Abstract
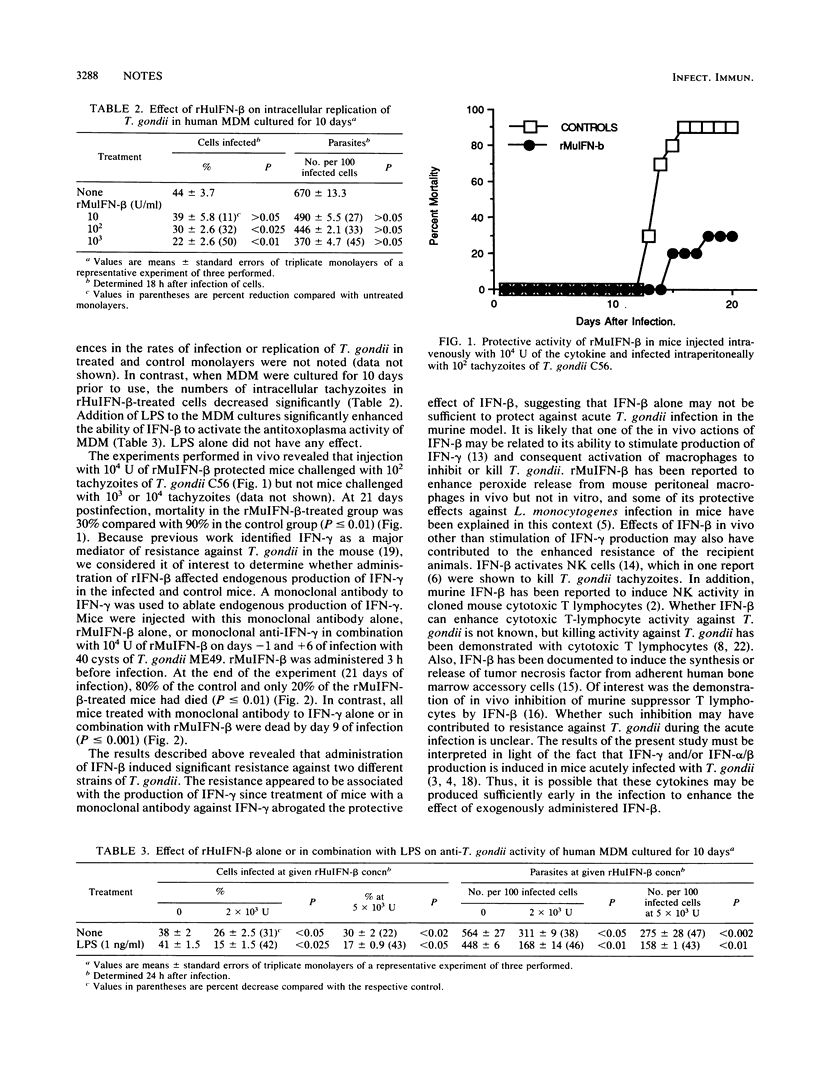
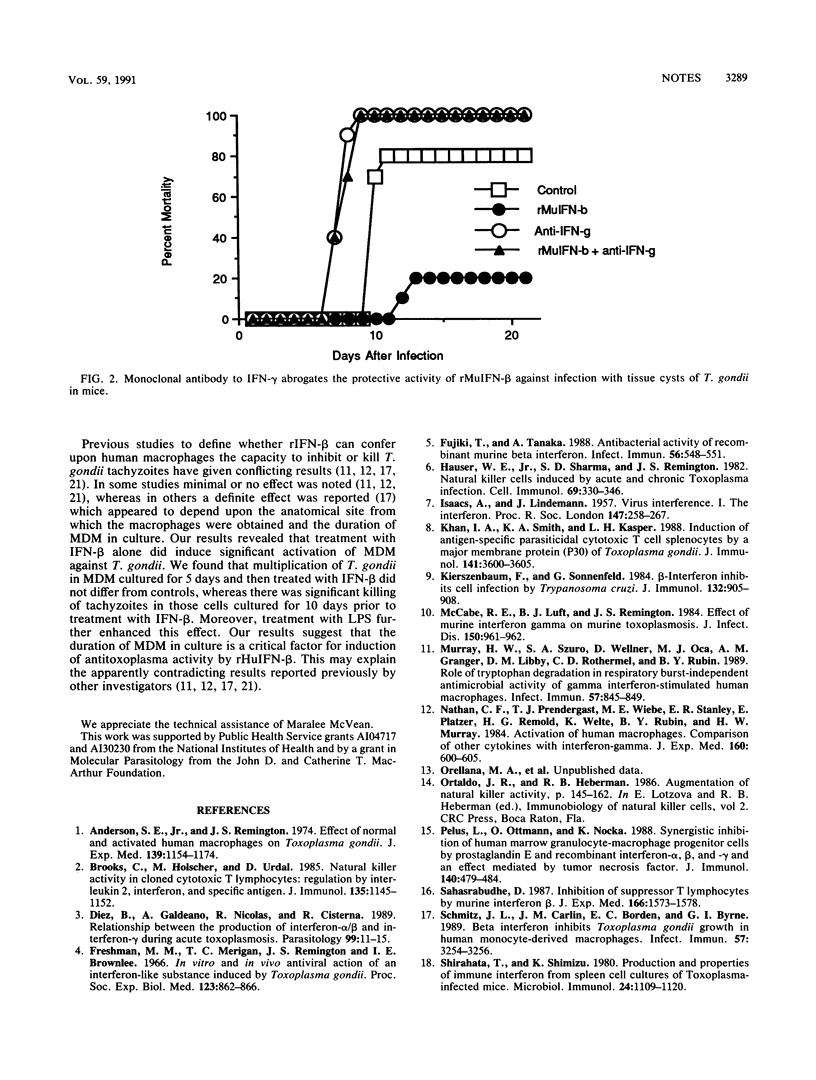
The role of recombinant murine beta interferon (rMuIFN-beta) and recombinant human IFN-beta (rHuIFN-beta) in resistance to Toxoplasma gondii was examined. rMuIFN-beta protected mice against a lethal infection with the parasite. The protective effect appeared to depend on the concomitant release of gamma interferon. rMuIFN-beta did not activate murine peritoneal macrophages to inhibit or kill T. gondii whether used alone or in combination with lipopolysaccharide (LPS). rHuIFN-beta did not activate human monocyte-derived macrophages to inhibit or kill T. gondii when 5-day-old monocyte-derived macrophages were used. In contrast, significant killing of T. gondii was noted when 10-day-old monocyte-derived macrophages were used. The addition of LPS enhanced this effect. These results revealed a role for IFN-beta in the mechanisms of defense against T. gondii and suggest its potential use in the treatment of toxoplasmosis in humans.
