Abstract
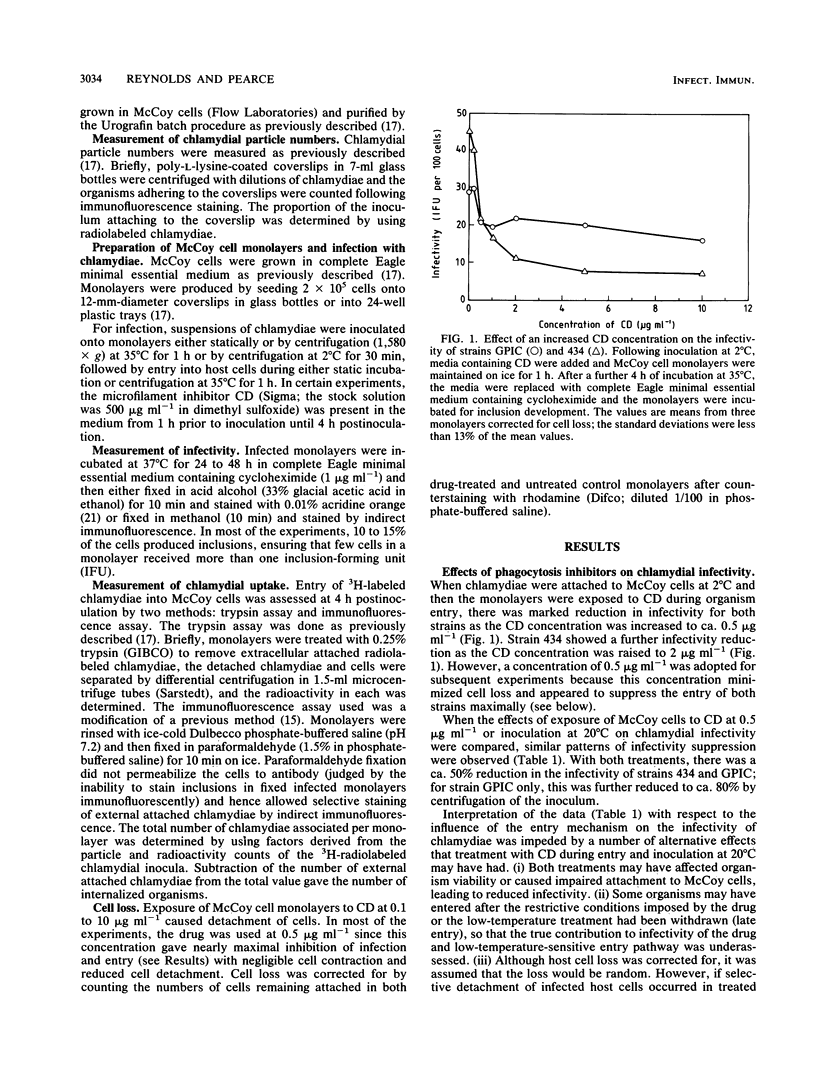
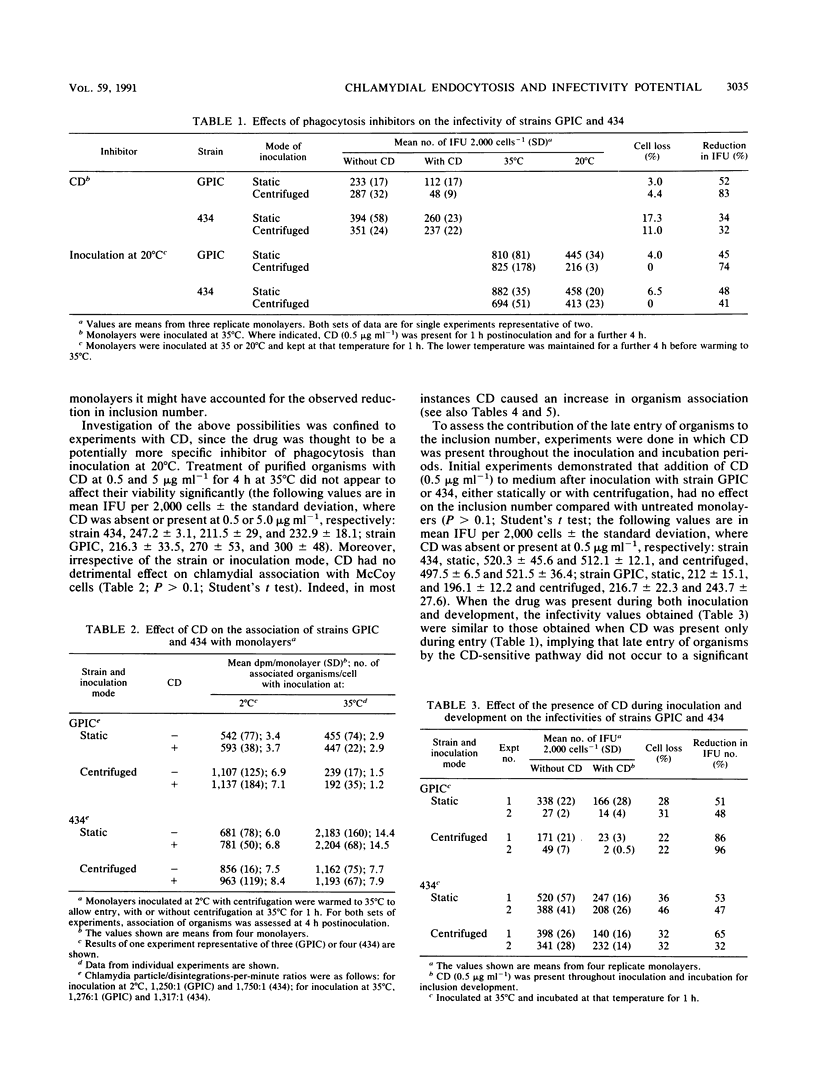
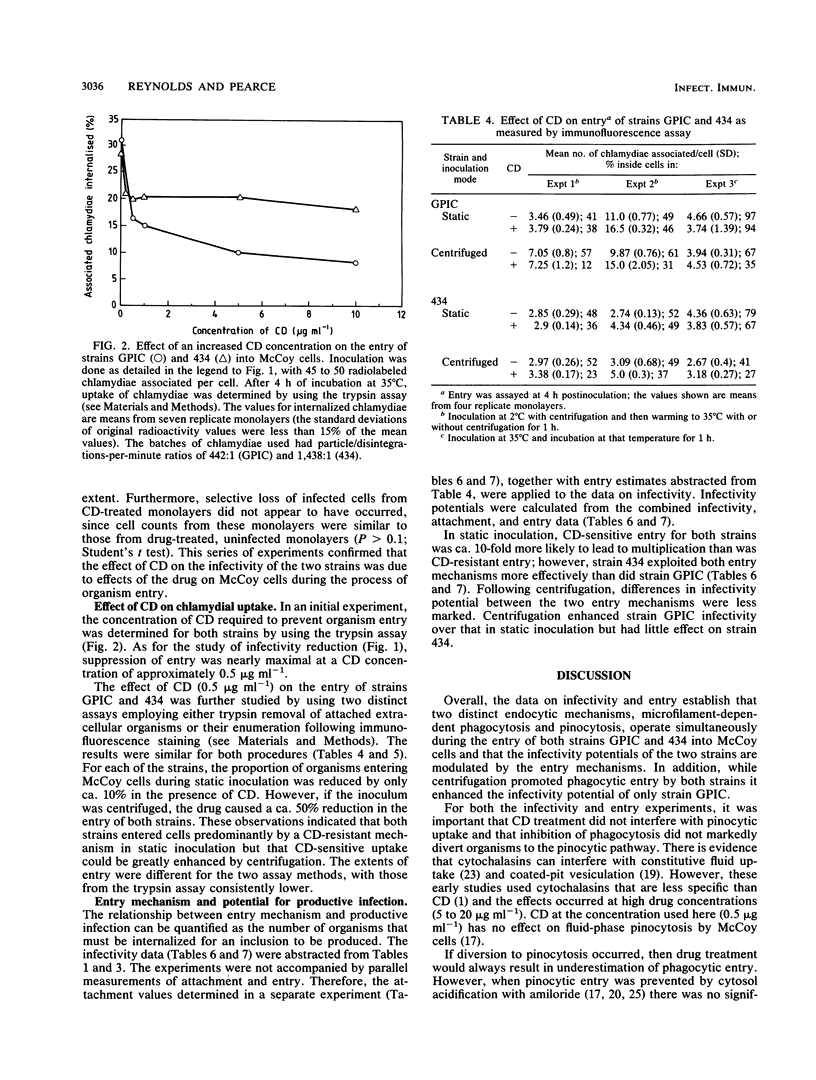
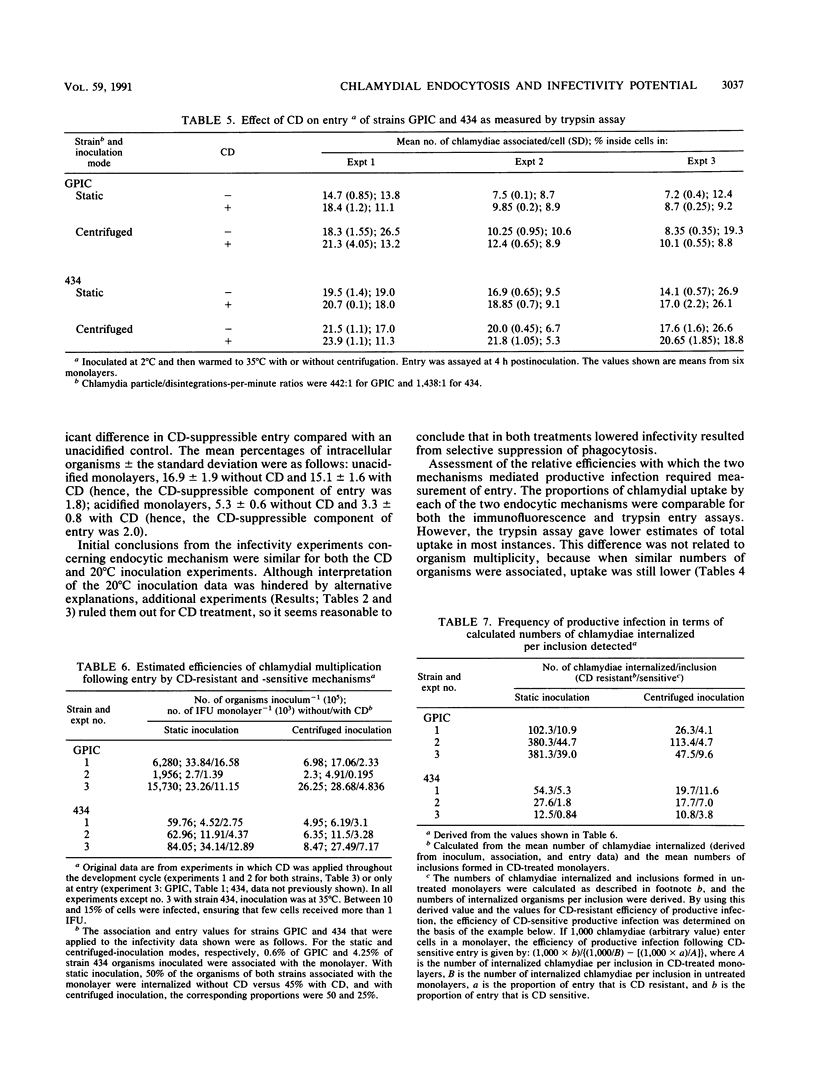
The microfilament-disrupting drug cytochalasin D and, initially, inoculation at 20 degrees C were used to differentiate between phagocytosis (sensitive to both treatments) and pinocytosis (resistant to both treatments) to assess whether chlamydial uptake into McCoy cells occurred by one or both mechanisms and whether each could contribute to productive infection. Both treatments suppressed the infectivity of Chlamydia trachomatis L2/434/Bu and C. psittaci GPIC (the guinea pig inclusion conjunctivitis strain) following static inoculation by only 50%, indicating that there was simultaneous operation of both phagocytosis and pinocytosis during uptake that led to productive infection. Measurement of the entry of organisms by two separate assays established that both strains predominantly used a cytochalasin D-resistant (pinocytic) mechanism, implying that phagocytic uptake was coupled to a higher frequency of productive infection. Integration of the data on infectivity and entry allowed the potential for an organism to infect a host cell to be quantified. This synthesis revealed that for both strains the infectivity potential following phagocytic entry was ca. 10-fold greater than that following pinocytic entry. However, both entry mechanisms were exploited more efficiently by strain L2/434/Bu than by strain GPIC (unless the latter was inoculated with centrifugation), indicating that intrinsic strain properties are more important for infectivity potential than the endocytic mechanism utilized.
