Abstract
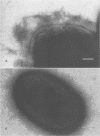
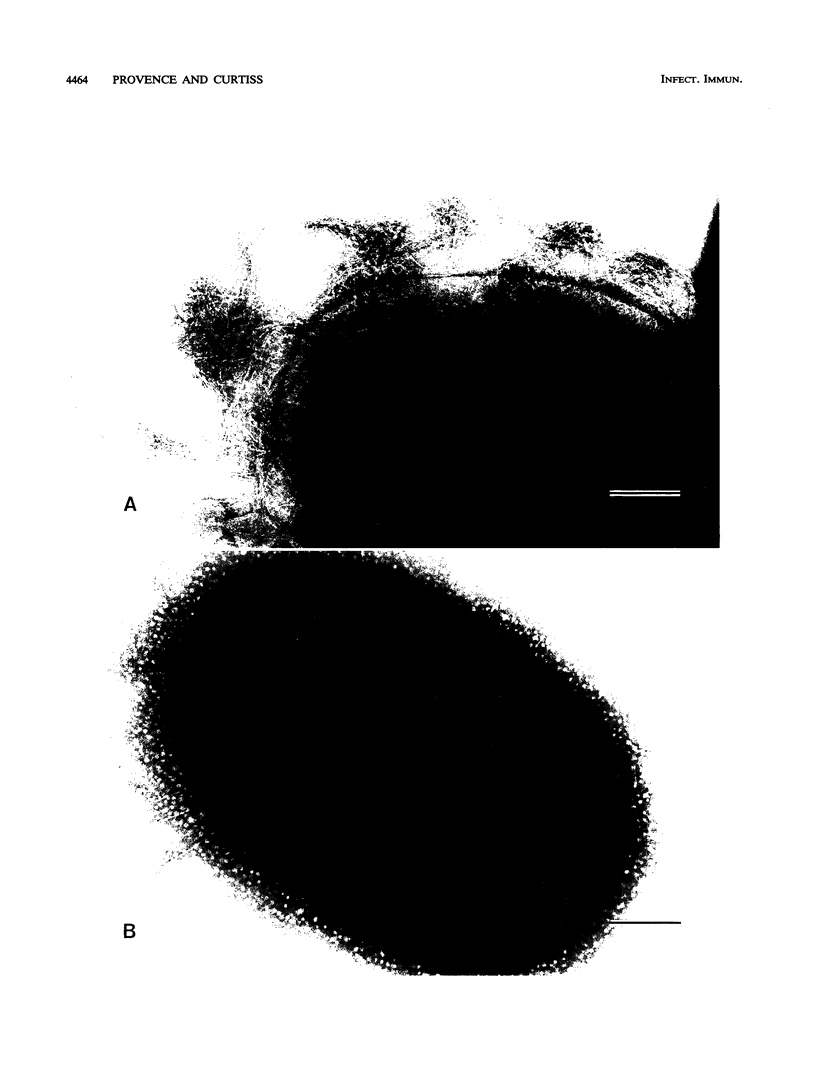
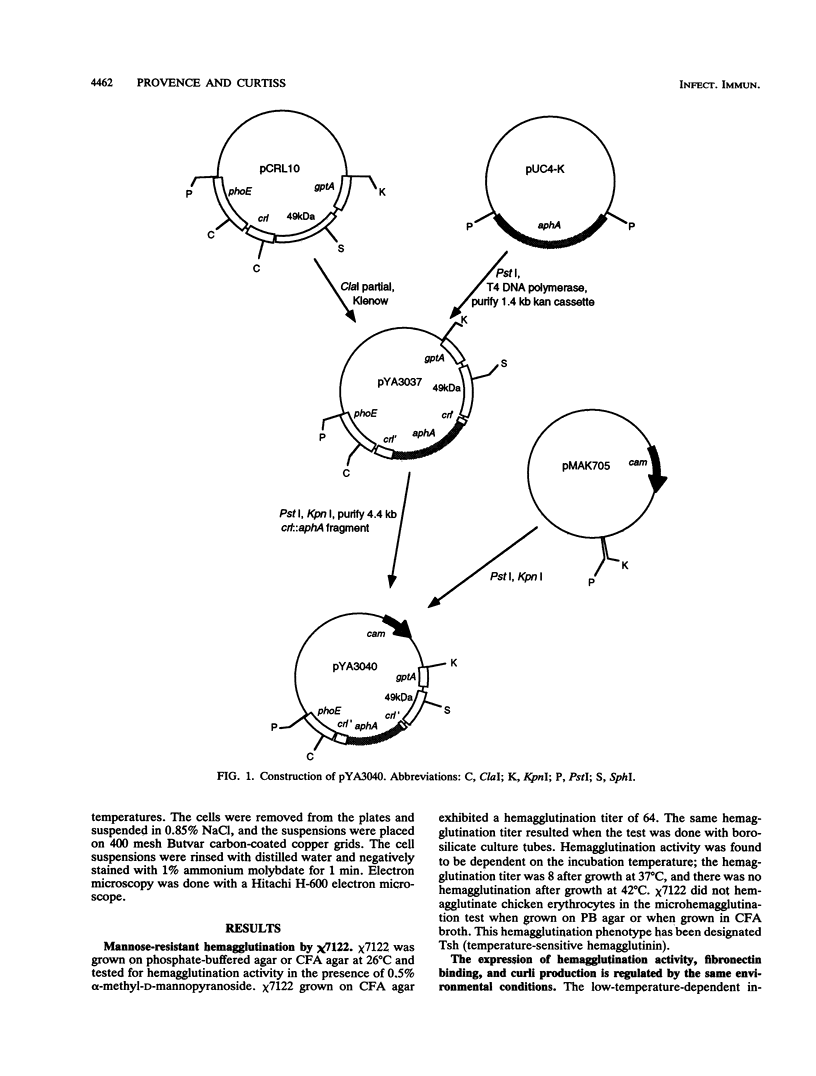
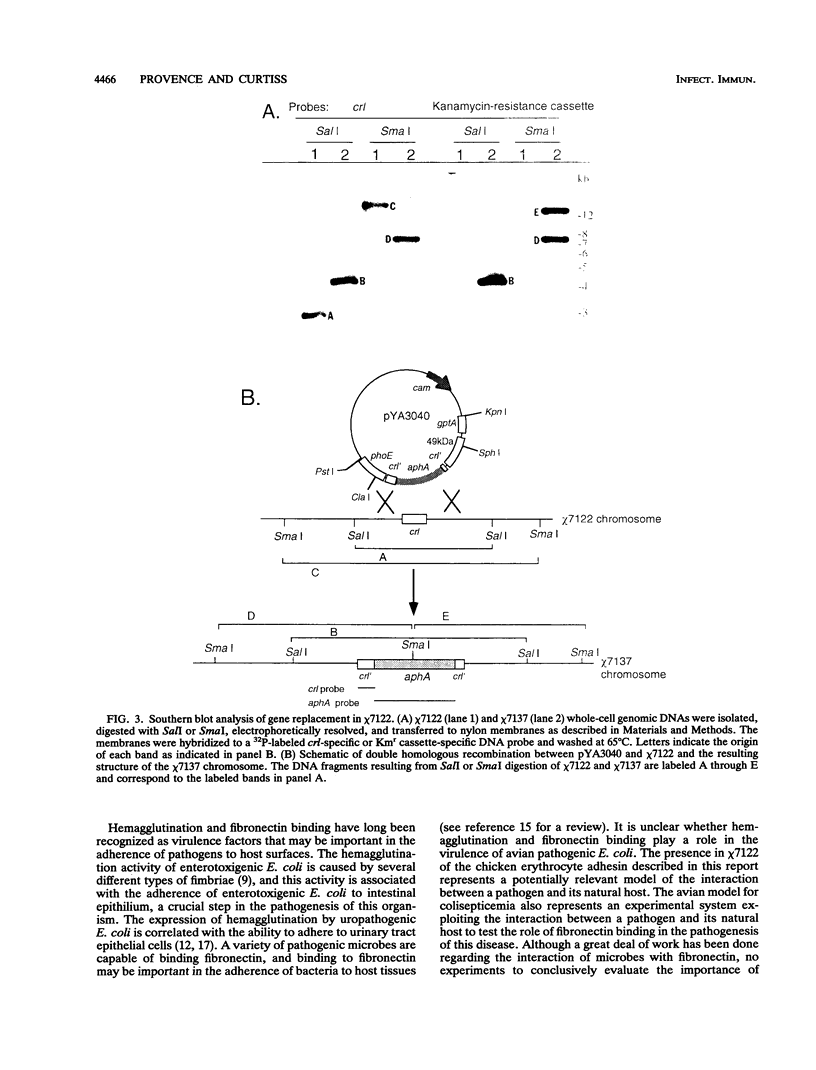
This study determined the role of crl in the production of curli by, the hemagglutination activity of, and fibronectin binding by avian pathogenic Escherichia coli chi 7122. Curli, an extracellular structure that binds fibronectin, was recently described (A. Olsén, A. Jonsson, and S. Normark, Nature [London] 338:652-655, 1989). The crl gene product was hypothesized to be the subunit monomer of curli and to bind fibronectin. E. coli HB101, which does not contain crl, binds fibronectin and produces curli when harboring a plasmid containing the crl gene. We show that HB101 hemagglutinates chicken erythrocytes when harboring the crl gene and that chi 7122 hemagglutinates chicken erythrocytes, binds fibronectin, and produces curli. Hemagglutination activity, fibronectin binding, and curli production are best expressed by chi 7122 and HB101 harboring the crl gene when the bacteria are grown on colonization factor antigen agar at 26 degrees C. The expression of hemagglutination activity, fibronectin binding, and curli production by both strains is decreased by growth on this agar at an increased temperature, of an increased osmolarity, or in an anaerobic atmosphere. This results indicates that the crl gene plays a role in the expression of the three phenotypes in HB101 and possibly in chi 7122 as well. We inactivated crl in chi 7122 by allele replacement in the expectation of abolishing hemagglutination activity, fibronectin binding, and curli production. The mutation was verified by Southern blot analysis and by a polymerase chain reaction, and there was no evidence of a second crl gene in chi 7122. However, the mutant of chi 7122 lacking crl hemagglutinated chicken erythrocytes, bound fibronectin, and produced curli at wild-type levels. This result indicates that crl plays a nonessential role in the expression of these three phenotypes in chi 7122.
