Abstract
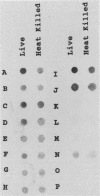
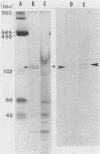
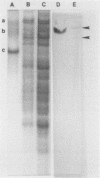
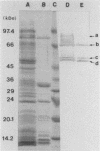
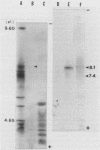
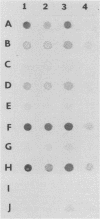
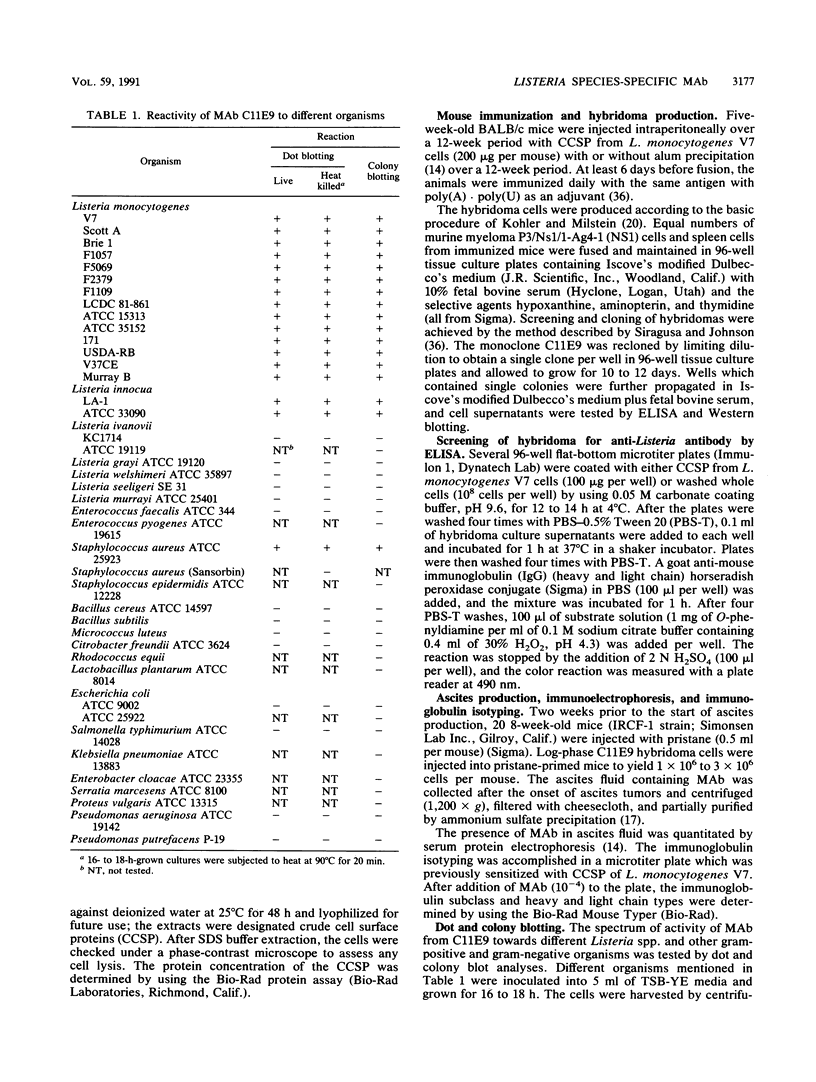
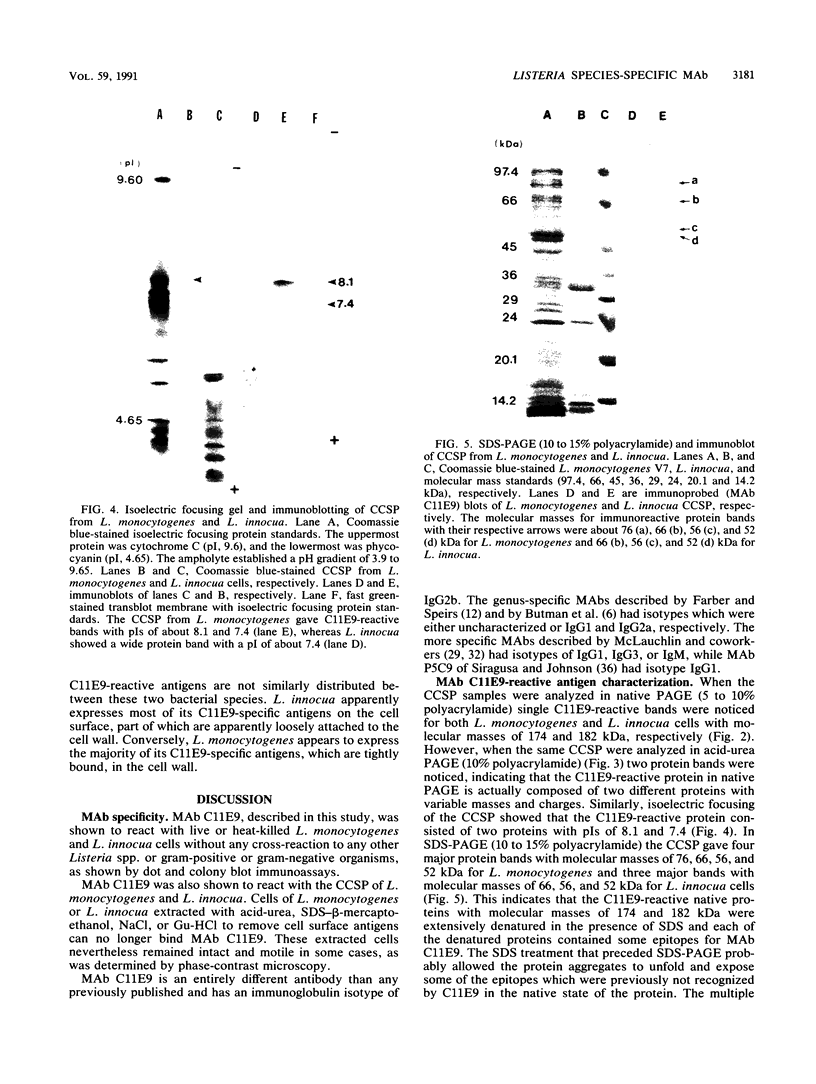
BALB/c mice were immunized with crude cell surface proteins of Listeria monocytogenes V7. Approximately 1,680 hybridomas were generated after two fusions, and the monoclone C11E9 was selected and used for further characterization. The monoclonal antibody (MAb) produced by C11E9 was immunoglobulin subclass G2b with kappa light chains. Dot and colony blot results indicated that MAb C11E9 was reactive to all the L. monocytogenes (34 of 34) and Listeria innocua (6 of 6) isolates without any cross-reaction to other organisms tested. Western blot (immunoblot) analysis of crude cell surface proteins in native polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis (PAGE) indicated that MAb C11E9 reacts with a single band in each species, with a molecular mass of 174 kDa for L. monocytogenes and 182 kDa for L. innocua. The MAb reacted with one major protein band in Western blot from acid-urea PAGE for both L. monocytogenes and L. innocua. Isoelectric focusing results indicated two immunoreactive protein bands with pIs of 8.1 and 7.4 for L. monocytogenes. Sodium dodecyl sulfate (SDS)-PAGE and Western blot analysis indicated several proteins with molecular masses of 76, 66, 56, and 52 kDa for L. monocytogenes and 66, 56, and 52 kDa for L. innocua. Reaction of MAb C11E9 to washed live cells indicated the possible binding of antibody to cell surface antigen. These cell surface antigens could be removed by 1 N HCl plus 9 M urea, 2% SDS-0.5% beta-mercaptoethanol, or 4 M guanidine-HCl. The epitope of MAb C11E9 binding site was shown to be protein in nature. Periodic acid-Schiff staining and glycoprotein immunoassay indicated that carbohydrate was absent in the epitope. The cellular locations of the MAb C11E9-reactive antigens were calculated to be 76 and 90% outside and 24 and 10% inside the cell membranes of L. monocytogenes and L. innocua, respectively, for 12- to 14-h cultures.
Full text
PDF





Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Barclay R., Threlfall D. R., Leighton I. Haemolysins and extracellular enzymes of Listeria monocytogenes and L. ivanovii. J Med Microbiol. 1989 Oct;30(2):111–118. doi: 10.1099/00222615-30-2-111. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Barclay R., Threlfall D. R., Leighton I. Separation and properties of the haemolysins and extracellular enzymes of Listeria monocytogenes and L. ivanovii. J Med Microbiol. 1989 Oct;30(2):119–127. doi: 10.1099/00222615-30-2-119. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bessesen M. T., Luo Q. A., Rotbart H. A., Blaser M. J., Ellison R. T., 3rd Detection of Listeria monocytogenes by using the polymerase chain reaction. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1990 Sep;56(9):2930–2932. doi: 10.1128/aem.56.9.2930-2932.