Abstract
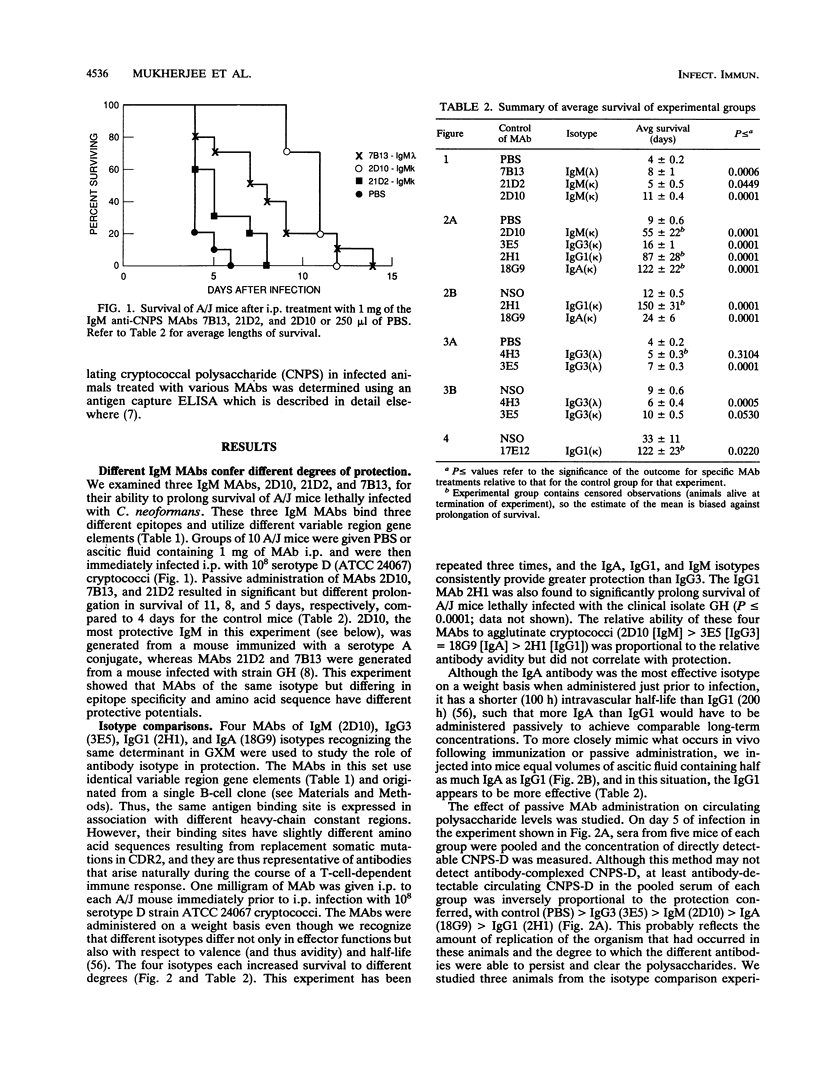
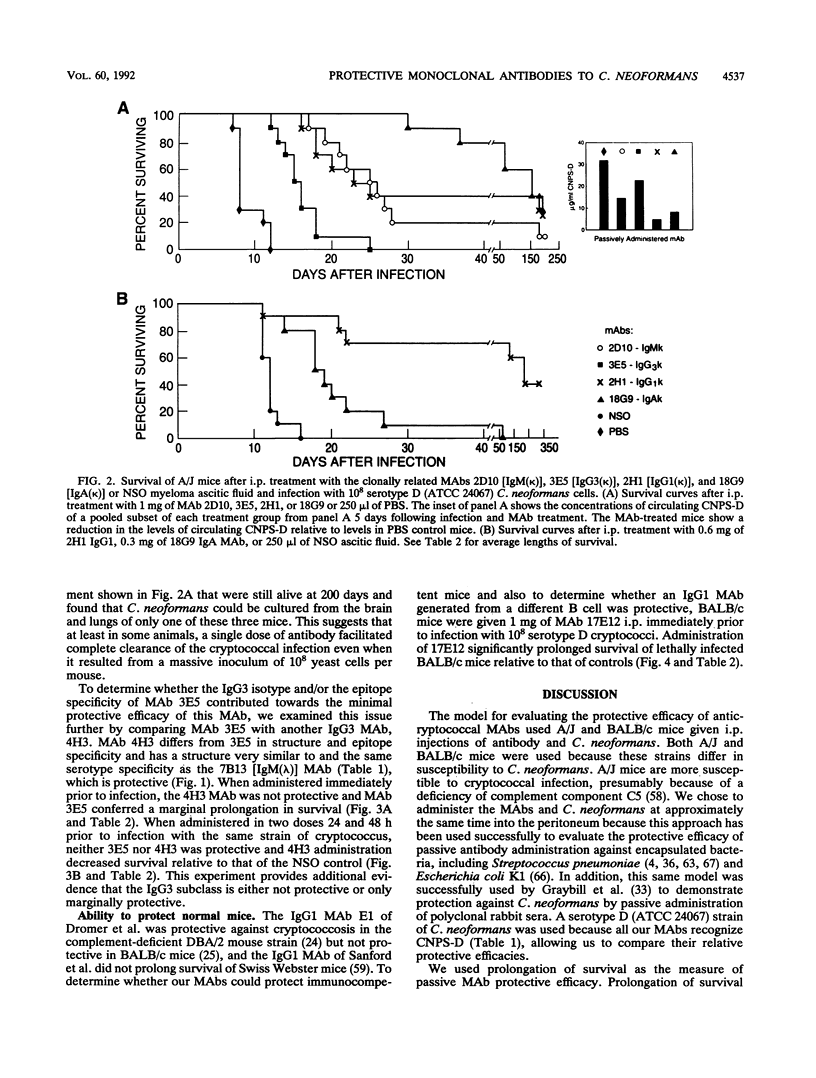
Several murine monoclonal antibodies (MAbs) specific for the capsular glucuronoxylomannan of Cryptococcus neoformans were studied for their capacity to confer protection when passively administered to lethally infected mice. The MAb group studied recognized at least three distinct epitopes and included immunoglobulin M (IgM), IgG3, IgG1, and IgA isotypes. The protection model used A/J and BALB/c mice infected intraperitoneally with 10(8) cryptococci. The MAbs were administered either immediately preceding or, in one experiment, 24 to 48 h prior to infection. Protective efficacy was assessed by the ability of passively administered MAbs to prolong the survival of lethally infected mice. Three IgM MAbs, each of which recognized a distinct epitope, were able to prolong survival of lethally infected mice to different extents. A set of IgM, IgG3, IgG1 and IgA MAbs which utilize the same immunoglobulin gene elements and were derived from the same B-cell clone exhibited significant class differences in protective efficacy with IgA, IgG1 > IgM > IgG3. The results confirm that protective MAbs against C. neoformans capsular polysaccharide exist and strongly suggest that both epitope specificity and isotype are important determinants of protective efficacy.
Full text
PDF





Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- BLOOMFIELD N., GORDON M. A., ELMENDORF D. F., Jr DETECTION OF CRYPTOCOCCUS NEOFORMANS ANTIGEN IN BODY FLUIDS BY LATEX PARTICLE AGGLUTINATION. Proc Soc Exp Biol Med. 1963 Oct;114:64–67. doi: 10.3181/00379727-114-28586. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Briles D. E., Claflin J. L., Schroer K., Forman C. Mouse Igg3 antibodies are highly protective against infection with Streptococcus pneumoniae. Nature. 1981 Nov 5;294(5836):88–90. doi: 10.1038/294088a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Briles D. E., Forman C., Hudak S., Claflin J. L. Anti-phosphorylcholine antibodies of the T15 idiotype are optimally protective against Streptococcus pneumoniae. J Exp Med. 1982 Oct 1;156(4):1177–1185. doi: 10.1084/jem.156.4.1177. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bulmer G. S., Tacker J. R. Phagocytosis of Cryptococcus neoformans by alveolar macrophages. Infect Immun. 1975 Jan;11(1):73–79. doi: 10.1128/iai.11.1.73-79.1975. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Casadevall A., Mukherjee J., Devi S. J., Schneerson R., Robbins J. B., Scharff M. D. Antibodies elicited by a Cryptococcus neoformans-tetanus toxoid conjugate vaccine have the same specificity as those elicited in infection. J Infect Dis. 1992 Jun;165(6):1086–1093. doi: 10.1093/infdis/165.6.1086. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Casadevall A., Scharff M. D. The mouse antibody response to infection with Cryptococcus neoformans: VH and VL usage in polysaccharide binding antibodies. J Exp Med. 1991 Jul 1;174(1):151–160. doi: 10.1084/jem.174.1.151. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Childers N. K., Bruce M. G., McGhee J. R. Molecular mechanisms of immunoglobulin A defense. Annu Rev Microbiol. 1989;43:503–536. doi: 10.1146/annurev.mi.43.100189.002443. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Collins H. L., Bancroft G. J. Encapsulation of Cryptococcus neoformans impairs antigen-specific T-cell responses. Infect Immun. 1991 Nov;59(11):3883–3888. doi: 10.1128/iai.59.11.3883-3888.