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Cooper J. A. Effects of cytochalasin and phalloidin on actin. J Cell Biol. 1987 Oct;105(4):1473–1478. doi: 10.1083/jcb.105.4.1473. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Elsinghorst E. A., Baron L. S., Kopecko D. J. Penetration of human intestinal epithelial cells by Salmonella: molecular cloning and expression of Salmonella typhi invasion determinants in Escherichia coli. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 Jul;86(13):5173–5177. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.13.5173. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Finlay B. B., Falkow S. Salmonella as an intracellular parasite. Mol Microbiol. 1989 Dec;3(12):1833–1841. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2958.1989.tb00170.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Friis R. R. Interaction of L cells and Chlamydia psittaci: entry of the parasite and host responses to its development. J Bacteriol. 1972 May;110(2):706–721. doi: 10.1128/jb.110.2.706-721.1972. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Furcht L. T., Wendelschafer-Crabb G. Trypsin-induced coordinate alterations in cell shape, cytoskeleton, and intrinsic membrane structure of contact-inhibited cells. Exp Cell Res. 1978 Jun;114(1):1–14. doi: 10.1016/0014-4827(78)90029-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hatch T. P., Miceli M., Sublett J. E. Synthesis of disulfide-bonded outer membrane proteins during the developmental cycle of Chlamydia psittaci and Chlamydia trachomatis. J Bacteriol. 1986 Feb;165(2):379–385. doi: 10.1128/jb.165.2.379-385.