Abstract
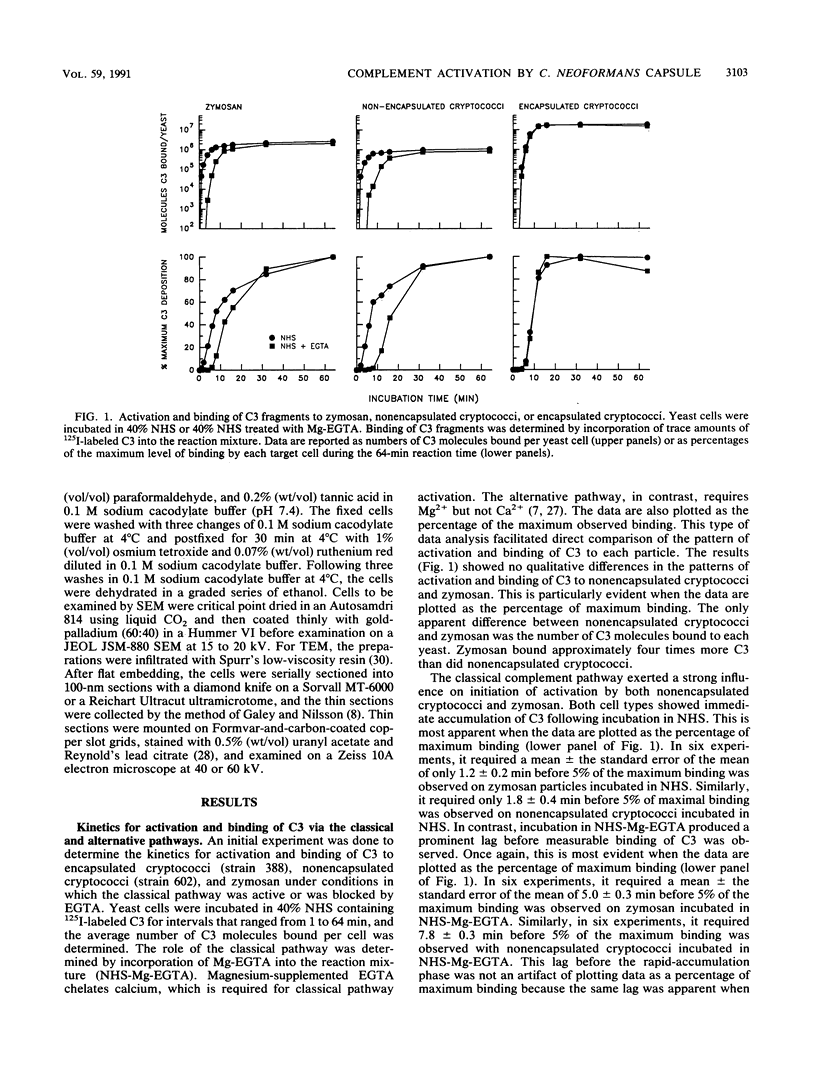
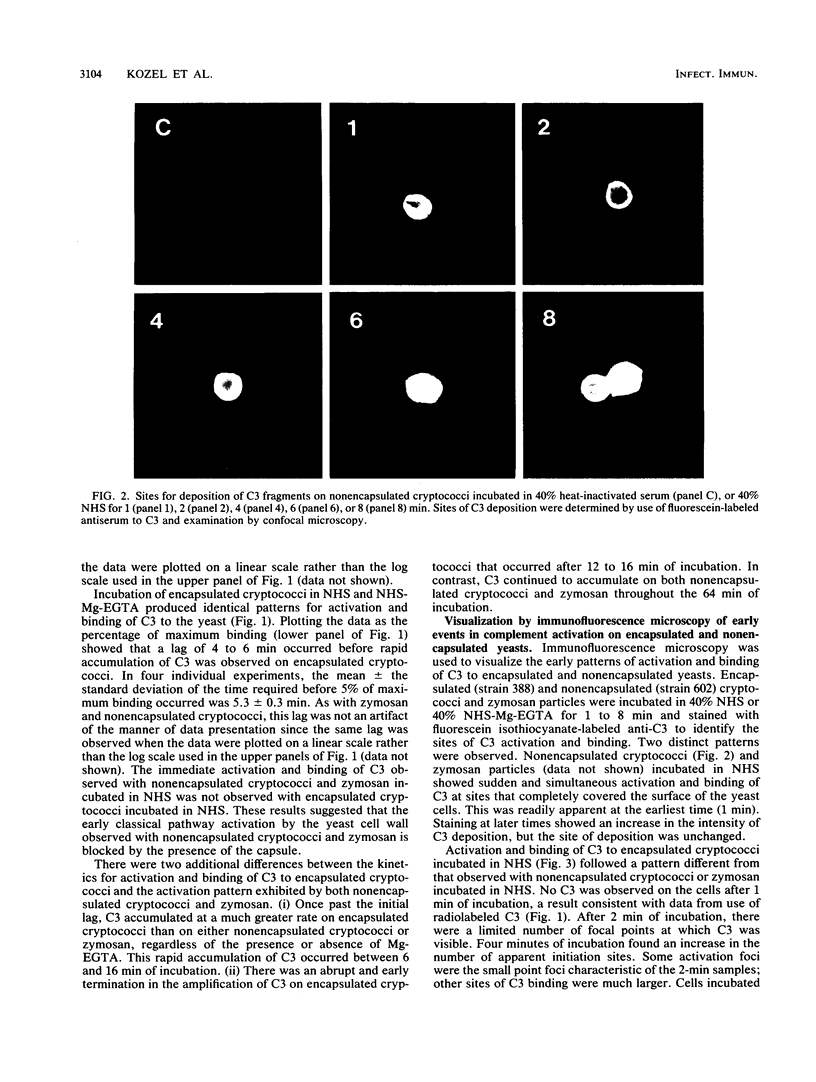
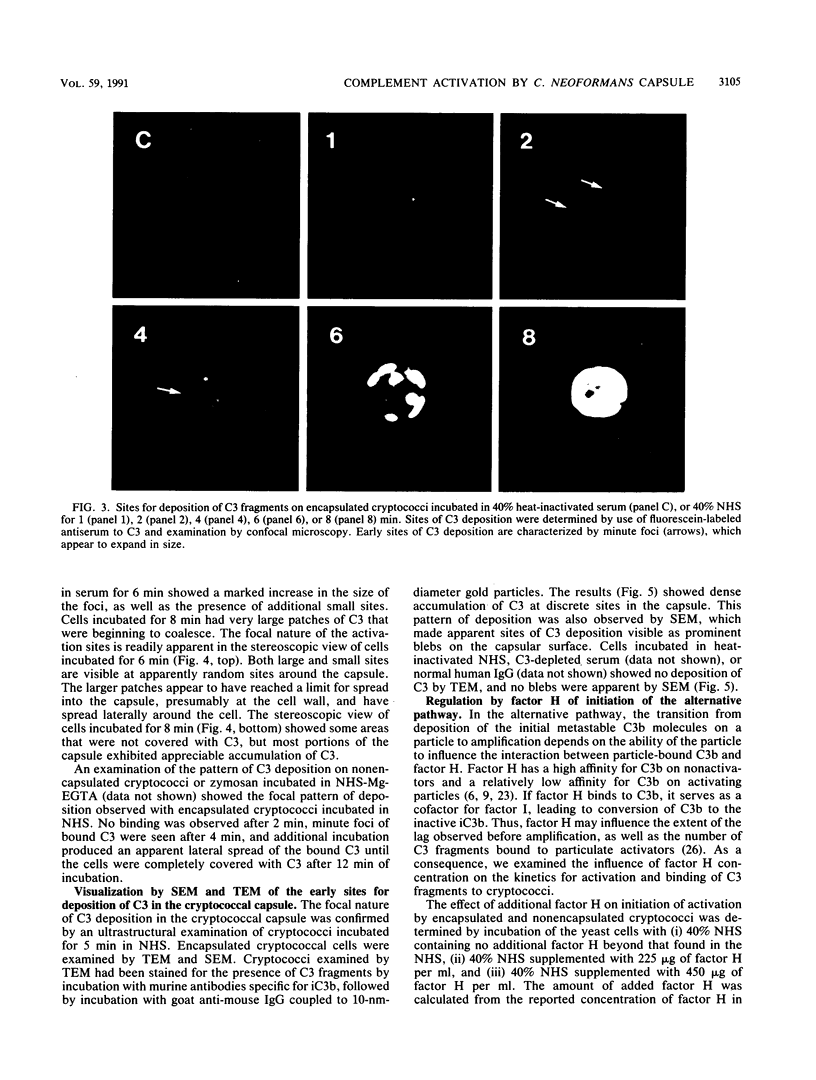
The capsule of Cryptococcus neoformans is a powerful activator of the alternative complement pathway. This study examined the manner in which the cryptococcal capsule influences initiation of and early events in complement activation by C. neoformans. These studies examined the effects of the classical and alternative pathways on the kinetics and early sites for deposition of C3 fragments on encapsulated cryptococci, nonencapsulated cryptococci, and zymosan. The results showed that nonencapsulated cryptococci and zymosan are qualitatively and quantitatively similar in the manner in which they initiate complement activation. Both utilize the classical and alternative pathways. Initiation via the classical pathway occurs suddenly and simultaneously at sites distributed over the entire cell surface. Initiation of the alternative pathway by zymosan and nonencapsulated cryptococci is characterized by a lag of 6 to 8 min before appreciable amounts of C3 accumulate on the cells. Alternative pathway initiation by zymosan and nonencapsulated cryptococci occurs at a limited number of focal initiation sites that expand with alternative pathway amplification to cover the cell surface. Presence of the cryptococcal capsule blocks classical pathway initiation, which would normally occur at the cryptococcal cell wall, and produces an initiation that is dependent solely on the alternative pathway. Initiation of the alternative pathway by the cryptococcal capsule is characterized by a lag in C3 accumulation and the appearance of a limited number of focal initiation sites which resemble those observed when the alternative pathway is activated by zymosan and nonencapsulated cryptococci.
