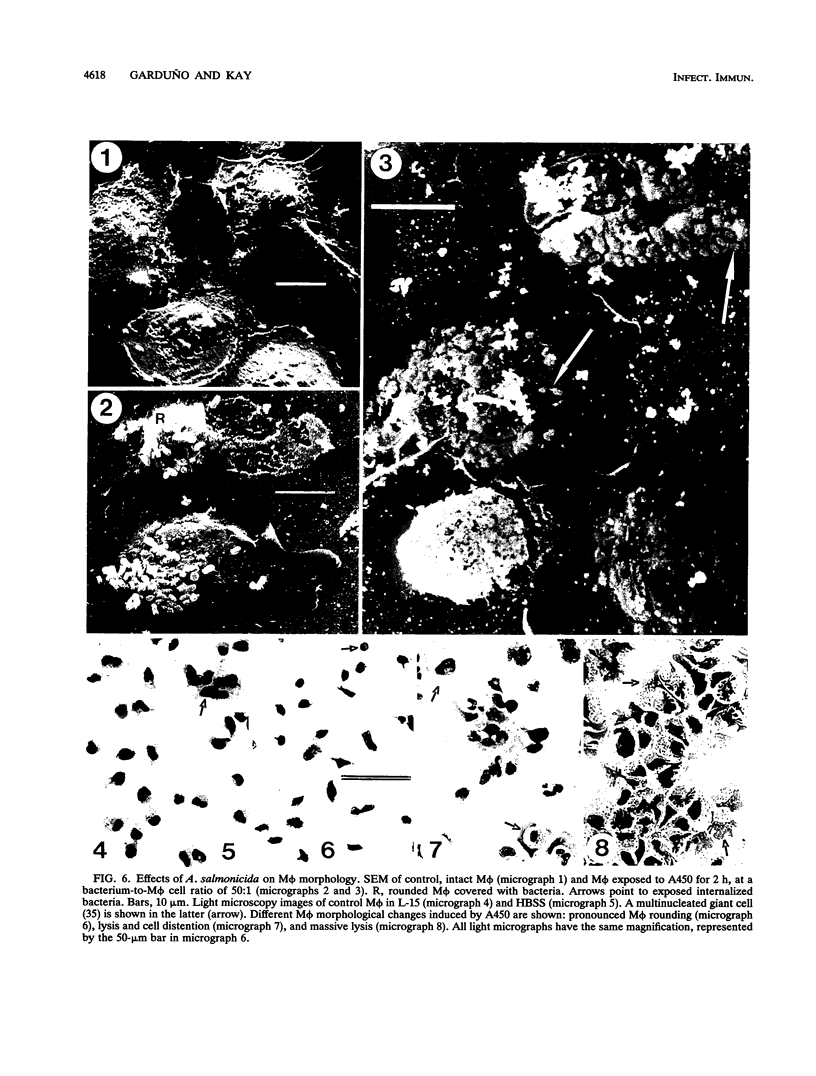
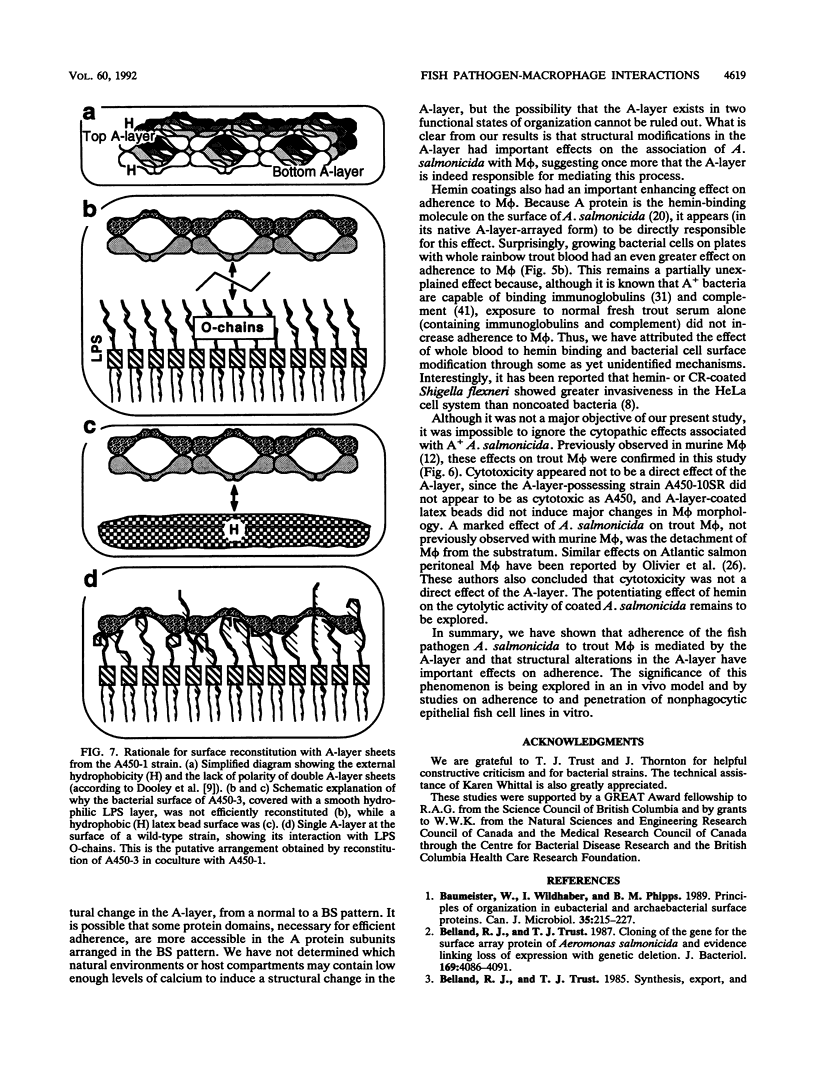
Abstract
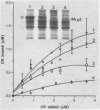
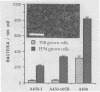
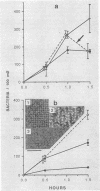
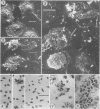
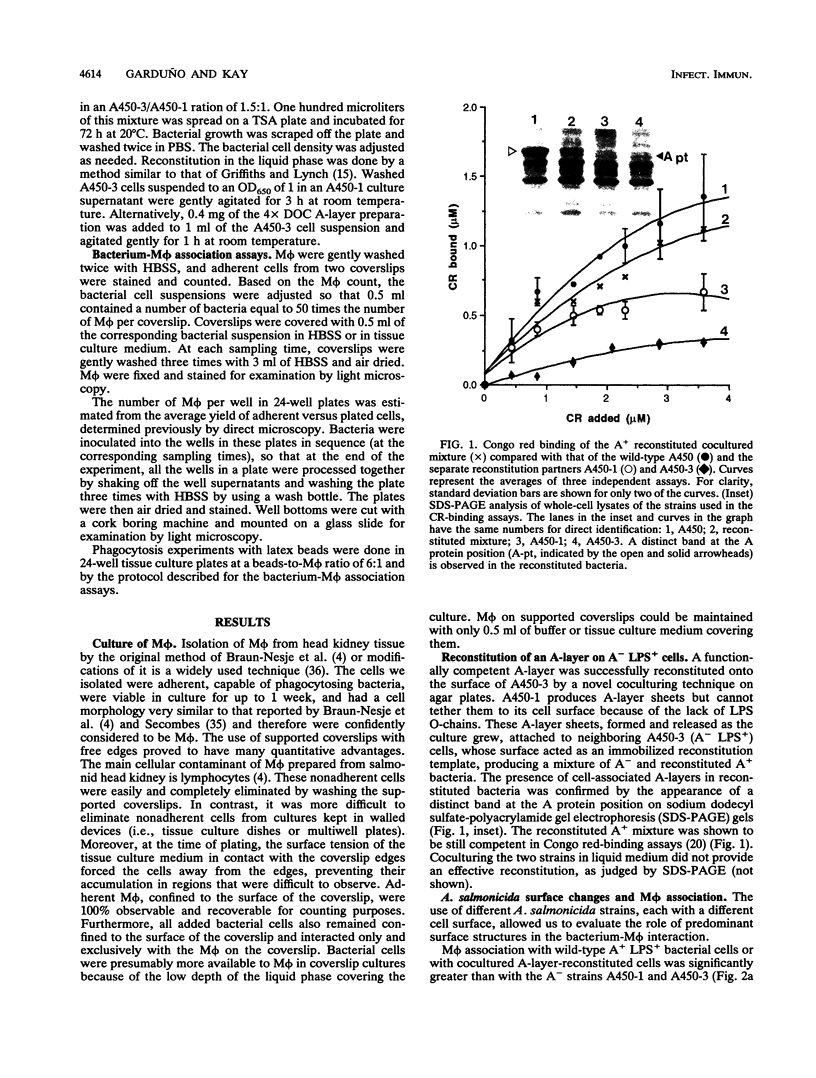
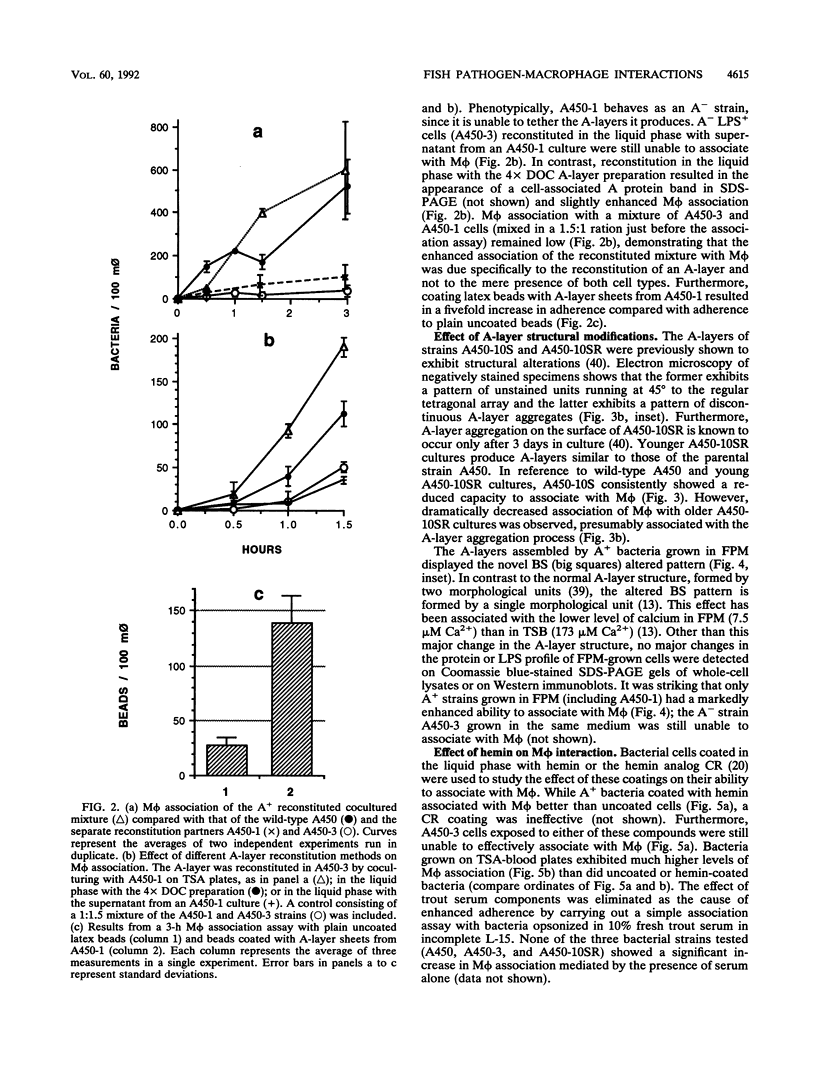
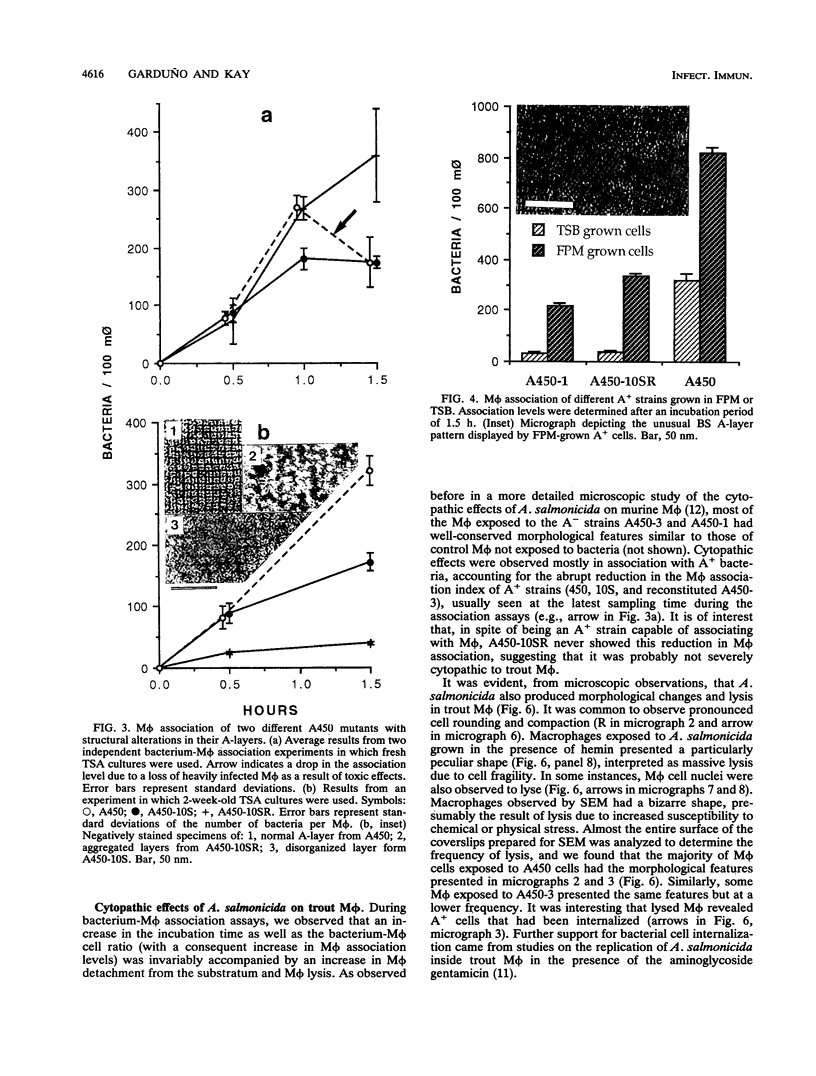
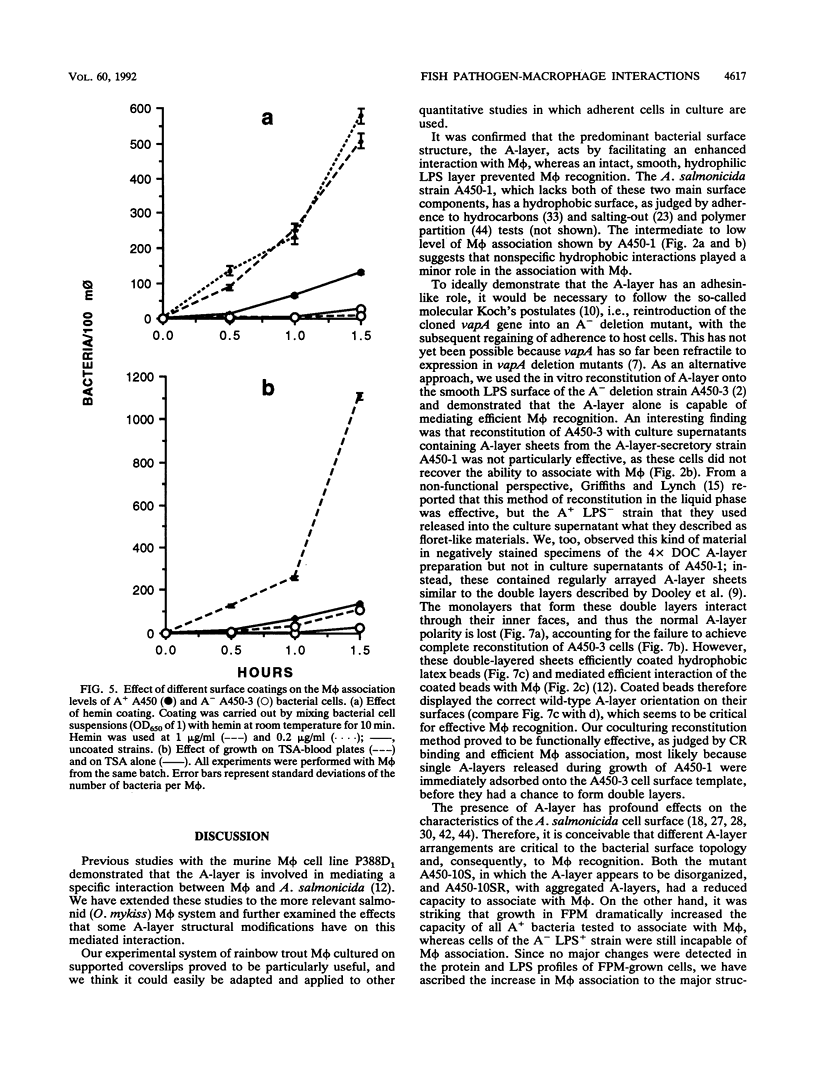
A procedure was developed to culture rainbow trout macrophages (M phi) on supported glass coverslips. Using this method and a variety of well-characterized Aeromonas salmonicida strains with normal or altered cell surfaces, we investigated the role of this unusual bacterial surface in the bacterium-M phi interaction. An intact crystalline protein array, the A-layer, mediated adherence of A. salmonicida cells to M phi even in the absence of opsonins. In contrast, unopsonized cells of an A-layer-negative (A-) mutant with a smooth lipopolysaccharide (LPS) layer were unable to interact with M phi. However, this ability was recovered when the A-layer was reconstituted onto the smooth LPS surface of these A- LPS+ cells. Two A. salmonicida mutants possessing the A-layer in different disorganized states had a reduced ability to interact with M phi. A+ cells grown under calcium limitation produced A-layers locked into an alternative conformation which mediated the highest levels of M phi association in the