Full text
PDF





Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Boyer H. W., Roulland-Dussoix D. A complementation analysis of the restriction and modification of DNA in Escherichia coli. J Mol Biol. 1969 May 14;41(3):459–472. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(69)90288-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cohen S. N., Chang A. C., Hsu L. Nonchromosomal antibiotic resistance in bacteria: genetic transformation of Escherichia coli by R-factor DNA. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1972 Aug;69(8):2110–2114. doi: 10.1073/pnas.69.8.2110. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Collinson S. K., Emödy L., Müller K. H., Trust T. J., Kay W. W. Purification and characterization of thin, aggregative fimbriae from Salmonella enteritidis. J Bacteriol. 1991 Aug;173(15):4773–4781. doi: 10.1128/jb.173.15.4773-4781.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Collinson S. K., Emödy L., Trust T. J., Kay W. W. Thin aggregative fimbriae from diarrheagenic Escherichia coli. J Bacteriol. 1992 Jul;174(13):4490–4495. doi: 10.1128/jb.174.13.4490-4495.1992. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Duguid J. P., Clegg S., Wilson M. I. The fimbrial and non-fimbrial haemagglutinins of Escherichia coli. J Med Microbiol. 1979 May;12(2):213–227. doi: 10.1099/00222615-12-2-213. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Erganiş O., Kaya O., Corlu M., Istanbulluoğlu E. Hemagglutination, hydrophobicity, enterotoxigenicity, and drug-resistance characteristics of avian Escherichia coli. Avian Dis. 1989 Oct-Dec;33(4):631–635. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Evans D. G., Evans D. J., Jr, Tjoa W. Hemagglutination of human group A erythrocytes by enterotoxigenic Escherichia coli isolated from adults with diarrhea: correlation with colonization factor. Infect Immun. 1977 Nov;18(2):330–337. doi: 10.1128/iai.18.2.330-337.1977. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Evans D. J., Jr, Evans D. G., DuPont H. L. Hemagglutination patterns of enterotoxigenic and enteropathogenic Escherichia coli determined with human, bovine, chicken, and guinea pig erythrocytes in the presence and absence of mannose. Infect Immun. 1979 Feb;23(2):336–346. doi: 10.1128/iai.23.2.336-346.1979. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gonzalez E. A., Blanco J., Baloda S. B., Fröman G., Dho M., Lafont J. P., Wadström T. Virulent Escherichia coli strains for chicks bind fibronectin and type II collagen. Microbios. 1990;62(251):113–127. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hagberg L., Jodal U., Korhonen T. K., Lidin-Janson G., Lindberg U., Svanborg Edén C. Adhesion, hemagglutination, and virulence of Escherichia coli causing urinary tract infections. Infect Immun. 1981 Feb;31(2):564–570. doi: 10.1128/iai.31.2.564-570.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hamilton C. M., Aldea M., Washburn B. K., Babitzke P., Kushner S. R. New method for generating deletions and gene replacements in Escherichia coli. J Bacteriol. 1989 Sep;171(9):4617–4622. doi: 10.1128/jb.171.9.4617-4622.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hull R. A., Gill R. E., Hsu P., Minshew B. H., Falkow S. Construction and expression of recombinant plasmids encoding type 1 or D-mannose-resistant pili from a urinary tract infection Escherichia coli isolate. Infect Immun. 1981 Sep;33(3):933–938. doi: 10.1128/iai.33.3.933-938.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jones G. W., Rutter J. M. The association of K88 antigen with haemagglutinating activity in porcine strains of Escherichia coli. J Gen Microbiol. 1974 Sep;84(1):135–144. doi: 10.1099/00221287-84-1-135. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LENNOX E. S. Transduction of linked genetic characters of the host by bacteriophage P1. Virology. 1955 Jul;1(2):190–206. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(55)90016-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nivas S. C., Peterson A. C., York M. D., Pomeroy B. S., Jacobson L. D., Jordan K. A. Epizootiological investigations of colibacillosis in turkeys. Avian Dis. 1977 Oct-Dec;21(4):514–530. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Olsén A., Jonsson A., Normark S. Fibronectin binding mediated by a novel class of surface organelles on Escherichia coli. Nature. 1989 Apr 20;338(6217):652–655. doi: 10.1038/338652a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vidotto M. C., Müller E. E., de Freitas J. C., Alfieri A. A., Guimarães I. G., Santos D. S. Virulence factors of avian Escherichia coli. Avian Dis. 1990 Jul-Sep;34(3):531–538. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vieira J., Messing J. The pUC plasmids, an M13mp7-derived system for insertion mutagenesis and sequencing with synthetic universal primers. Gene. 1982 Oct;19(3):259–268. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(82)90015-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yerushalmi Z., Smorodinsky N. I., Naveh M. W., Ron E. Z. Adherence pili of avian strains of Escherichia coli O78. Infect Immun. 1990 Apr;58(4):1129–1131. doi: 10.1128/iai.58.4.1129-1131.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]