Abstract
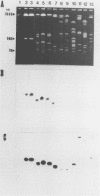
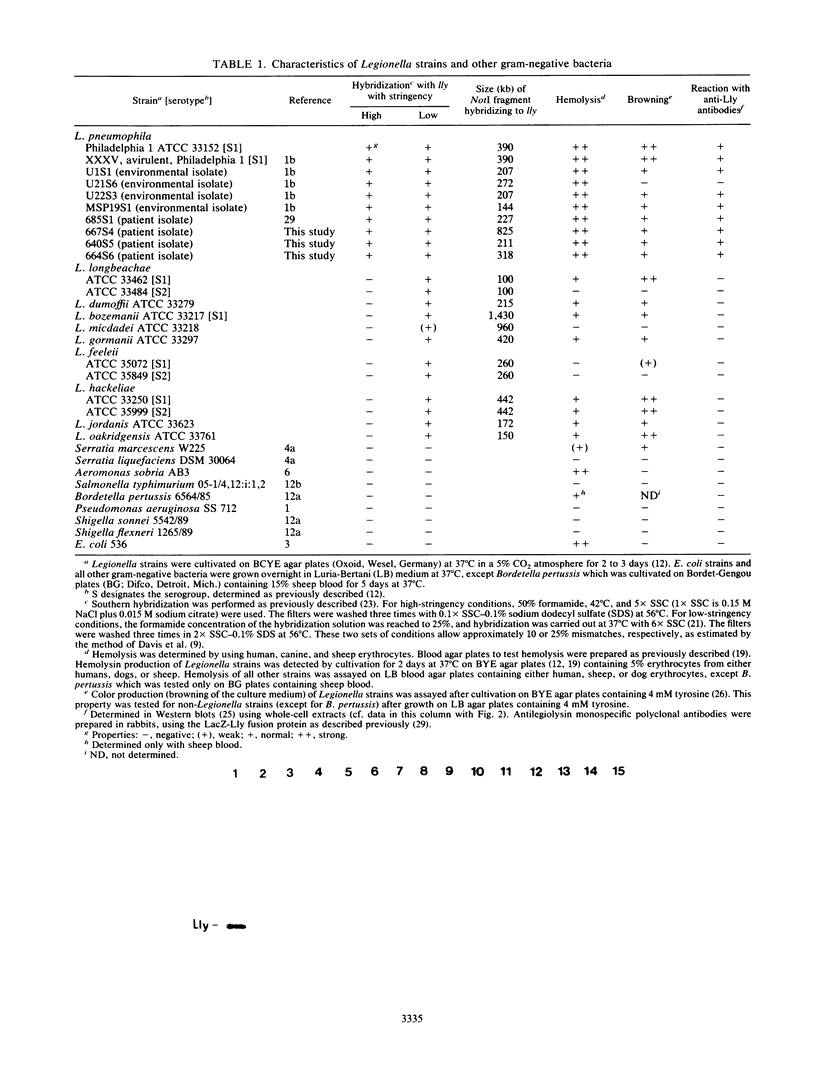
The legiolysin gene (lly) cloned from Legionella pneumophila Philadelphia 1 confers the phenotypes of hemolysis and browning of the culture medium. An internal lly-specific DNA probe was used in Southern hybridizations for the detection of lly-specific DNA in the genomes of legionellae and other gram-negative pathogenic bacteria. Under conditions of high stringency, the lly DNA probe specifically reacted with DNA fragments from L. pneumophila isolates; by reducing stringency, hybridization was also observed for all other Legionella strains tested. No hybridization occurred with DNAs isolated from bacteria of other genera. The lly gene was mapped by pulsed-field gel electrophoresis to the respective genomic NotI fragments of Legionella isolates. By using antilegiolysin monospecific polyclonal antibodies in Western blots (immunoblots), Lly proteins could be detected only in L. pneumophila isolates.