Full text
PDF

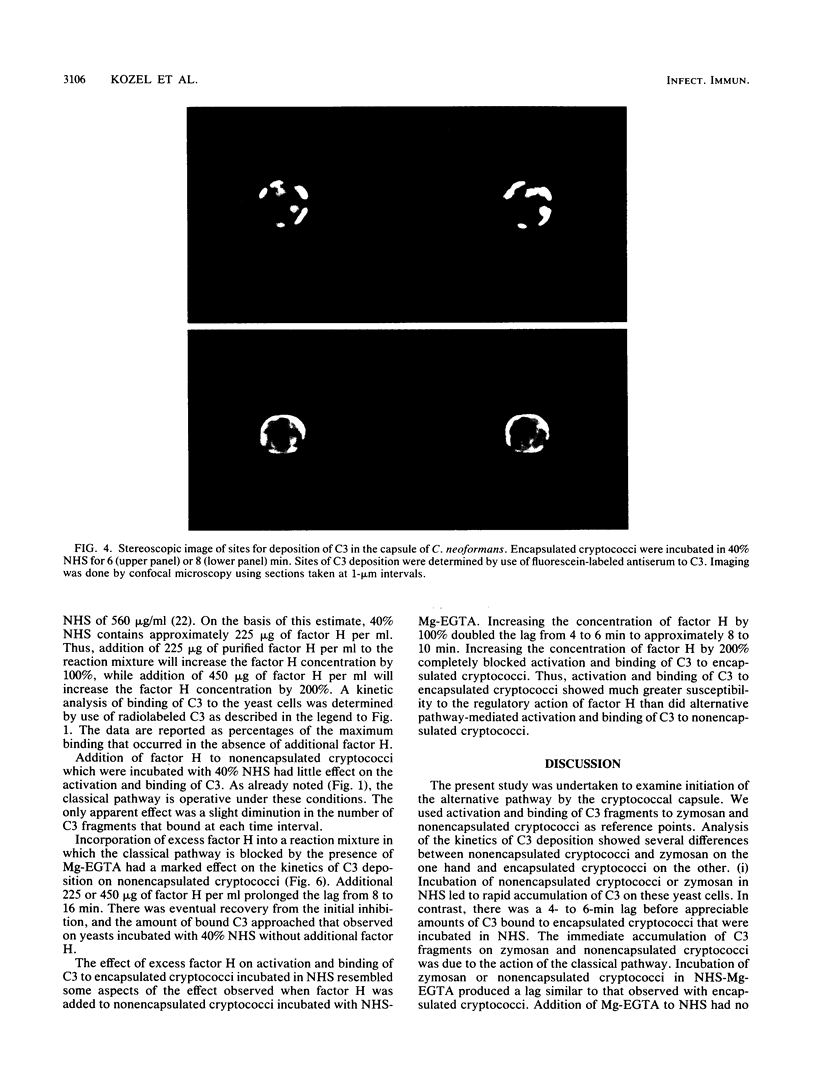
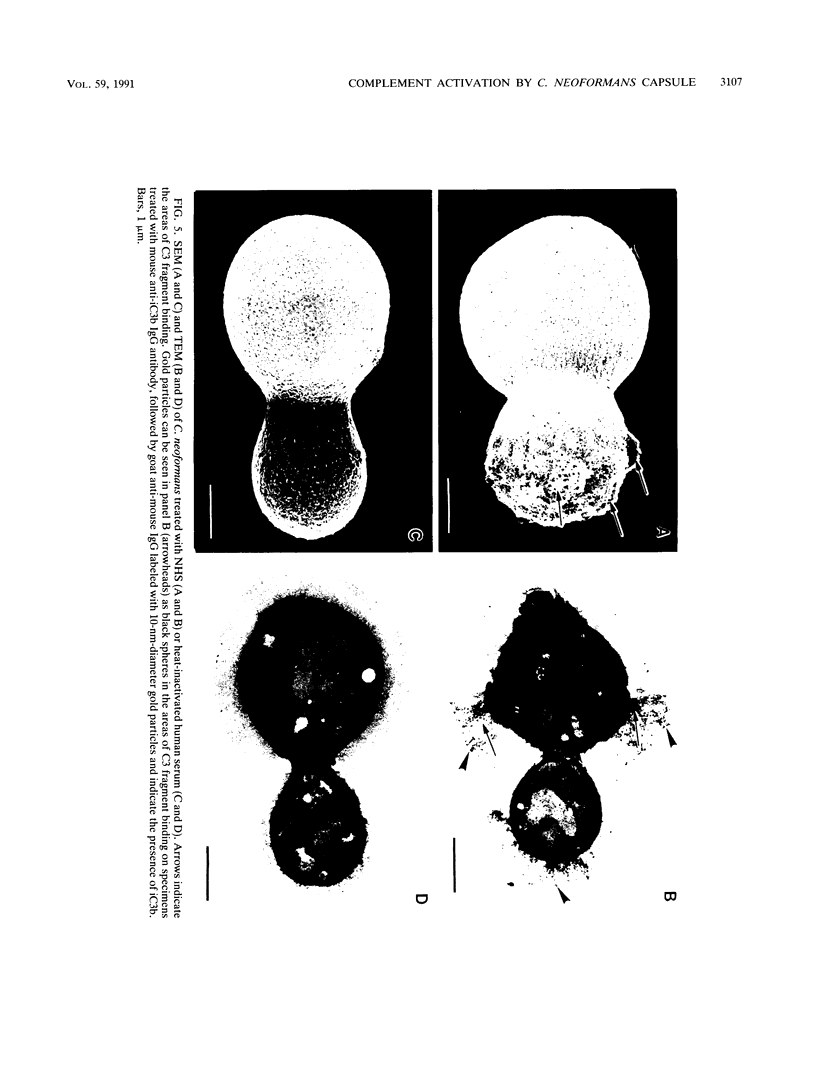
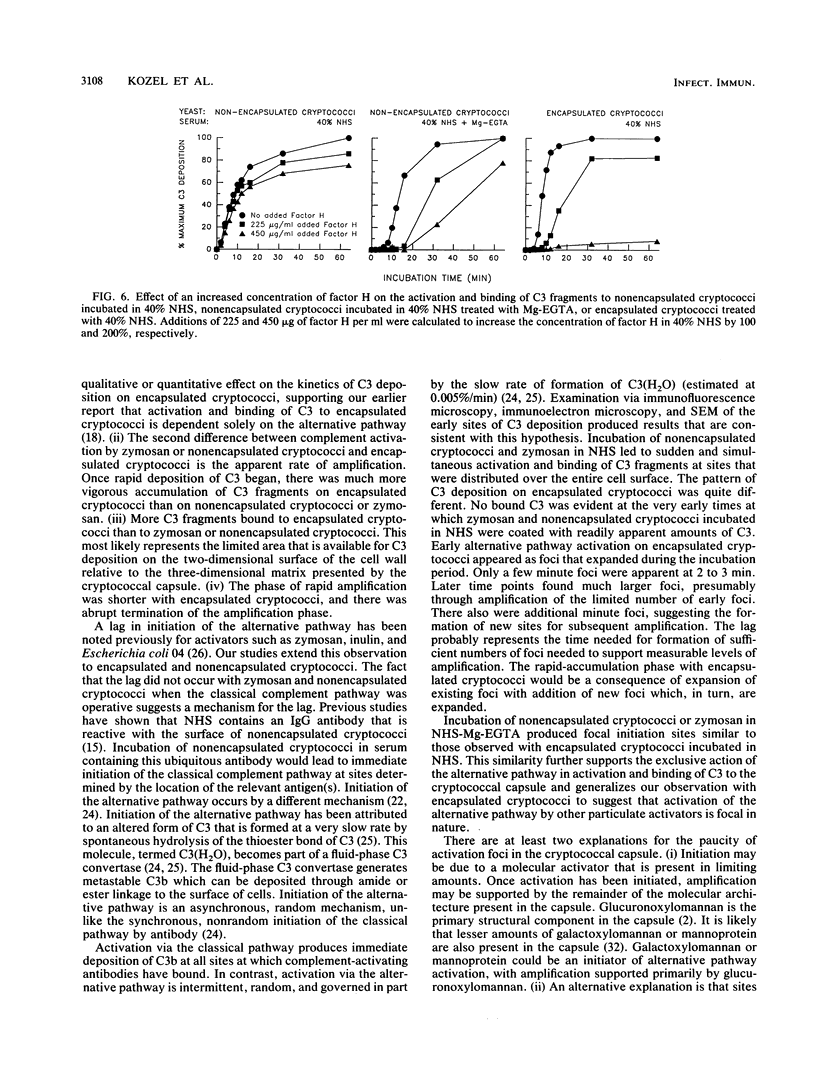


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bhattacharjee A. K., Bennett J. E., Glaudemans C. P. Capsular polysaccharides of Cryptococcus neoformans. Rev Infect Dis. 1984 Sep-Oct;6(5):619–624. doi: 10.1093/clinids/6.5.619. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cherniak R., Reiss E., Slodki M. E., Plattner R. D., Blumer S. O. Structure and antigenic activity of the capsular polysaccharide of Cryptococcus neoformans serotype A. Mol Immunol. 1980 Aug;17(8):1025–1032. doi: 10.1016/0161-5890(80)90096-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Czop J. K., Austen K. F. Properties of glycans that activate the human alternative complement pathway and interact with the human monocyte beta-glucan receptor. J Immunol. 1985 Nov;135(5):3388–3393. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Czop J. K. Phagocytosis of particulate activators of the alternative complement pathway: effects of fibronectin. Adv Immunol. 1986;38:361–398. doi: 10.1016/s0065-2776(08)60011-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fearon D. T., Austen K. F. Activation of the alternative complement pathway due to resistance of zymosan-bound amplification convertase to endogenous regulatory mechanisms. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Apr;74(4):1683–1687. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.4.1683. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fine D. P., Marney S. R., Jr, Colley D. G., Sergent J. S., Des Prez R. M. C3 shunt activation in human serum chelated with EGTA. J Immunol. 1972 Oct;109(4):807–809. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Galey F. R., Nilsson S. E. A new method for transferring sections from the liquid surface of the trough through staining solutions to the supporting film of a grid. J Ultrastruct Res. 1966 Feb;14(3):405–410. doi: 10.1016/s0022-5320(66)80057-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Horstmann R. D., Pangburn M. K., Müller-Eberhard H. J. Species specificity of recognition by the alternative pathway of complement. J Immunol. 1985 Feb;134(2):1101–1104. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hostetter M. K. Serotypic variations among virulent pneumococci in deposition and degradation of covalently bound C3b: implications for phagocytosis and antibody production. J Infect Dis. 1986 Apr;153(4):682–693. doi: 10.1093/infdis/153.4.682. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- James P. G., Cherniak R., Jones R. G., Stortz C. A., Reiss E. Cell-wall glucans of Cryptococcus neoformans Cap 67. Carbohydr Res. 1990 Apr 2;198(1):23–38. doi: 10.1016/0008-6215(90)84273-w. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kozel T. R., Cazin J. Nonencapsulated Variant of Cryptococcus neoformans I. Virulence Studies and Characterization of Soluble Polysaccharide. Infect Immun. 1971 Feb;3(2):287–294. doi: 10.1128/iai.3.2.287-294.1971. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kozel T. R., Highison B., Stratton C. J. Localization on encapsulated Cryptococcus neoformans of serum components opsonic for phagocytosis by macrophages and neutrophils. Infect Immun. 