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bhunia A. K., Johnson M. C., Ray B., Belden E. L. Antigenic property of pediocin AcH produced by Pediococcus acidilactici H. J Appl Bacteriol. 1990 Aug;69(2):211–215. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2672.1990.tb01511.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Butman B. T., Plank M. C., Durham R. J., Mattingly J. A. Monoclonal antibodies which identify a genus-specific Listeria antigen. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1988 Jun;54(6):1564–1569. doi: 10.1128/aem.54.6.1564-1569.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carlier Y., Bout D., Capron A., Delvallez M., Martin G., Strecker G., Duriez T. Physicochemical characteristics of Listeria specific antigen 2. J Gen Microbiol. 1980 Feb;116(2):549–552. doi: 10.1099/00221287-116-2-549. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Datta A. R., Wentz B. A., Shook D., Trucksess M. W. Synthetic oligodeoxyribonucleotide probes for detection of Listeria monocytogenes. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1988 Dec;54(12):2933–2937. doi: 10.1128/aem.54.12.2933-2937.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Delvallez M., Carlier Y., Bout D., Capron A., Martin G. R. Purification of a surface-specific soluble antigen from Listeria monocytogenes. Infect Immun. 1979 Sep;25(3):971–977. doi: 10.1128/iai.25.3.971-977.1979. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fairbanks G., Steck T. L., Wallach D. F. Electrophoretic analysis of the major polypeptides of the human erythrocyte membrane. Biochemistry. 1971 Jun 22;10(13):2606–2617. doi: 10.1021/bi00789a030. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ison C. A., Kolator B., Reid J. H., Dermott E., Clark J., Easmon C. S. Characterisation of monoclonal antibodies for detection of Mobiluncus spp. in genital specimens. J Med Microbiol. 1989 Oct;30(2):129–136. doi: 10.1099/00222615-30-2-129. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jarvis B. W., Dworkin M. Purification and properties of Myxococcus xanthus cell surface antigen 1604. J Bacteriol. 1989 Sep;171(9):4655–4666. doi: 10.1128/jb.171.9.4655-4666.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kamisango K., Nagaoka M., Fujii H., Azuma I. Enzyme immunoassay of teichoic acids from Listeria monocytogenes. J Clin Microbiol. 1985 Jan;21(1):135–137. doi: 10.1128/jcm.21.1.135-137.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- King W., Raposa S., Warshaw J., Johnson A., Halbert D., Klinger J. D. A new colorimetric nucleic acid hybridization assay for Listeria in foods. Int J Food Microbiol. 1989 Jun;8(3):225–232. doi: 10.1016/0168-1605(89)90017-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kuhn M., Goebel W. Identification of an extracellular protein of Listeria monocytogenes possibly involved in intracellular uptake by mammalian cells. Infect Immun. 1989 Jan;57(1):55–61. doi: 10.1128/iai.57.1.55-61.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Köhler G., Milstein C. Continuous cultures of fused cells secreting antibody of predefined specificity. Nature. 