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Davies S. F., Clifford D. P., Hoidal J. R., Repine J. E. Opsonic requirements for the uptake of Cryptococcus neoformans by human polymorphonuclear leukocytes and monocytes. J Infect Dis. 1982 Jun;145(6):870–874. doi: 10.1093/infdis/145.6.870. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Diamond B., Birshtein B. K., Scharff M. D. Site of binding of mouse IgG2b to the Fc receptor on mouse macrophages. J Exp Med. 1979 Sep 19;150(3):721–726. doi: 10.1084/jem.150.3.721. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Diamond B., Scharff M. D. IgG1 and IgG2b share the Fc receptor on mouse macrophages. J Immunol. 1980 Aug;125(2):631–633. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Diamond B., Yelton D. E. A new Fc receptor on mouse macrophages binding IgG3. J Exp Med. 1981 Mar 1;153(3):514–519. doi: 10.1084/jem.153.3.514. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Diamond R. D., Allison A. C. Nature of the effector cells responsible for antibody-dependent cell-mediated killing of Cryptococcus neoformans. Infect Immun. 1976 Sep;14(3):716–720. doi: 10.1128/iai.14.3.716-720.1976. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Diamond R. D. Antibody-dependent killing of Cryptococcus neopormans by human peripheral blood mononuclear cells. Nature. 1974 Jan 18;247(5437):148–150. doi: 10.1038/247148a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Diamond R. D., Bennett J. E. Prognostic factors in cryptococcal meningitis. A study in 111 cases. Ann Intern Med. 1974 Feb;80(2):176–181. doi: 10.7326/0003-4819-80-2-176. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Diamond R. D., May J. E., Kane M. A., Frank M. M., Bennett J. E. The role of the classical and alternate complement pathways in host defenses against Cryptococcus neoformans infection. J Immunol. 1974 Jun;112(6):2260–2270. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dromer F., Aucouturier P., Clauvel J. P., Saimot G., Yeni P. Cryptococcus neoformans antibody levels in patients with AIDS. Scand J Infect Dis. 1988;20(3):283–285. doi: 10.3109/00365548809032452. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dromer F., Barbet J., Bolard J., Charreire J., Yeni P. Improvement of amphotericin B activity during experimental cryptococcosis by incorporation into specific immunoliposomes. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1990 Nov;34(11):2055–2060. doi: 10.1128/aac.34.11.2055. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dromer F., Charreire J., Contrepois A., Carbon C., Yeni P. Protection of mice against experimental cryptococcosis by anti-Cryptococcus neoformans monoclonal antibody. Infect Immun. 1987 Mar;55(3):749–752. doi: 10.1128/iai.55.3.749-752.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dromer F., Charreire J. Improved amphotericin B activity by a monoclonal anti-Cryptococcus neoformans antibody: study during murine cryptococcosis and mechanisms of action. J Infect Dis. 1991 May;163(5):1114–1120. doi: 10.1093/infdis/163.5.1114. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dromer F., Perronne C., Barge J., Vilde J. L., Yeni P. Role of IgG and complement component C5 in the initial course of experimental cryptococcosis. Clin Exp Immunol. 1989 Dec;78(3):412–417. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eng R. H., Bishburg E., Smith S. M., Kapila R. Cryptococcal infections in patients with acquired immune deficiency syndrome. Am J Med. 1986 Jul;81(1):19–23. doi: 10.1016/0002-9343(86)90176-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- FARQUHARSON R. F. WILBERT HURST BROWN, 1899--1964. Trans Assoc Am Physicians. 1964;77:14–16. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- GADEBUSCH H. H. Passive immunization against Cryptococcus neoformans. Proc Soc Exp Biol Med. 1958 Jul;98(3):611–614. doi: 10.3181/00379727-98-24123. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gauldie J., Richards C., Lamontagne L. Fc receptors for IgA and other immunoglobulins on resident and activated alveolar macrophages. Mol Immunol. 1983 Sep;20(9):1029–1037. doi: 10.1016/0161-5890(83)90044-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goren M. B. Experimental murine cryptococcosis: effect of hyperimmunization to capsular polysaccharide. J Immunol. 1967 May;98(5):914–922. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Graybill J. R., Alford R. H. Cell-mediated immunity in Cryptococcosis. Cell Immunol. 1974 Oct;14(1):12–21. doi: 10.1016/0008-8749(74)90164-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Graybill J. R., Hague M., Drutz D. J. Passive immunization in murine cryptococcosis. Sabouraudia. 1981 Dec;19(4):237–244. doi: 10.1080/00362178185380411. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Greenspan N. S., Dacek D. A., Cooper L. J. Fc region-dependence of IgG3 anti-streptococcal group A carbohydrate antibody functional affinity. I. The effect of temperature. J Immunol. 1988 Dec 15;141(12):4276–4282. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gupta S., Ellis M., Cesario T., Ruhling M., Vayuvegula B. Disseminated cryptococcal infection in a patient with hypogammaglobulinemia and normal T cell functions. Am J Med. 1987 Jan;82(1):129–131. doi: 10.1016/0002-9343(87)90388-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hill W. C., Robbins J. B. Horse anti-pneumococcal immunoglobulins. II. Specific mouse protective activity. Proc Soc Exp Biol Med. 1966 Oct;123(1):105–108. doi: 10.3181/00379727-123-31414. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Huffnagle G. B., Yates J. L., Lipscomb M. F. T cell-mediated immunity in the lung: a Cryptococcus neoformans pulmonary infection model using SCID and athymic nude mice. Infect Immun. 1991 Apr;59(4):1423–1433. doi: 10.1128/iai.59.4.1423-1433.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jimenez-Lucho V., Ginsburg V., Krivan H. C. Cryptococcus neoformans, Candida albicans, and other fungi bind specifically to the glycosphingolipid lactosylceramide (Gal beta 1-4Glc beta 1-1Cer), a possible adhesion receptor for yeasts. Infect Immun. 1990 Jul;58(7):2085–2090. doi: 10.1128/iai.58.7.2085-2090.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kozel T. R., Cazin J. Nonencapsulated Variant of Cryptococcus neoformans I. Virulence Studies and Characterization of Soluble Polysaccharide. Infect Immun. 1971 Feb;3(2):287–294. doi: 10.1128/iai.3.2.287-294.1971. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kozel T. R., Follette J. L. Opsonization of encapsulated Cryptococcus neoformans by specific anticapsular antibody. Infect Immun. 1981 Mar;31(3):978–984. doi: 10.1128/iai.31.3.978-984.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kozel T. R., Gulley W. F., Cazin J., Jr Immune response to Cryptococcus neoformans soluble polysaccharide: immunological unresponsiveness. Infect Immun. 1977 Dec;18(3):701–707. doi: 10.1128/iai.18.3.701-707.1977. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kozel T. R., Pfrommer G. S., Guerlain A. S., Highison B. A., Highison G. J. Role of the capsule in phagocytosis of Cryptococcus neoformans. Rev Infect Dis. 1988 Jul-Aug;10 (Suppl 2):S436–S439. doi: 10.1093/cid/10.supplement_2.s436. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Levitz S. M., DiBenedetto D. J. Differential stimulation of murine resident peritoneal cells by selectively opsonized encapsulated and acapsular Cryptococcus neoformans. Infect Immun. 1988 Oct;56(10):2544–2551. doi: 10.1128/iai.56.10.2544-2551.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Levitz S. M., Farrell T. P., Maziarz R. T. Killing of Cryptococcus neoformans by human peripheral blood mononuclear cells stimulated in culture. J Infect Dis. 1991 May;163(5):1108–1113. doi: 10.1093/infdis/163.5.1108. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lipscomb M. F., Alvarellos T., Toews G. B., Tompkins R., Evans Z., Koo G., Kumar V. Role of natural killer cells in resistance to Cryptococcus neoformans infections in mice. Am J Pathol. 1987 Aug;128(2):354–361. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Louria D. B., Kaminski T. Passively-acquired immunity in experimental cryptococcosis. Sabouraudia. 1965 Jun;4(2):80–84. doi: 10.1080/00362176685190211. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miller M. F., Mitchell T. G., Storkus W. J., Dawson J. R. Human natural killer cells do not inhibit growth of Cryptococcus neoformans in the absence of antibody. Infect Immun. 1990 Mar;58(3):639–645. doi: 10.1128/iai.58.3.639-645.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mitchell T. G., Friedman L. In vitro phagocytosis and intracellular fate of variously encapsulated strains of Cryptococcus neoformans. Infect Immun. 1972 Apr;5(4):491–498. doi: 10.1128/iai.5.4.491-498.1972. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Monga D. P., Kumar R., Mohapatra L. N., Malaviya A. N. Experimental cryptococcosis in normal and B-cell-deficient mice. Infect Immun. 1979 Oct;26(1):1–3. doi: 10.1128/iai.26.1.1-3.1979. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nabavi N., Murphy J. W. Antibody-dependent natural killer cell-mediated growth inhibition of Cryptococcus neoformans. Infect Immun. 1986 Feb;51(2):556–562. doi: 10.1128/iai.51.2.556-562.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Oishi K., Koles N. L., Guelde G., Pollack M. Antibacterial and protective properties of monoclonal antibodies reactive with Escherichia coli O111:B4 lipopolysaccharide: relation to antibody isotype and complement-fixing activity. J Infect Dis. 1992 Jan;165(1):34–45. doi: 10.1093/infdis/165.1.34. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pelkonen S., Pluschke G. Use of hybridoma immunoglobulin switch variants in the analysis of the protective properties of anti-lipopolysaccharide antibodies in Escherichia coli K1 infection. Immunology. 1989 Oct;68(2):260–264. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pettoello-Mantovani M., Casadevall A., Kollmann T. R., Rubinstein A., Goldstein H. Enhancement of HIV-1 infection by the capsular polysaccharide of Cryptococcus neoformans. Lancet. 1992 Jan 4;339(8784):21–23. doi: 10.1016/0140-6736(92)90142-p. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pfaffenbach G., Lamm M. E., Gigli I. Activation of the guinea pig alternative complement pathway by mouse IgA immune complexes. J Exp Med. 1982 Jan 1;155(1):231–247. doi: 10.1084/jem.155.1.231. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pollock R. R., French D. L., Metlay J. P., Birshtein B. K., Scharff M. D. Intravascular metabolism of normal and mutant mouse immunoglobulin molecules. Eur J Immunol. 1990 Sep;20(9):2021–2027. doi: 10.1002/eji.1830200921. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ravetch J. V., Kinet J. P. Fc receptors. Annu Rev Immunol. 1991;9:457–492. doi: 10.1146/annurev.iy.09.040191.002325. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rhodes J. C., Wicker L. S., Urba W. J. Genetic control of susceptibility to Cryptococcus neoformans in mice. Infect Immun. 1980 Aug;29(2):494–499. doi: 10.1128/iai.29.2.494-499.1980. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sanford J. E., Lupan D. M., Schlageter A. M., Kozel T. R. Passive immunization against Cryptococcus neoformans with an isotype-switch family of monoclonal antibodies reactive with cryptococcal polysaccharide. Infect Immun. 1990 Jun;58(6):1919–1923. doi: 10.1128/iai.58.6.1919-1923.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Small J. M., Mitchell T. G. Strain variation in antiphagocytic activity of capsular polysaccharides from Cryptococcus neoformans serotype A. Infect Immun. 1989 Dec;57(12):3751–3756. doi: 10.1128/iai.57.12.3751-3756.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Spiegelberg H. L. Biological activities of immunoglobulins of different classes and subclasses. Adv Immunol. 1974;19(0):259–294. doi: 10.1016/s0065-2776(08)60254-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Spiropulu C., Eppard R. A., Otteson E., Kozel T. R. Antigenic variation within serotypes of Cryptococcus neoformans detected by monoclonal antibodies specific for the capsular polysaccharide. Infect Immun. 1989 Oct;57(10):3240–3242. doi: 10.1128/iai.57.10.3240-3242.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Szu S. C., Schneerson R., Robbins J. B. Rabbit antibodies to the cell wall polysaccharide of Streptococcus pneumoniae fail to protect mice from lethal challenge with encapsulated pneumococci. Infect Immun. 1986 Nov;54(2):448–455. doi: 10.1128/iai.54.2.448-455.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Underdown B. J., Schiff J. M. Immunoglobulin A: strategic defense initiative at the mucosal surface. Annu Rev Immunol. 1986;4:389–417. doi: 10.1146/annurev.iy.04.040186.002133. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Unkeless J. C., Eisen H. N. Binding of monomeric immunoglobulins to Fc receptors of mouse macrophages. J Exp Med. 1975 Dec 1;142(6):1520–1533. doi: 10.1084/jem.142.6.1520. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wolff E. A., Esselstyn J., Maloney G., Raff H. V. Human monoclonal antibody homodimers. Effect of valency on in vitro and in vivo antibacterial activity. J Immunol. 1992 Apr 15;148(8):2469–2474. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yother J., Forman C., Gray B. M., Briles D. E. Protection of mice from infection with Streptococcus pneumoniae by anti-phosphocholine antibody. Infect Immun. 1982 Apr;36(1):184–188. doi: 10.1128/iai.36.1.184-188.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zuger A., Louie E., Holzman R. S., Simberkoff M. S., Rahal J. J. Cryptococcal disease in patients with the acquired immunodeficiency syndrome. Diagnostic features and outcome of treatment. Ann Intern Med. 1986 Feb;104(2):234–240. doi: 10.7326/0003-4819-104-2-234. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