1984 Feb;43(2):574–579. doi: 10.1128/iai.43.2.574-579.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kozel T. R., McGaw T. G. Opsonization of Cryptococcus neoformans by human immunoglobulin G: role of immunoglobulin G in phagocytosis by macrophages. Infect Immun. 1979 Jul;25(1):255–261. doi: 10.1128/iai.25.1.255-261.1979. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kozel T. R., Pfrommer G. S. Activation of the complement system by Cryptococcus neoformans leads to binding of iC3b to the yeast. Infect Immun. 1986 Apr;52(1):1–5. doi: 10.1128/iai.52.1.1-5.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kozel T. R., Pfrommer G. S., Guerlain A. S., Highison B. A., Highison G. J. Strain variation in phagocytosis of Cryptococcus neoformans: dissociation of susceptibility to phagocytosis from activation and binding of opsonic fragments of C3. Infect Immun. 1988 Nov;56(11):2794–2800. doi: 10.1128/iai.56.11.2794-2800.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kozel T. R., Wilson M. A., Pfrommer G. S., Schlageter A. M. Activation and binding of opsonic fragments of C3 on encapsulated Cryptococcus neoformans by using an alternative complement pathway reconstituted from six isolated proteins. Infect Immun. 1989 Jul;57(7):1922–1927. doi: 10.1128/iai.57.7.1922-1927.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Law S. K., Levine R. P. Interaction between the third complement protein and cell surface macromolecules. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Jul;74(7):2701–2705. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.7.2701. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Law S. K., Lichtenberg N. A., Levine R. P. Evidence for an ester linkage between the labile binding site of C3b and receptive surfaces. J Immunol. 1979 Sep;123(3):1388–1394. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laxalt K. A., Kozel T. R. Chemotaxigenesis and activation of the alternative complement pathway by encapsulated and non-encapsulated Cryptococcus neoformans. Infect Immun. 1979 Nov;26(2):435–440. doi: 10.1128/iai.26.2.435-440.1979. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pangburn M. K., Müller-Eberhard H. J. Complement C3 convertase: cell surface restriction of beta1H control and generation of restriction on neuraminidase-treated cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1978 May;75(5):2416–2420. doi: 10.1073/pnas.75.5.2416. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pangburn M. K., Müller-Eberhard H. J. The alternative pathway of complement. Springer Semin Immunopathol. 1984;7(2-3):163–192. doi: 10.1007/BF01893019. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pangburn M. K., Schreiber R. D., Müller-Eberhard H. J. C3b deposition during activation of the alternative complement pathway and the effect of deposition on the activating surface. J Immunol. 1983 Oct;131(4):1930–1935. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pangburn M. K., Schreiber R. D., Müller-Eberhard H. J. Formation of the initial C3 convertase of the alternative complement pathway. Acquisition of C3b-like activities by spontaneous hydrolysis of the putative thioester in native C3. J Exp Med. 1981 Sep 1;154(3):856–867. doi: 10.1084/jem.154.3.856. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Platts-Mills T. A., Ishizaka K. Activation of the alternate pathway of human complements by rabbit cells. J Immunol. 