Abstract
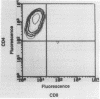
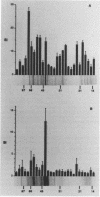
Chlamydia-specific short-term T-cell lines were used in conjunction with immunoblot techniques to examine Chlamydia trachomatis proteins for T-cell-stimulatory activity. This study was undertaken because of the known role of T cells in the resolution and pathogenesis of chlamydial infections. Therefore, determination of which chlamydial proteins are T-cell antigens and whether they evoke protective immunity or contribute to immunopathology is crucial. Immune lymph node cells were stimulated with whole chlamydial organism (elementary body) to derive predominantly CD4+ T-cell lines. Proteins from the elementary body and the outer membrane and cloned proteins were examined for antigenicity with these T-cell lines in a proliferation assay. Although a majority of the elementary body protein fractions were positive in this assay, only four of the outer membrane fractions were stimulatory. The cloned major outer membrane protein and outer membrane protein 2 were stimulatory in the assay and may account for the reactivity in three of the four positive outer membrane fractions. The C. trachomatis heat shock protein 60, examined because of its putative role in causing delayed-type hypersensitivity, was found to stimulate the CD4+ T cells. This approach with short-term T-cell lines with polyclonal reactivity was sensitive and specific in identifying chlamydial proteins as T-cell antigens.
Full text
PDF

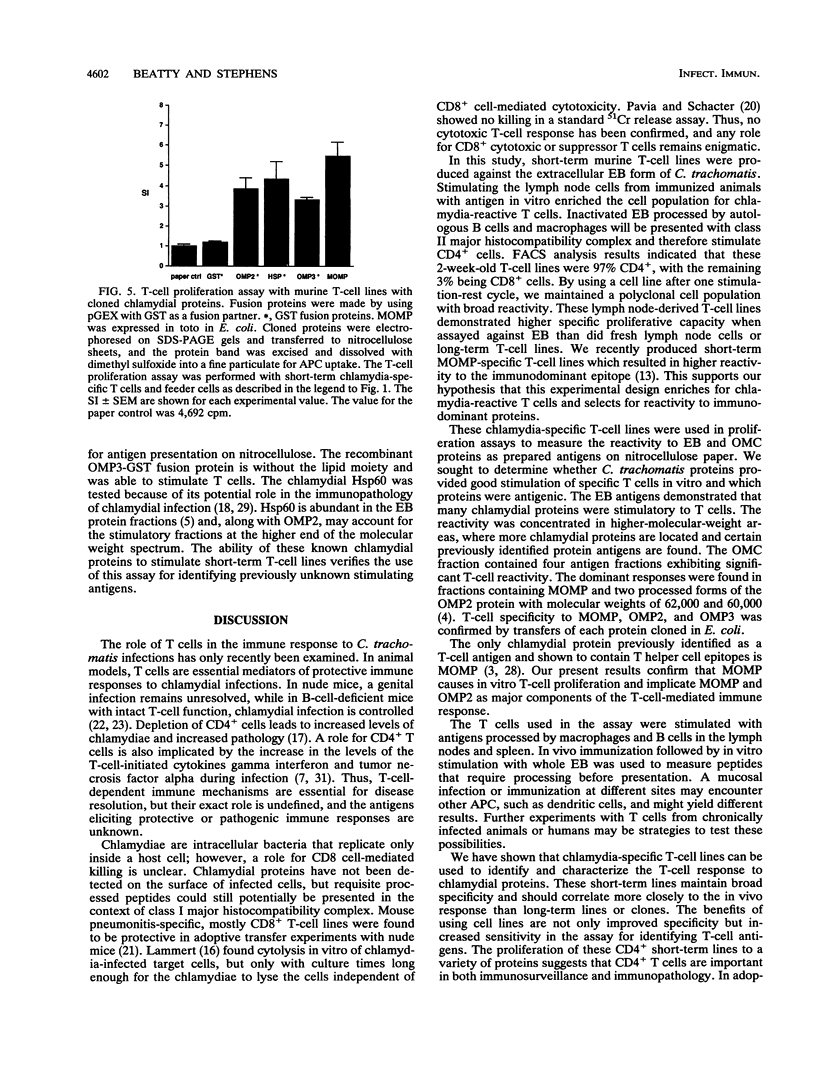

Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Abou-Zeid C., Filley E., Steele J., Rook G. A. A simple new method for using antigens separated by polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis to stimulate lymphocytes in vitro after converting bands cut from Western blots into antigen-bearing particles. J Immunol Methods. 1987 Apr 2;98(1):5–10. doi: 10.1016/0022-1759(87)90429-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Allen J. E., Cerrone M. C., Beatty P. R., Stephens R. S. Cysteine-rich outer membrane proteins of Chlamydia trachomatis display compensatory sequence changes between biovariants. Mol Microbiol. 1990 Sep;4(9):1543–1550. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2958.1990.tb02065.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Allen J. E., Locksley R. M., Stephens R. S. A single peptide from the major outer membrane protein of Chlamydia trachomatis elicits T cell help for the production of antibodies to protective determinants. J Immunol. 1991 Jul 15;147(2):674–679. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Allen J. E., Stephens R. S. Identification by sequence analysis of two-site posttranslational processing of the cysteine-rich outer membrane protein 2 of Chlamydia trachomatis serovar L2. J Bacteriol. 1989 Jan;171(1):285–291. doi: 10.1128/jb.171.1.285-291.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bavoil P., Stephens R. S., Falkow S. A soluble 60 kiloDalton antigen of Chlamydia spp. is a homologue of Escherichia coli GroEL. Mol Microbiol. 1990 Mar;4(3):461–469. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2958.1990.tb00612.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brunham R. C., Martin D. H., Kuo C. C., Wang S. P., Stevens C. E., Hubbard T., Holmes K. K. Cellular immune response during uncomplicated genital infection with Chlamydia trachomatis in humans. Infect Immun. 1981 Oct;34(1):98–104. doi: 10.1128/iai.34.1.98-104.