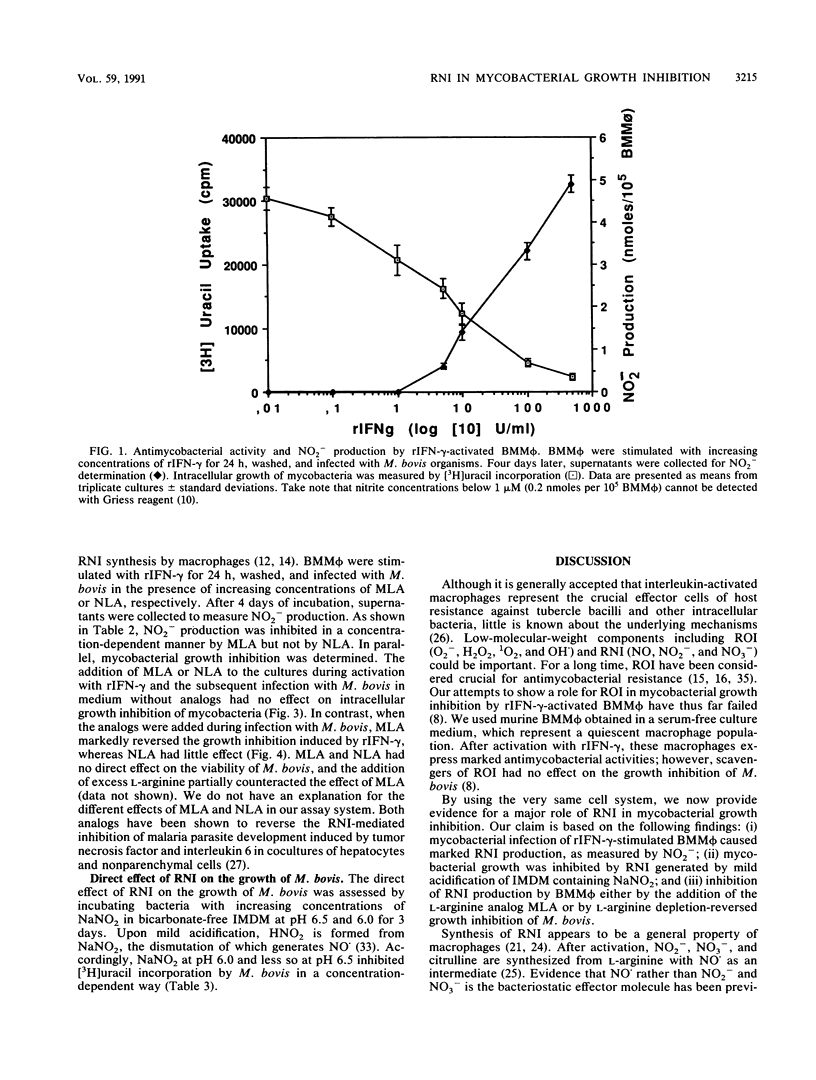
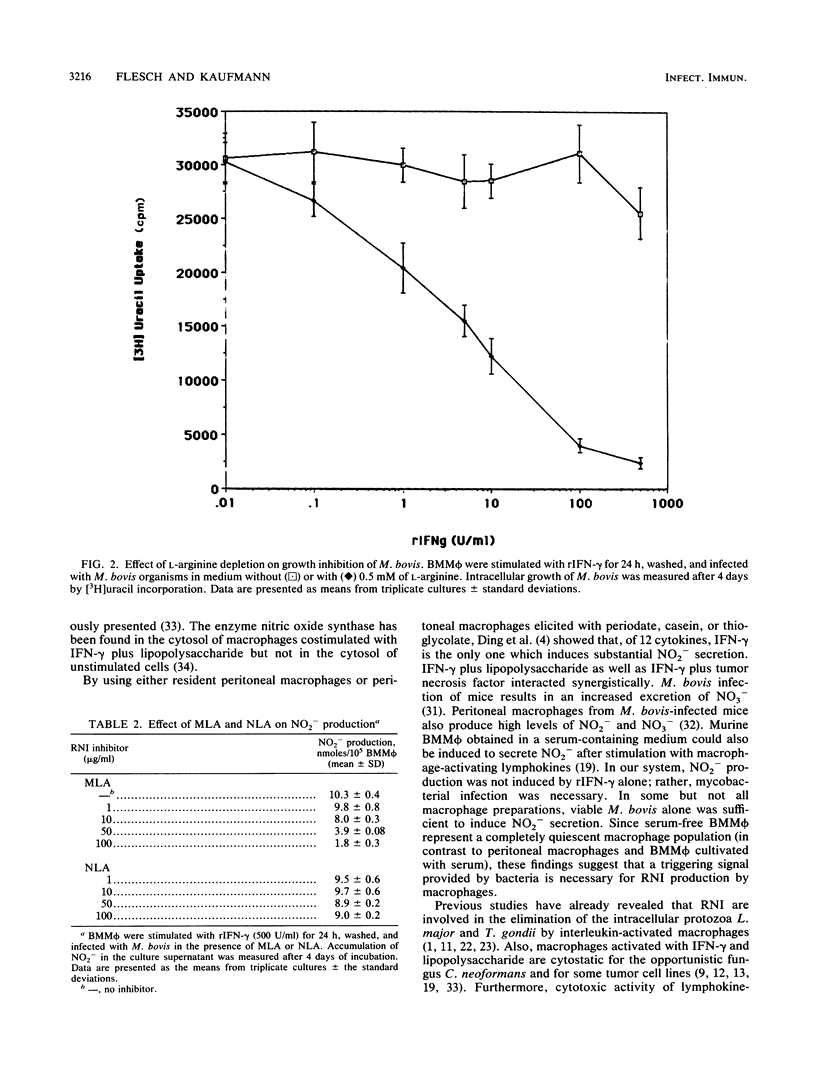
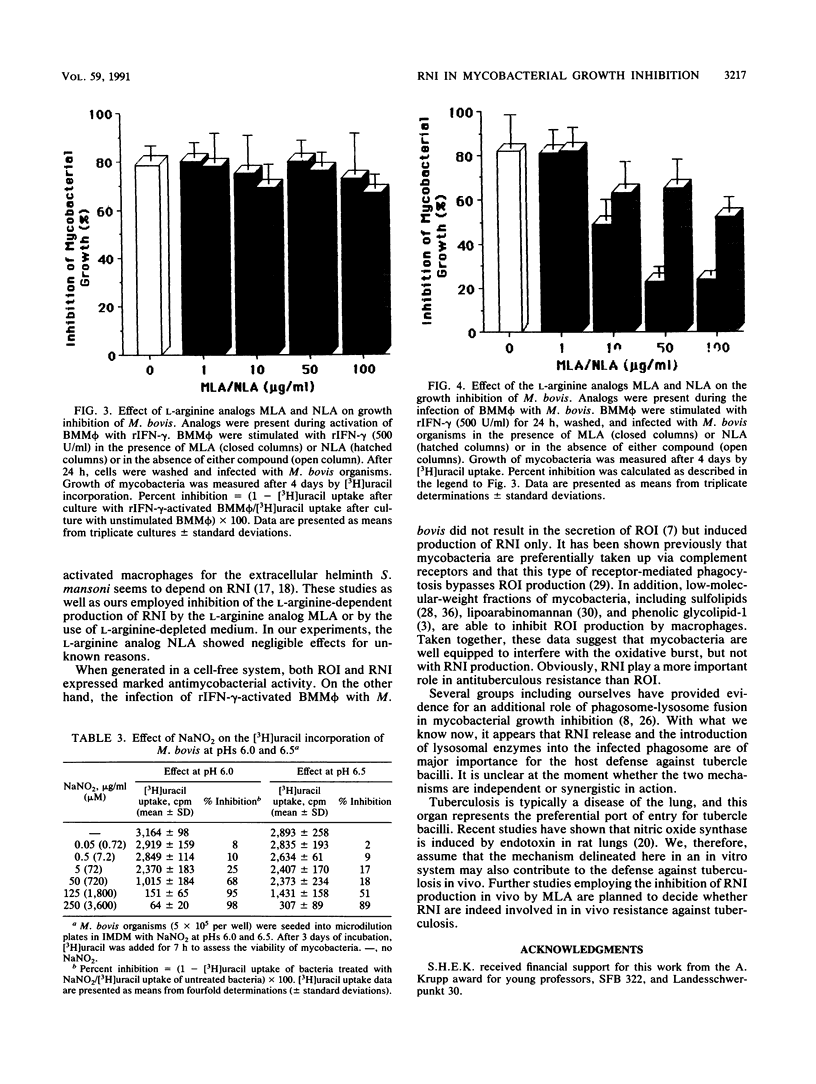
Abstract
Murine bone marrow-derived macrophages are able to inhibit the growth of Mycobacterium bovis after stimulation with recombinant gamma interferon. This antimycobacterial activity was inhibited by NG-monomethyl-L-arginine, a specific inhibitor of nitrite and nitrate synthesis from L-arginine. Furthermore, there was a complete lack of mycobacterial growth inhibition in a medium deficient in L-arginine. Nitrite is generated by gamma interferon-activated bone marrow-derived macrophages after infection with M. bovis, and a correlation between mycobacterial growth inhibition and nitrite production was observed. These results indicate that reactive nitrogen intermediates derived from L-arginine are crucially involved in macrophage antimycobacterial activity.