1974 Jul;113(1):348–358. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- REYNOLDS E. S. The use of lead citrate at high pH as an electron-opaque stain in electron microscopy. J Cell Biol. 1963 Apr;17:208–212. doi: 10.1083/jcb.17.1.208. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sim R. B., DiScipio R. G. Purification and structural studies on the complement-system control protein beta 1H (Factor H). Biochem J. 1982 Aug 1;205(2):285–293. doi: 10.1042/bj2050285. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Spurr A. R. A low-viscosity epoxy resin embedding medium for electron microscopy. J Ultrastruct Res. 1969 Jan;26(1):31–43. doi: 10.1016/s0022-5320(69)90033-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Turner S. H., Cherniak R., Reiss E. Fractionation and characterization of galactoxylomannan from Cryptococcus neoformans. Carbohydr Res. 1984 Feb 15;125(2):343–349. doi: 10.1016/0008-6215(84)85172-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Van Dijk W. C., Verbrugh H. A., van der Tol M. E., Peters R., Verhoef J. Role of Escherichia coli K capsular antigens during complement activation, C3 fixation, and opsonization. Infect Immun. 1979 Aug;25(2):603–609. doi: 10.1128/iai.25.2.603-609.1979. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wilkinson B. J., Sisson S. P., Kim Y., Peterson P. K. Localization of the third component of complement on the cell wall of encapsulated Staphylococcus aureus M: implications for the mechanism of resistance to phagocytosis. Infect Immun. 1979 Dec;26(3):1159–1163. doi: 10.1128/iai.26.3.1159-1163.1979. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]