Full text
PDF

Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Anderson S. E., Jr, Remington J. S. Effect of normal and activated human macrophages on Toxoplasma gondii. J Exp Med. 1974 May 1;139(5):1154–1174. doi: 10.1084/jem.139.5.1154. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brooks C. G., Holscher M., Urdal D. Natural killer activity in cloned cytotoxic T lymphocytes: regulation by interleukin 2, interferon, and specific antigen. J Immunol. 1985 Aug;135(2):1145–1152. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Diez B., Galdeano A., Nicolas R., Cisterna R. Relationship between the production of interferon-alpha/beta and interferon-gamma during acute toxoplasmosis. Parasitology. 1989 Aug;99(Pt 1):11–15. doi: 10.1017/s0031182000060972. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Freshman M. M., Merigan T. C., Remington J. S., Brownlee I. E. In vitro and in vivo antiviral action of an interferon-like substance induced by Toxoplasma gondii. Proc Soc Exp Biol Med. 1966 Dec;123(3):862–866. doi: 10.3181/00379727-123-31625. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fujiki T., Tanaka A. Antibacterial activity of recombinant murine beta interferon. Infect Immun. 1988 Mar;56(3):548–551. doi: 10.1128/iai.56.3.548-551.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hauser W. E., Jr, Sharma S. D., Remington J. S. Natural killer cells induced by acute and chronic toxoplasma infection. Cell Immunol. 1982 May 15;69(2):330–346. doi: 10.1016/0008-8749(82)90076-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Khan I. A., Smith K. A., Kasper L. H. Induction of antigen-specific parasiticidal cytotoxic T cell splenocytes by a major membrane protein (P30) of Toxoplasma gondii. J Immunol. 1988 Nov 15;141(10):3600–3605. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kierszenbaum F., Sonnenfeld G. Beta-interferon inhibits cell infection by Trypanosoma cruzi. J Immunol. 1984 Feb;132(2):905–908. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McCabe R. E., Luft B. J., Remington J. S. Effect of murine interferon gamma on murine toxoplasmosis. J Infect Dis. 1984 Dec;150(6):961–962. doi: 10.1093/infdis/150.6.961. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Murray H. W., Szuro-Sudol A., Wellner D., Oca M. J., Granger A. M., Libby D. M., Rothermel C. D., Rubin B. Y. Role of tryptophan degradation in respiratory burst-independent antimicrobial activity of gamma interferon-stimulated human macrophages. Infect Immun. 1989 Mar;57(3):845–849. doi: 10.1128/iai.57.3.845-849.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nathan C. F., Prendergast T. J., Wiebe M. E., Stanley E. R., Platzer E., Remold H. G., Welte K., Rubin B. Y., Murray H. W. Activation of human macrophages. Comparison of other cytokines with interferon-gamma. J Exp Med. 1984 Aug 1;160(2):600–605. doi: 10.1084/jem.160.2.600. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pelus L. M., Ottmann O. G., Nocka K. H. Synergistic inhibition of human marrow granulocyte-macrophage progenitor cells by prostaglandin E and recombinant interferon-alpha, -beta, and -gamma and an effect mediated by tumor necrosis factor. J Immunol. 1988 Jan 15;140(2):479–484. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sahasrabudhe D. M. Inhibition of suppressor T lymphocytes by murine interferon beta. J Exp Med. 1987 Nov 1;166(5):1573–1578. doi: 10.1084/jem.166.5.1573. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schmitz J. L., Carlin J. M., Borden E. C., Byrne G. I. Beta interferon inhibits Toxoplasma gondii growth in human monocyte-derived macrophages. Infect Immun. 1989 Oct;57(10):3254–3256. doi: 10.1128/iai.57.10.3254-3256.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shirahata T., Shimizu K. Production and properties of immune interferon from spleen cell cultures of Toxoplasma-infected mice. Microbiol Immunol. 1980;24(11):1109–1120. doi: 10.1111/j.1348-0421.1980.tb02915.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Suzuki Y., Orellana M. A., Schreiber R. D., Remington J. S. Interferon-gamma: the major mediator of resistance against Toxoplasma gondii. Science. 1988 Apr 22;240(4851):516–518. doi: 10.1126/science.3128869. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wilson C. B., Tsai V., Remington J. S. Failure to trigger the oxidative metabolic burst by normal macrophages: possible mechanism for survival of intracellular pathogens. J Exp Med. 1980 Feb 1;151(2):328–346. doi: 10.1084/jem.151.2.328. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wilson C. B., Westall J. Activation of neonatal and adult human macrophages by alpha, beta, and gamma interferons. Infect Immun. 1985 Aug;49(2):351–356. doi: 10.1128/iai.49.2.351-356.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yano A., Aosai F., Ohta M., Hasekura H., Sugane K., Hayashi S. Antigen presentation by Toxoplasma gondii-infected cells to CD4+ proliferative T cells and CD8+ cytotoxic cells. J Parasitol. 1989 Jun;75(3):411–416. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