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hodinka R. L., Davis C. H., Choong J., Wyrick P. B. Ultrastructural study of endocytosis of Chlamydia trachomatis by McCoy cells. Infect Immun. 1988 Jun;56(6):1456–1463. doi: 10.1128/iai.56.6.1456-1463.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hodinka R. L., Wyrick P. B. Ultrastructural study of mode of entry of Chlamydia psittaci into L-929 cells. Infect Immun. 1986 Dec;54(3):855–863. doi: 10.1128/iai.54.3.855-863.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Isberg R. R. Mammalian cell adhesion functions and cellular penetration of enteropathogenic Yersinia species. Mol Microbiol. 1989 Oct;3(10):1449–1453. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2958.1989.tb00128.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lawn A. M., Blyth W. A., Taverne J. Interactions of TRIC agents with macrophages and BHK-21 cells observed by electron microscopy. J Hyg (Lond) 1973 Sep;71(3):515–528. doi: 10.1017/s0022172400046507. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mellman I., Fuchs R., Helenius A. Acidification of the endocytic and exocytic pathways. Annu Rev Biochem. 1986;55:663–700. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.55.070186.003311. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Monnickendam M. A., Pearce J. H. Immune responses and chlamydial infections. Br Med Bull. 1983 Apr;39(2):187–193. doi: 10.1093/oxfordjournals.bmb.a071814. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pearce J. H. Early events in chlamydial infection. Ann Inst Pasteur Microbiol. 