absence of opsonins or any other surface coating. Coating A+ cells with hemin greatly increased their levels of M phi association, and bacterial cells grown on trout blood agar plates also had a dramatic increase in their ability to interact with M phi. Only A+ A. salmonicida cells were highly cytotoxic to trout M phi, especially after being coated with hemin, presumably due to a more focused targeting of the bacterial cell onto the M phi surface and/or into the intracellular regions of the M phi.
Full text
PDF


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Baumeister W., Wildhaber I., Phipps B. M. Principles of organization in eubacterial and archaebacterial surface proteins. Can J Microbiol. 1989 Jan;35(1):215–227. doi: 10.1139/m89-034. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Belland R. J., Trust T. J. Cloning of the gene for the surface array protein of Aeromonas salmonicida and evidence linking loss of expression with genetic deletion. J Bacteriol. 1987 Sep;169(9):4086–4091. doi: 10.1128/jb.169.9.4086-4091.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chart H., Shaw D. H., Ishiguro E. E., Trust T. J. Structural and immunochemical homogeneity of Aeromonas salmonicida lipopolysaccharide. J Bacteriol. 1984 Apr;158(1):16–22. doi: 10.1128/jb.158.1.16-22.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chu S., Cavaignac S., Feutrier J., Phipps B. M., Kostrzynska M., Kay W. W., Trust T. J. Structure of the tetragonal surface virulence array protein and gene of Aeromonas salmonicida. J Biol Chem. 1991 Aug 15;266(23):15258–15265. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Daskaleros P. A., Payne S. M. Congo red binding phenotype is associated with hemin binding and increased infectivity of Shigella flexneri in the HeLa cell model. Infect Immun. 1987 Jun;55(6):1393–1398. doi: 10.1128/iai.55.6.1393-1398.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dooley J. S., Engelhardt H., Baumeister W., Kay W. W., Trust T. J. Three-dimensional structure of an open form of the surface layer from the fish pathogen Aeromonas salmonicida. J Bacteriol. 1989 Jan;171(1):190–197. doi: 10.1128/jb.171.1.190-197.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Garduño R. A., Lee E. J., Kay W. W. S-layer-mediated association of Aeromonas salmonicida with murine macrophages. Infect Immun. 1992 Oct;60(10):4373–4382. doi: 10.1128/iai.60.10.4373-4382.1992. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Griffiths S. G., Lynch W. H. Characterization of Aeromonas salmonicida variants with altered cell surfaces and their use in studying surface protein assembly. Arch Microbiol. 1990;154(3):308–312. doi: 10.1007/BF00248973. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ishiguro E. E., Ainsworth T., Trust T. J., Kay W. W. Congo red agar, a differential medium for Aeromonas salmonicida, detects the presence of the cell surface protein array involved in virulence. J Bacteriol. 