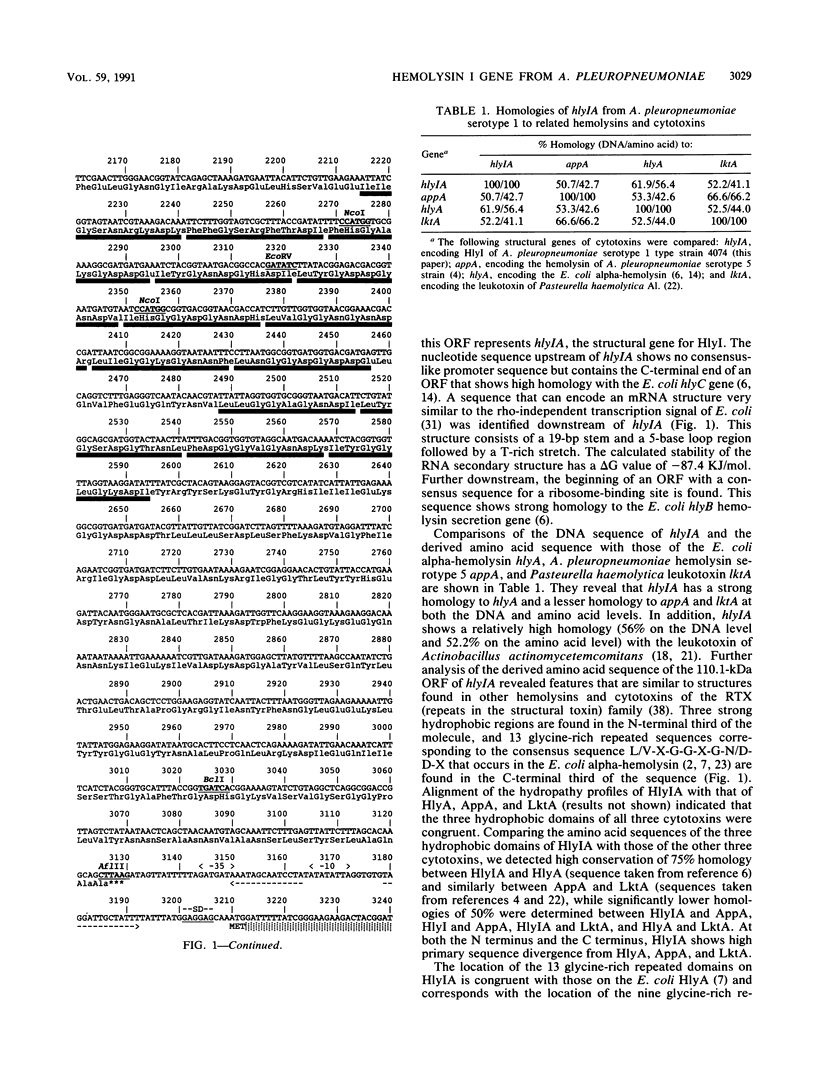
The DNA sequence of the gene encoding the structural protein of hemolysin I (HlyI) of Actinobacillus pleuropneumoniae serotype 1 strain 4074 was analyzed. The nucleotide sequence shows a 3,072-bp reading frame encoding a protein of 1,023 amino acids with a calculated molecular size of 110.1 kDa. This corresponds to the HlyI protein, which has an apparent molecular size on sodium dodecyl sulfate gels of 105 kDa. The structure of the protein derived from the DNA sequence shows three hydrophobic regions in the N-terminal part of the protein, 13 glycine-rich domains in the second half of the protein, and a hydrophilic C-terminal area, all of which are typical of the cytotoxins of the RTX (repeats in the structural toxin) toxin family. The derived amino acid sequence of HlyI shows 42% homology with the hemolysin of A. pleuropneumoniae serotype 5, 41% homology with the leukotoxin of Pasteurella haemolytica, and 56% homology with the Escherichia coli alpha-hemolysin. The 13 glycine-rich repeats and three hydrophobic areas of the HlyI sequence show more similarity to the E. coli alpha-hemolysin than to either the A. pleuropneumoniae serotype 5 hemolysin or the leukotoxin (while the last two are more similar to each other). Two types of RTX hemolysins therefore seem to be present in A. pleuropneumoniae, one (HlyI) resembling the alpha-hemolysin and a second more closely related to the leukotoxin. Ca(2+)-binding experiments using HlyI and recombinant A. pleuropneumoniae prohemolysin (HlyIA) that was produced in E. coli shows that HlyI binds 45Ca2+, probably because of the 13 glycine-rich repeated domains. Activation of the prohemolysin is not required for Ca2+ binding.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Boehm D. F., Welch R. A., Snyder I. S. Calcium is required for binding of Escherichia coli hemolysin (HlyA) to erythrocyte membranes. Infect Immun. 1990 Jun;58(6):1951–1958. doi: 10.1128/iai.58.6.1951-1958.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Boehm D. F., Welch R. A., Snyder I. S. Domains of Escherichia coli hemolysin (HlyA) involved in binding of calcium and erythrocyte membranes. Infect Immun. 1990 Jun;58(6):1959–1964. doi: 10.1128/iai.58.6.1959-1964.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chang Y. F., Young R., Struck D. K. Cloning and characterization of a hemolysin gene from Actinobacillus (Haemophilus) pleuropneumoniae. DNA. 1989 Nov;8(9):635–647. doi: 10.1089/dna.1.1989.8.635. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Devenish J., Rosendal S., Bossé J. T., Wilkie B. N., Johnson R. Prevalence of seroreactors to the 104-kilodalton hemolysin of Actinobacillus pleuropneumoniae in swine herds. J Clin Microbiol. 1990 Apr;28(4):789–791. doi: 10.1128/jcm.28.4.789-791.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Felmlee T., Pellett S., Welch R. A. Nucleotide sequence of an Escherichia coli chromosomal hemolysin. J Bacteriol. 1985 Jul;163(1):94–105. doi: 10.1128/jb.163.1.94-105.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Felmlee T., Welch R. A. Alterations of amino acid repeats in the Escherichia coli hemolysin affect cytolytic activity and secretion. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Jul;85(14):5269–5273. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.14.5269. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Frey J., Nicolet J. Hemolysin patterns of Actinobacillus pleuropneumoniae. J Clin Microbiol. 1990 Feb;28(2):232–236. doi: 10.1128/jcm.28.2.232-236.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Frey J., Nicolet J. Immunological properties of Actinobacillus pleuropneumoniae hemolysin I. Vet Microbiol. 