1986 May-Jun;137A(3):325–332. doi: 10.1016/s0769-2609(86)80043-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Prain C. J., Pearce J. H. Ultrastructural studies on the intracellular fate of Chlamydia psittaci (strain guinea pig inclusion conjunctivitis) and Chlamydia trachomatis (strain lymphogranuloma venereum 434): modulation of intracellular events and relationship with endocytic mechanism. J Gen Microbiol. 1989 Jul;135(7):2107–2123. doi: 10.1099/00221287-135-7-2107. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reynolds D. J., Pearce J. H. Characterization of the cytochalasin D-resistant (pinocytic) mechanisms of endocytosis utilized by chlamydiae. Infect Immun. 1990 Oct;58(10):3208–3216. doi: 10.1128/iai.58.10.3208-3216.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ripa K. T., Mårdh P. A. Cultivation of Chlamydia trachomatis in cycloheximide-treated mccoy cells. J Clin Microbiol. 1977 Oct;6(4):328–331. doi: 10.1128/jcm.6.4.328-331.1977. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- STARR T. J., POLLARD M., TANAMI Y., MOORE R. W. Cytochemical studies with psittacosis virus by fluorescence microscopy. Tex Rep Biol Med. 1960;18:501–514. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Salisbury J. L., Condeelis J. S., Satir P. Role of coated vesicles, microfilaments, and calmodulin in receptor-mediated endocytosis by cultured B lymphoblastoid cells. J Cell Biol. 1980 Oct;87(1):132–141. doi: 10.1083/jcb.87.1.132. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sandvig K., Olsnes S., Petersen O. W., van Deurs B. Acidification of the cytosol inhibits endocytosis from coated pits. J Cell Biol. 1987 Aug;105(2):679–689. doi: 10.1083/jcb.105.2.679. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ukkonen P., Lewis V., Marsh M., Helenius A., Mellman I. Transport of macrophage Fc receptors and Fc receptor-bound ligands to lysosomes. J Exp Med. 1986 Apr 1;163(4):952–971. doi: 10.1084/jem.163.4.952. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wagner R., Rosenberg M., Estensen R. Endocytosis in Chang liver cells. Quantitation by sucrose- 3 H uptake and inhibition by cytochalasin B. J Cell Biol. 1971 Sep;50(3):804–817. doi: 10.1083/jcb.50.3.804. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ward M. E., Murray A. Control mechanisms governing the infectivity of Chlamydia trachomatis for HeLa cells: mechanisms of endocytosis. J Gen Microbiol. 1984 Jul;130(7):1765–1780. doi: 10.1099/00221287-130-7-1765. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- West M. A., Bretscher M. S., Watts C. Distinct endocytotic pathways in epidermal growth factor-stimulated human carcinoma A431 cells. J Cell Biol. 1989 Dec;109(6 Pt 1):2731–2739. doi: 10.1083/jcb.109.6.2731. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wyrick P. B., Choong J., Davis C. H., Knight S. T., Royal M. O., Maslow A. S., Bagnell C. R. Entry of genital Chlamydia trachomatis into polarized human epithelial cells. Infect Immun. 1989 Aug;57(8):2378–2389. doi: 10.1128/iai.57.8.2378-2389.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zeichner S. L. Isolation and characterization of macrophage phagosomes containing infectious and heat-inactivated Chlamydia psittaci: two phagosomes with different intracellular behaviors. Infect Immun. 1983 Jun;40(3):956–966. doi: 10.1128/iai.40.3.956-966.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