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Adams L. B., Hibbs J. B., Jr, Taintor R. R., Krahenbuhl J. L. Microbiostatic effect of murine-activated macrophages for Toxoplasma gondii. Role for synthesis of inorganic nitrogen oxides from L-arginine. J Immunol. 1990 Apr 1;144(7):2725–2729. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Albina J. E., Caldwell M. D., Henry W. L., Jr, Mills C. D. Regulation of macrophage functions by L-arginine. J Exp Med. 1989 Mar 1;169(3):1021–1029. doi: 10.1084/jem.169.3.1021. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chan J., Fujiwara T., Brennan P., McNeil M., Turco S. J., Sibille J. C., Snapper M., Aisen P., Bloom B. R. Microbial glycolipids: possible virulence factors that scavenge oxygen radicals. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 Apr;86(7):2453–2457. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.7.2453. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Denis M. Interferon-gamma-treated murine macrophages inhibit growth of tubercle bacilli via the generation of reactive nitrogen intermediates. Cell Immunol. 1991 Jan;132(1):150–157. doi: 10.1016/0008-8749(91)90014-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ding A. H., Nathan C. F., Stuehr D. J. Release of reactive nitrogen intermediates and reactive oxygen intermediates from mouse peritoneal macrophages. Comparison of activating cytokines and evidence for independent production. J Immunol. 1988 Oct 1;141(7):2407–2412. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Drapier J. C., Wietzerbin J., Hibbs J. B., Jr Interferon-gamma and tumor necrosis factor induce the L-arginine-dependent cytotoxic effector mechanism in murine macrophages. Eur J Immunol. 1988 Oct;18(10):1587–1592. doi: 10.1002/eji.1830181018. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Flesch I. E., Kaufmann S. H. Attempts to characterize the mechanisms involved in mycobacterial growth inhibition by gamma-interferon-activated bone marrow macrophages. Infect Immun. 1988 Jun;56(6):1464–1469. doi: 10.1128/iai.56.6.1464-1469.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Flesch I., Ferber E. Growth requirements of murine bone marrow macrophages in serum-free cell culture. Immunobiology. 1986 Mar;171(1-2):14–26. doi: 10.1016/S0171-2985(86)80014-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Flesch I., Kaufmann S. H. Mycobacterial growth inhibition by interferon-gamma-activated bone marrow macrophages and differential susceptibility among strains of Mycobacterium tuberculosis. J Immunol. 1987 Jun 15;138(12):4408–4413. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Granger D. L., Hibbs J. B., Jr, Perfect J. R., Durack D. T. Specific amino acid (L-arginine) requirement for the microbiostatic activity of murine macrophages. J Clin Invest. 1988 Apr;81(4):1129–1136. doi: 10.1172/JCI113427. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Green L. C., Wagner D. A., Glogowski J., Skipper P. L., Wishnok J. S., Tannenbaum S. R. Analysis of nitrate, nitrite, and [15N]nitrate in biological fluids. Anal Biochem. 1982 Oct;126(1):131–138. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(82)90118-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Green S. J., Meltzer M. S., Hibbs J. B., Jr, Nacy C. A. Activated macrophages destroy intracellular Leishmania major amastigotes by an L-arginine-dependent killing mechanism. J Immunol. 1990 Jan 1;144(1):278–283. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hibbs J. B., Jr, Taintor R. R., Vavrin Z., Rachlin E. M. Nitric oxide: a cytotoxic activated macrophage effector molecule. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1988 Nov 30;157(1):87–94. doi: 10.1016/s0006-291x(88)80015-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Higuchi M., Higashi N., Taki H., Osawa T. Cytolytic mechanisms of activated macrophages. Tumor necrosis factor and L-arginine-dependent mechanisms act synergistically as the major cytolytic mechanisms of activated macrophages. J Immunol. 1990 Feb 15;144(4):1425–1431. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Iyengar R., Stuehr D. J., Marletta M. A. Macrophage synthesis of nitrite, nitrate, and N-nitrosamines: precursors and role of the respiratory burst. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 Sep;84(18):6369–6373. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.18.6369. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jackett P. S., Aber V. R., Mitchison D. A., Lowrie D. B. The contribution of hydrogen peroxide resistance to virulence of Mycobacterium tuberculosis during the first six days after intravenous infection of normal and BCG-vaccinated guinea-pigs. Br J Exp Pathol. 1981 Feb;62(1):34–40. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jackett P. S., Andrew P. W., Aber V. R., Lowrie D. B. Guinea pig alveolar macrophages probably kill M. tuberculosis H37Rv and H37Ra in vivo by producing hydrogen peroxide. Adv Exp Med Biol. 1983;162:99–104. doi: 10.1007/978-1-4684-4481-0_10. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- James S. L., Glaven J. Macrophage cytotoxicity against schistosomula of Schistosoma mansoni involves arginine-dependent production of reactive nitrogen intermediates. J Immunol. 1989 Dec 15;143(12):4208–4212. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- James S. L., Hibbs J. B., Jr The role of nitrogen oxides as effector molecules of parasite killing. Parasitol Today. 1990 Sep;6(9):303–305. doi: 10.1016/0169-4758(90)90261-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Keller R., Keist R. Abilities of activated macrophages to manifest tumoricidal activity and to generate reactive nitrogen intermediates: a comparative study in vitro and ex vivo. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1989 Nov 15;164(3):968–973. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(89)91764-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Knowles R. G., Merrett M., Salter M., Moncada S. Differential induction of brain, lung and liver nitric oxide synthase by endotoxin in the rat. Biochem J. 1990 Sep 15;270(3):833–836. doi: 10.1042/bj2700833. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Liew F. Y., Cox F. E. Nonspecific defence mechanism: the role of nitric oxide. Immunol Today. 1991 Mar;12(3):A17–A21. doi: 10.1016/S0167-5699(05)80006-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Liew F. Y., Li Y., Millott S. Tumor necrosis factor-alpha synergizes with IFN-gamma in mediating killing of Leishmania major through the induction of nitric oxide. J Immunol. 1990 Dec 15;145(12):4306–4310. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Liew F. Y., Millott S., Parkinson C., Palmer R. M., Moncada S. Macrophage killing of Leishmania parasite in vivo is mediated by nitric oxide from L-arginine. J Immunol. 1990 Jun 15;144(12):4794–4797. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marletta M. A. Nitric oxide: biosynthesis and biological significance. Trends Biochem Sci. 1989 Dec;14(12):488–492. doi: 10.1016/0968-0004(89)90181-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marletta M. A., Yoon P. S., Iyengar R., Leaf C. D., Wishnok J. S. Macrophage oxidation of L-arginine to nitrite and nitrate: nitric oxide is an intermediate. Biochemistry. 1988 Nov 29;27(24):8706–8711. doi: 10.1021/bi00424a003. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moulder J. W. Comparative biology of intracellular parasitism. Microbiol Rev. 1985 Sep;49(3):298–337. doi: 10.1128/mr.49.3.298-337.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nüssler A., Drapier J. C., Rénia L., Pied S., Miltgen F., Gentilini M., Mazier D. L-arginine-dependent destruction of intrahepatic malaria parasites in response to tumor necrosis factor and/or interleukin 6 stimulation. Eur J Immunol. 1991 Jan;21(1):227–230. doi: 10.1002/eji.1830210134. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pabst M. J., Gross J. M., Brozna J. P., Goren M. B. Inhibition of macrophage priming by sulfatide from Mycobacterium tuberculosis. J Immunol. 1988 Jan 15;140(2):634–640. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schlesinger L. S., Bellinger-Kawahara C. G., Payne N. R., Horwitz M. A. Phagocytosis of Mycobacterium tuberculosis is mediated by human monocyte complement receptors and complement component C3. J Immunol. 1990 Apr 1;144(7):2771–2780. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sibley L. D., Hunter S. W., Brennan P. J., Krahenbuhl J. L. Mycobacterial lipoarabinomannan inhibits gamma interferon-mediated activation of macrophages. Infect Immun. 1988 May;56(5):1232–1236. doi: 10.1128/iai.56.5.1232-1236.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stuehr D. J., Marletta M. A. Induction of nitrite/nitrate synthesis in murine macrophages by BCG infection, lymphokines, or interferon-gamma. J Immunol. 1987 Jul 15;139(2):518–525. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stuehr D. J., Marletta M. A. Mammalian nitrate biosynthesis: mouse macrophages produce nitrite and nitrate in response to Escherichia coli lipopolysaccharide. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Nov;82(22):7738–7742. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.22.7738. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stuehr D. J., Nathan C. F. Nitric oxide. A macrophage product responsible for cytostasis and respiratory inhibition in tumor target cells. J Exp Med. 1989 May 1;169(5):1543–1555. doi: 10.1084/jem.169.5.1543. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tayeh M. A., Marletta M. A. Macrophage oxidation of L-arginine to nitric oxide, nitrite, and nitrate. Tetrahydrobiopterin is required as a cofactor. J Biol Chem. 1989 Nov 25;264(33):19654–19658. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Walker L., Lowrie D. B. Killing of Mycobacterium microti by immunologically activated macrophages. Nature. 1981 Sep 3;293(5827):69–71. doi: 10.1038/293069a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zhang L., Goren M. B., Holzer T. J., Andersen B. R. Effect of Mycobacterium tuberculosis-derived sulfolipid I on human phagocytic cells. Infect Immun. 1988 Nov;56(11):2876–2883. doi: 10.1128/iai.56.11.2876-2883.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