Full text
PDF


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bender L., Ott M., Marre R., Hacker J. Genome analysis of Legionella ssp. by orthogonal field alternation gel electrophoresis (OFAGE). FEMS Microbiol Lett. 1990 Nov;60(3):253–257. doi: 10.1016/0378-1097(90)90313-f. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blander S. J., Szeto L., Shuman H. A., Horwitz M. A. An immunoprotective molecule, the major secretory protein of Legionella pneumophila, is not a virulence factor in a guinea pig model of Legionnaires' disease. J Clin Invest. 1990 Sep;86(3):817–824. doi: 10.1172/JCI114779. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blum G., Ott M., Cross A., Hacker J. Virulence determinants of Escherichia coli O6 extraintestinal isolates analysed by Southern hybridizations and DNA long range mapping techniques. Microb Pathog. 1991 Feb;10(2):127–136. doi: 10.1016/0882-4010(91)90073-j. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bornstein N., Nowicki M., Fleurette J. Haemolytic activity in the genus Legionella. Ann Inst Pasteur Microbiol. 1988 May-Jun;139(3):325–329. doi: 10.1016/0769-2609(88)90024-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Butler P. D., Moxon E. R. A physical map of the genome of Haemophilus influenzae type b. J Gen Microbiol. 1990 Dec;136(12):2333–2342. doi: 10.1099/00221287-136-12-2333. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cianciotto N. P., Bangsborg J. M., Eisenstein B. I., Engleberg N. C. Identification of mip-like genes in the genus Legionella. Infect Immun. 1990 Sep;58(9):2912–2918. doi: 10.1128/iai.58.9.2912-2918.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cianciotto N., Eisenstein B. I., Engleberg N. C., Shuman H. Genetics and molecular pathogenesis of Legionella pneumophila, an intracellular parasite of macrophages. Mol Biol Med. 1989 Oct;6(5):409–424. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Feinberg A. P., Vogelstein B. A technique for radiolabeling DNA restriction endonuclease fragments to high specific activity. Anal Biochem. 1983 Jul 1;132(1):6–13. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(83)90418-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hoffman P. S., Butler C. A., Quinn F. D. Cloning and temperature-dependent expression in Escherichia coli of a Legionella pneumophila gene coding for a genus-common 60-kilodalton antigen. Infect Immun. 1989 Jun;57(6):1731–1739. doi: 10.1128/iai.57.6.1731-1739.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laemmli U. K. Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature. 1970 Aug 15;227(5259):680–685. doi: 10.1038/227680a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marra A., Horwitz M. A., Shuman H. A. The HL-60 model for the interaction of human macrophages with the Legionnaires' disease bacterium. J Immunol. 1990 Apr 1;144(7):2738–2744. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ott M., Bender L., Marre R., Hacker J. Pulsed field electrophoresis of genomic restriction fragments for the detection of nosocomial Legionella pneumophila in hospital water supplies. J Clin Microbiol. 1991 Apr;29(4):813–815. doi: 10.1128/jcm.29.4.813-815.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pearlman E., Jiwa A. H., Engleberg N. C., Eisenstein B. I. Growth of Legionella pneumophila in a human macrophage-like (U937) cell line. Microb Pathog. 1988 Aug;5(2):87–95. doi: 10.1016/0882-4010(88)90011-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Quinn F. D., Keen M. G., Tompkins L. S. Genetic, immunological, and cytotoxic comparisons of Legionella proteolytic activities. Infect Immun. 1989 Sep;57(9):2719–2725. doi: 10.1128/iai.57.9.2719-2725.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Quinn F. D., Tompkins L. S. Analysis of a cloned sequence of Legionella pneumophila encoding a 38 kD metalloprotease possessing haemolytic and cytotoxic activities. Mol Microbiol. 1989 Jun;3(6):797–805. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2958.1989.tb00228.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rdest U., Wintermeyer E., Ludwig B., Hacker J. Legiolysin, a new hemolysin from L. pneumophila. Zentralbl Bakteriol. 1991 Jan;274(4):471–474. doi: 10.1016/s0934-8840(11)80083-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith C. L., Condemine G. New approaches for physical mapping of small genomes. J Bacteriol. 1990 Mar;172(3):1167–1172. doi: 10.1128/jb.172.3.1167-1172.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Southern E. M. Detection of specific sequences among DNA fragments separated by gel electrophoresis. J Mol Biol. 1975 Nov 5;98(3):503–517. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(75)80083-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Szeto L., Shuman H. A. The Legionella pneumophila major secretory protein, a protease, is not required for intracellular growth or cell killing. Infect Immun. 1990 Aug;58(8):2585–2592. doi: 10.1128/iai.58.8.2585-2592.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Towbin H., Staehelin T., Gordon J. Electrophoretic transfer of proteins from polyacrylamide gels to nitrocellulose sheets: procedure and some applications. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Sep;76(9):4350–4354. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.9.4350. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vickers R. M., Yu V. L. Clinical laboratory differentiation of Legionellaceae family members with pigment production and fluorescence on media supplemented with aromatic substrates. J Clin Microbiol. 1984 May;19(5):583–587. doi: 10.1128/jcm.19.5.583-587.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Winn W. C., Jr Legionnaires disease: historical perspective. Clin Microbiol Rev. 1988 Jan;1(1):60–81. doi: 10.1128/cmr.1.1.60. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wintermeyer E., Rdest U., Ludwig B., Debes A., Hacker J. Characterization of legiolysin (lly), responsible for haemolytic activity, colour production and fluorescence of Legionella pneumophila. Mol Microbiol. 1991 May;5(5):1135–1143. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2958.1991.tb01886.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]