1991 Jun;28(1):61–73. doi: 10.1016/0378-1135(91)90099-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Frey J., Nicolet J. Regulation of hemolysin expression in Actinobacillus pleuropneumoniae serotype 1 by Ca2+. Infect Immun. 1988 Oct;56(10):2570–2575. doi: 10.1128/iai.56.10.2570-2575.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gray L., Mackman N., Nicaud J. M., Holland I. B. The carboxy-terminal region of haemolysin 2001 is required for secretion of the toxin from Escherichia coli. Mol Gen Genet. 1986 Oct;205(1):127–133. doi: 10.1007/BF02428042. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gygi D., Nicolet J., Frey J., Cross M., Koronakis V., Hughes C. Isolation of the Actinobacillus pleuropneumoniae haemolysin gene and the activation and secretion of the prohaemolysin by the HlyC, HlyB and HlyD proteins of Escherichia coli. Mol Microbiol. 1990 Jan;4(1):123–128. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2958.1990.tb02021.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Koronakis V., Cross M., Hughes C. Expression of the E.coli hemolysin secretion gene hlyB involves transcript anti-termination within the hly operon. Nucleic Acids Res. 1988 Jun 10;16(11):4789–4800. doi: 10.1093/nar/16.11.4789. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Koronakis V., Cross M., Hughes C. Transcription antitermination in an Escherichia coli haemolysin operon is directed progressively by cis-acting DNA sequences upstream of the promoter region. Mol Microbiol. 1989 Oct;3(10):1397–1404. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2958.1989.tb00122.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Koronakis V., Koronakis E., Hughes C. Isolation and analysis of the C-terminal signal directing export of Escherichia coli hemolysin protein across both bacterial membranes. EMBO J. 1989 Feb;8(2):595–605. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1989.tb03414.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kraig E., Dailey T., Kolodrubetz D. Nucleotide sequence of the leukotoxin gene from Actinobacillus actinomycetemcomitans: homology to the alpha-hemolysin/leukotoxin gene family. Infect Immun. 1990 Apr;58(4):920–929. doi: 10.1128/iai.58.4.920-929.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kume K., Nakai T., Sawata A. Interaction between heat-stable hemolytic substance from Haemophilus pleuropneumoniae and porcine pulmonary macrophages in vitro. Infect Immun. 1986 Feb;51(2):563–570. doi: 10.1128/iai.51.2.563-570.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laemmli U. K. Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature. 1970 Aug 15;227(5259):680–685. doi: 10.1038/227680a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lo R. Y., Strathdee C. A., Shewen P. E. Nucleotide sequence of the leukotoxin genes of Pasteurella haemolytica A1. Infect Immun. 1987 Sep;55(9):1987–1996. doi: 10.1128/iai.55.9.1987-1996.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ludwig A., Jarchau T., Benz R., Goebel W. The repeat domain of Escherichia coli haemolysin (HlyA) is responsible for its Ca2+-dependent binding to erythrocytes. Mol Gen Genet. 1988 Nov;214(3):553–561. doi: 10.1007/BF00330494. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ludwig A., Vogel M., Goebel W. Mutations affecting activity and transport of haemolysin in Escherichia coli. Mol Gen Genet. 1987 Feb;206(2):238–245. doi: 10.1007/BF00333579. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ma J. N., Inzana T. J. Indirect enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay for detection of antibody to a 110,000-molecular-weight hemolysin of Actinobacillus pleuropneumoniae. J Clin Microbiol. 1990 Jun;28(6):1356–1361. doi: 10.1128/jcm.28.6.1356-1361.