1985 Dec;164(3):1233–1237. doi: 10.1128/jb.164.3.1233-1237.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ishiguro E. E., Kay W. W., Ainsworth T., Chamberlain J. B., Austen R. A., Buckley J. T., Trust T. J. Loss of virulence during culture of Aeromonas salmonicida at high temperature. J Bacteriol. 1981 Oct;148(1):333–340. doi: 10.1128/jb.148.1.333-340.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kay W. W., Buckley J. T., Ishiguro E. E., Phipps B. M., Monette J. P., Trust T. J. Purification and disposition of a surface protein associated with virulence of Aeromonas salmonicida. J Bacteriol. 1981 Sep;147(3):1077–1084. doi: 10.1128/jb.147.3.1077-1084.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kay W. W., Phipps B. M., Ishiguro E. E., Trust T. J. Porphyrin binding by the surface array virulence protein of Aeromonas salmonicida. J Bacteriol. 1985 Dec;164(3):1332–1336. doi: 10.1128/jb.164.3.1332-1336.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kay W. W., Trust T. J. Form and functions of the regular surface array (S-layer) of Aeromonas salmonicida. Experientia. 1991 May 15;47(5):412–414. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lindahl M., Faris A., Wadström T., Hjertén S. A new test based on 'salting out' to measure relative surface hydrophobicity of bacterial cells. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1981 Nov 5;677(3-4):471–476. doi: 10.1016/0304-4165(81)90261-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Munn C. B., Ishiguro E. E., Kay W. W., Trust T. J. Role of surface components in serum resistance of virulent Aeromonas salmonicida. Infect Immun. 1982 Jun;36(3):1069–1075. doi: 10.1128/iai.36.3.1069-1075.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Olivier G., Moore A. R., Fildes J. Toxicity of Aeromonas salmonicida cells to Atlantic salmon Salmo salar peritoneal macrophages. Dev Comp Immunol. 1992 Jan-Feb;16(1):49–61. doi: 10.1016/0145-305x(92)90051-d. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Phipps B. M., Kay W. W. Immunoglobulin binding by the regular surface array of Aeromonas salmonicida. J Biol Chem. 1988 Jul 5;263(19):9298–9303. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Phipps B. M., Trust T. J., Ishiguro E. E., Kay W. W. Purification and characterization of the cell surface virulent A protein from Aeromonas salmonicida. Biochemistry. 1983 Jun 7;22(12):2934–2939. doi: 10.1021/bi00281a023. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Saxton W. O., Baumeister W. Principles of organization in S layers. J Mol Biol. 1986 Jan 20;187(2):251–253. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(86)90232-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sleytr U. B., Messner P. Crystalline surface layers in procaryotes. J Bacteriol. 