1975 Aug 7;256(5517):495–497. doi: 10.1038/256495a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Köhler S., Leimeister-Wächter M., Chakraborty T., Lottspeich F., Goebel W. The gene coding for protein p60 of Listeria monocytogenes and its use as a specific probe for Listeria monocytogenes. Infect Immun. 1990 Jun;58(6):1943–1950. doi: 10.1128/iai.58.6.1943-1950.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lee W. H., McClain D. Improved Listeria monocytogenes selective agar. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1986 Nov;52(5):1215–1217. doi: 10.1128/aem.52.5.1215-1217.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Loessner M. J., Bell R. H., Jay J. M., Shelef L. A. Comparison of seven plating media for enumeration of Listeria spp. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1988 Dec;54(12):3003–3007. doi: 10.1128/aem.54.12.3003-3007.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lovett J. Isolation and identification of Listeria monocytogenes in dairy products. J Assoc Off Anal Chem. 1988 May-Jun;71(3):658–660. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mattingly J. A., Butman B. T., Plank M. C., Durham R. J., Robison B. J. Rapid monoclonal antibody-based enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay for detection of Listeria in food products. J Assoc Off Anal Chem. 1988 May-Jun;71(3):679–681. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McClain D., Lee W. H. Development of USDA-FSIS method for isolation of Listeria monocytogenes from raw meat and poultry. J Assoc Off Anal Chem. 1988 May-Jun;71(3):660–664. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McLauchlin J., Black A., Green H. T., Nash J. Q., Taylor A. G. Monoclonal antibodies show Listeria monocytogenes in necropsy tissue samples. J Clin Pathol. 1988 Sep;41(9):983–988. doi: 10.1136/jcp.41.9.983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Peel M., Donachie W., Shaw A. Physical and antigenic heterogeneity in the flagellins of Listeria monocytogenes and L. ivanovii. J Gen Microbiol. 1988 Sep;134(9):2593–2598. doi: 10.1099/00221287-134-9-2593. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Peel M., Donachie W., Shaw A. Temperature-dependent expression of flagella of Listeria monocytogenes studied by electron microscopy, SDS-PAGE and western blotting. J Gen Microbiol. 1988 Aug;134(8):2171–2178. doi: 10.1099/00221287-134-8-2171. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Siragusa G. R., Johnson M. G. Monoclonal antibody specific for Listeria monocytogenes, Listeria innocua, and Listeria welshimeri. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1990 Jun;56(6):1897–1904. doi: 10.1128/aem.56.6.1897-1904.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Towbin H., Staehelin T., Gordon J. Electrophoretic transfer of proteins from polyacrylamide gels to nitrocellulose sheets: procedure and some applications. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Sep;76(9):4350–4354. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.9.4350. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ziegler H. K., Orlin C. A. Analysis of Listeria monocytogenes antigens with monoclonal antibodies. Clin Invest Med. 1984;7(4):239–242. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]