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mackman N., Nicaud J. M., Gray L., Holland I. B. Genetical and functional organisation of the Escherichia coli haemolysin determinant 2001. Mol Gen Genet. 1985;201(2):282–288. doi: 10.1007/BF00425672. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Myers E. W., Miller W. Optimal alignments in linear space. Comput Appl Biosci. 1988 Mar;4(1):11–17. doi: 10.1093/bioinformatics/4.1.11. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nicaud J. M., Mackman N., Gray L., Holland I. B. The C-terminal, 23 kDa peptide of E. coli haemolysin 2001 contains all the information necessary for its secretion by the haemolysin (Hly) export machinery. FEBS Lett. 1986 Aug 18;204(2):331–335. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(86)80838-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Prentki P., Binda A., Epstein A. Plasmid vectors for selecting IS1-promoted deletions in cloned DNA: sequence analysis of the omega interposon. Gene. 1991 Jul 15;103(1):17–23. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(91)90385-o. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rosenberg M., Court D. Regulatory sequences involved in the promotion and termination of RNA transcription. Annu Rev Genet. 1979;13:319–353. doi: 10.1146/annurev.ge.13.120179.001535. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rosendal S., Devenish J., MacInnes J. I., Lumsden J. H., Watson S., Xun H. Evaluation of heat-sensitive, neutrophil-toxic, and hemolytic activity of Haemophilus (Actinobacillus) pleuropneumoniae. Am J Vet Res. 1988 Jul;49(7):1053–1058. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SHOPE R. E. PORCINE CONTAGIOUS PLEUROPNEUMONIA. I. EXPERIMENTAL TRANSMISSION, ETIOLOGY, AND PATHOLOGY. J Exp Med. 1964 Mar 1;119:357–368. doi: 10.1084/jem.119.3.357. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shine J., Dalgarno L. The 3'-terminal sequence of Escherichia coli 16S ribosomal RNA: complementarity to nonsense triplets and ribosome binding sites. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1974 Apr;71(4):1342–1346. doi: 10.1073/pnas.71.4.1342. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Strathdee C. A., Lo R. Y. Cloning, nucleotide sequence, and characterization of genes encoding the secretion function of the Pasteurella haemolytica leukotoxin determinant. J Bacteriol. 1989 Feb;171(2):916–928. doi: 10.1128/jb.171.2.916-928.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Strathdee C. A., Lo R. Y. Extensive homology between the leukotoxin of Pasteurella haemolytica A1 and the alpha-hemolysin of Escherichia coli. Infect Immun. 1987 Dec;55(12):3233–3236. doi: 10.1128/iai.55.12.3233-3236.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Strathdee C. A., Lo R. Y. Regulation of expression of the Pasteurella haemolytica leukotoxin determinant. J Bacteriol. 1989 Nov;171(11):5955–5962. doi: 10.1128/jb.171.11.5955-5962.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tinoco I., Jr, Borer P. N., Dengler B., Levin M. D., Uhlenbeck O. C., Crothers D. M., Bralla J. Improved estimation of secondary structure in ribonucleic acids. Nat New Biol. 1973 Nov 14;246(150):40–41. doi: 10.1038/newbio246040a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wagner W., Vogel M., Goebel W. Transport of hemolysin across the outer membrane of Escherichia coli requires two functions. J Bacteriol. 1983 Apr;154(1):200–210. doi: 10.1128/jb.154.1.200-210.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zhang H., Scholl R., Browse J., Somerville C. Double stranded DNA sequencing as a choice for DNA sequencing. Nucleic Acids Res. 1988 Feb 11;16(3):1220–1220. doi: 10.1093/nar/16.3.1220. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]