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Byrne G. I., Grubbs B., Dickey T. J., Schachter J., Williams D. M. Interferon in recovery from pneumonia due to Chlamydia trachomatis in the mouse. J Infect Dis. 1987 Dec;156(6):993–996. doi: 10.1093/infdis/156.6.993. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Caldwell H. D., Kromhout J., Schachter J. Purification and partial characterization of the major outer membrane protein of Chlamydia trachomatis. Infect Immun. 1981 Mar;31(3):1161–1176. doi: 10.1128/iai.31.3.1161-1176.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cerrone M. C., Ma J. J., Stephens R. S. Cloning and sequence of the gene for heat shock protein 60 from Chlamydia trachomatis and immunological reactivity of the protein. Infect Immun. 1991 Jan;59(1):79–90. doi: 10.1128/iai.59.1.79-90.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Davern K. M., Tiu W. U., Morahan G., Wright M. D., Garcia E. G., Mitchell G. F. Responses in mice to Sj26, a glutathione S-transferase of Schistosoma japonicum worms. Immunol Cell Biol. 1987 Dec;65(Pt 6):473–482. doi: 10.1038/icb.1987.56. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Everett K. D., Hatch T. P. Sequence analysis and lipid modification of the cysteine-rich envelope proteins of Chlamydia psittaci 6BC. J Bacteriol. 1991 Jun;173(12):3821–3830. doi: 10.1128/jb.173.12.3821-3830.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grayston J. T., Wang S. P., Yeh L. J., Kuo C. C. Importance of reinfection in the pathogenesis of trachoma. Rev Infect Dis. 1985 Nov-Dec;7(6):717–725. doi: 10.1093/clinids/7.6.717. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ishizaki M., Allen J. E., Beatty P. R., Stephens R. S. Immune specificity of murine T-cell lines to the major outer membrane protein of Chlamydia trachomatis. Infect Immun. 1992 Sep;60(9):3714–3718. doi: 10.1128/iai.60.9.3714-3718.1992. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Koehler J. E., Birkelund S., Stephens R. S. Overexpression and surface localization of the Chlamydia trachomatis major outer membrane protein in Escherichia coli. Mol Microbiol. 1992 May;6(9):1087–1094. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2958.1992.tb01545.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Koehler J. E., Burgess R. R., Thompson N. E., Stephens R. S. Chlamydia trachomatis RNA polymerase major sigma subunit. Sequence and structural comparison of conserved and unique regions with Escherichia coli sigma 70 and Bacillus subtilis sigma 43. J Biol Chem. 1990 Aug 5;265(22):13206–13214. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lammert J. K. Cytotoxic cells induced after Chlamydia psittaci infection in mice. Infect Immun. 1982 Mar;35(3):1011–1017. doi: 10.1128/iai.35.3.1011-1017.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Landers D. V., Erlich K., Sung M., Schachter J. Role of L3T4-bearing T-cell populations in experimental murine chlamydial salpingitis. Infect Immun. 1991 Oct;59(10):3774–3777. doi: 10.1128/iai.59.10.3774-3777.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morrison R. P., Belland R. J., Lyng K., Caldwell H. D. Chlamydial disease pathogenesis. The 57-kD chlamydial hypersensitivity antigen is a stress response protein. J Exp Med. 1989 Oct 1;170(4):1271–1283. doi: 10.1084/jem.170.4.1271. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morrison R. P., Lyng K., Caldwell H. D. Chlamydial disease pathogenesis. Ocular hypersensitivity elicited by a genus-specific 57-kD protein. J Exp Med. 1989 Mar 1;169(3):663–675. doi: 10.1084/jem.169.3.663. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pavia C. S., Schachter J. Failure to detect cell-mediated cytotoxicity against Chlamydia trachomatis-infected cells. Infect Immun. 1983 Mar;39(3):1271–1274. doi: 10.1128/iai.39.3.1271-1274.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ramsey K. H., Rank R. G. Resolution of chlamydial genital infection with antigen-specific T-lymphocyte lines. Infect Immun. 1991 Mar;59(3):925–931. doi: 10.1128/iai.59.3.925-931.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ramsey K. H., Soderberg L. S., Rank R. G. Resolution of chlamydial genital infection in B-cell-deficient mice and immunity to reinfection. Infect Immun. 1988 May;56(5):1320–1325. doi: 10.1128/iai.56.5.1320-1325.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rank R. G., Soderberg L. S., Barron A. L. Chronic chlamydial genital infection in congenitally athymic nude mice. Infect Immun. 1985 Jun;48(3):847–849. doi: 10.1128/iai.48.3.847-849.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shemer-Avni Y., Wallach D., Sarov I. Inhibition of Chlamydia trachomatis growth by recombinant tumor necrosis factor. Infect Immun. 1988 Sep;56(9):2503–2506. doi: 10.1128/iai.56.9.2503-2506.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith D. B., Johnson K. S. Single-step purification of polypeptides expressed in Escherichia coli as fusions with glutathione S-transferase. Gene. 1988 Jul 15;67(1):31–40. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(88)90005-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stephens R. S., Chen W. J., Kuo C. C. Effects of corticosteroids and cyclophosphamide on a mouse model of Chlamydia trachomatis pneumonitis. Infect Immun. 1982 Feb;35(2):680–684. doi: 10.1128/iai.35.2.680-684.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stephens R. S., Wagar E. A., Schoolnik G. K. High-resolution mapping of serovar-specific and common antigenic determinants of the major outer membrane protein of Chlamydia trachomatis. J Exp Med. 1988 Mar 1;167(3):817–831. doi: 10.1084/jem.167.3.817. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Su H., Morrison R. P., Watkins N. G., Caldwell H. D. Identification and characterization of T helper cell epitopes of the major outer membrane protein of Chlamydia trachomatis. J Exp Med. 1990 Jul 1;172(1):203–212. doi: 10.1084/jem.172.1.203. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wagar E. A., Schachter J., Bavoil P., Stephens R. S. Differential human serologic response to two 60,000 molecular weight Chlamydia trachomatis antigens. J Infect Dis. 1990 Oct;162(4):922–927. doi: 10.1093/infdis/162.4.922. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Williams D. M., Grubbs B., Schachter J. Primary murine Chlamydia trachomatis pneumonia in B-cell-deficient mice. Infect Immun. 1987 Oct;55(10):2387–2390. doi: 10.1128/iai.55.10.2387-2390.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Williams D. M., Schachter J., Drutz D. J., Sumaya C. V. Pneumonia due to Chlamydia trachomatis in the immunocompromised (nude) mouse. J Infect Dis. 1981 Feb;143(2):238–241. doi: 10.1093/infdis/143.2.238. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zhang Y. X., Stewart S., Joseph T., Taylor H. R., Caldwell H. D. Protective monoclonal antibodies recognize epitopes located on the major outer membrane protein of Chlamydia trachomatis. J Immunol. 1987 Jan 15;138(2):575–581. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]