Fig. 2.
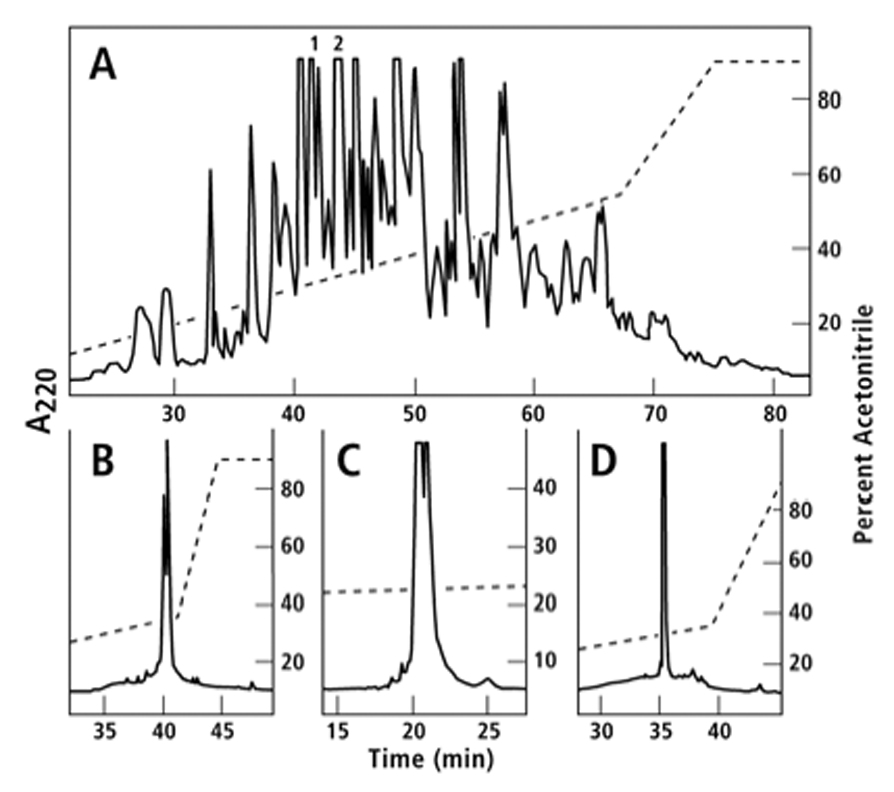
Purification of gsp9a and gsp9b. The components of the G. speciosa venom duct extract prepared as described under Methods were separated by sequential elution with gradients of 4.5% to 54% acetonitrile in 55 min and 54% to 90% acetonitrile in 8 min in the presence of 0.1% TFA. The absorbance profile at 220 nm is shown in Fig. 2, Panel A. An aliquot of Peak 1 in Panel A was reduced and pyridylethylated. The pyridylethylated mixture was fractionated on an analytical C18 column employing a gradient of 0.45% acetonitrile/min in 0/1% TFA, (Panel B). The more hydrophobic peak was determined as described in Methods to be gsp9a and the sequence is shown in Table 2. Peak 2 in Panel A was subfractionated on an analytical C18 HPLC column with a gradient of 0.18% acetonitrile/min in 0.1% TFA (Panel C). The components of the more hydrophobic peak were reduced, pyridylethylated, and then fractionated with a gradient of 0.45% acetonitrile/min in 0.1% TFA on an analytical C18 HPLC column (Panel D). The main peak in Panel D was determined by MALDI and amino acid sequencing to be gsp9b (Table 2).