1988 Jul;170(7):2891–2897. doi: 10.1128/jb.170.7.2891-2897.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith H. Microbial surfaces in relation to pathogenicity. Bacteriol Rev. 1977 Jun;41(2):475–500. doi: 10.1128/br.41.2.475-500.1977. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stewart M., Beveridge T. J., Trust T. J. Two patterns in the Aeromonas salmonicida A-layer may reflect a structural transformation that alters permeability. J Bacteriol. 1986 Apr;166(1):120–127. doi: 10.1128/jb.166.1.120-127.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thornton J. C., Garduño R. A., Newman S. G., Kay W. W. Surface-disorganized, attenuated mutants of Aeromonas salmonicida as furunculosis live vaccines. Microb Pathog. 1991 Aug;11(2):85–99. doi: 10.1016/0882-4010(91)90002-r. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Van Alstine J. M., Trust T. J., Brooks D. E. Differential partition of virulent Aeromonas salmonicida and attenuated derivatives possessing specific cell surface alterations in polymer aqueous-phase systems. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1986 Jun;51(6):1309–1313. doi: 10.1128/aem.51.6.1309-1313.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Williams P. Role of the cell envelope in bacterial adaptation to growth in vivo in infections. Biochimie. 1988 Aug;70(8):987–1011. doi: 10.1016/0300-9084(88)90263-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]