Abstract
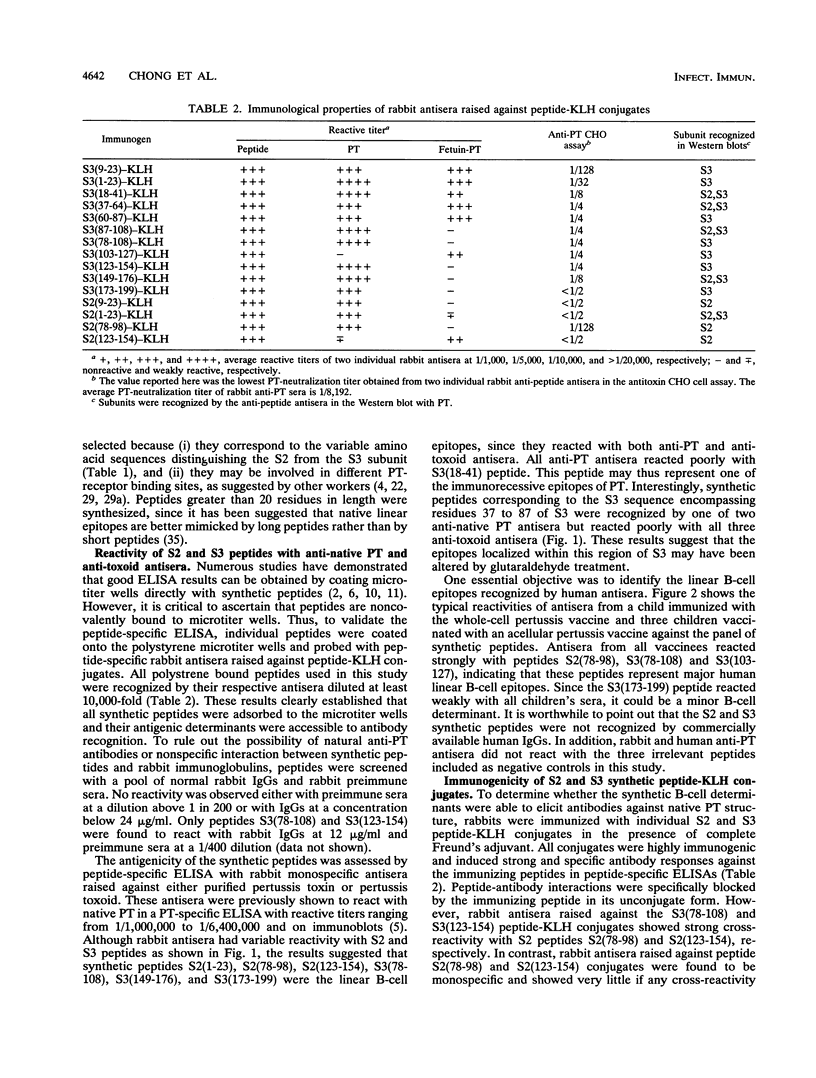
To design an optimized synthetic vaccine against whooping cough, we have studied the biological and immunological properties of three peptides of the S2 subunit and nine overlapping synthetic peptides covering the entire sequence of the S3 subunit of pertussis toxin (PT). Synthetic peptides corresponding to sequences 18 to 41, 78 to 108, 134 to 154, and 149 to 176 of S3 were found to be consistently capable of stimulating the proliferation of PT-specific T-cell lines primed with pertussis toxoid in both BALB/c and A/J strains of mice. All synthetic peptides were recognized by rabbit antisera raised against PT or pertussis toxoid. Both S2 and S3 peptide-keyhole limpet hemocyanin (KLH) conjugates in the presence of complete Freund's adjuvant induced peptide-specific antibody responses in rabbits, and the antisera raised against S2(1-23), S3(18-41), S3(37-64), and S3(149-176) peptide-KLH conjugates cross-reacted with both subunits in the immunoblots. All antisera except those against S2(123-154) and S3(103-127) reacted with native PT in an enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay (ELISA) with PT directly coated onto microtiter wells. In contrast, antisera raised against S2(123-154), S3(1-23), S3(18-41), S3(37-64), S3(60-87), and S3(103-127) peptide-KLH conjugates recognized native PT in a fetuin-PT capture ELISA. S2(78-98), S3(1-23), and S3(149-176) peptide-KLH conjugates elicited good PT-neutralizing antibody responses as judged by the antitoxin CHO cell assay. Identification of these B-cell neutralization epitopes and T-cell immunodominant determinants represents a first step towards the rational design of a synthetic vaccine against whooping cough.
Full text
PDF




Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Askelöf P., Rodmalm K., Wrangsell G., Larsson U., Svenson S. B., Cowell J. L., Undén A., Bartfai T. Protective immunogenicity of two synthetic peptides selected from the amino acid sequence of Bordetella pertussis toxin subunit S1. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1990 Feb;87(4):1347–1351. doi: 10.1073/pnas.87.4.1347. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Briand J. P., Muller S., Van Regenmortel M. H. Synthetic peptides as antigens: pitfalls of conjugation methods. J Immunol Methods. 1985 Apr 8;78(1):59–69. doi: 10.1016/0022-1759(85)90329-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Burns D. L., Kenimer J. G., Manclark C. R. Role of the A subunit of pertussis toxin in alteration of Chinese hamster ovary cell morphology. Infect Immun. 1987 Jan;55(1):24–28. doi: 10.1128/iai.55.1.24-28.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Capiau C., Petre J., Van Damme J., Puype M., Vandekerckhove J. Protein-chemical analysis of pertussis toxin reveals homology between the subunits S2 and S3, between S1 and the A chains of enterotoxins of Vibrio cholerae and Escherichia coli and identifies S2 as the haptoglobin-binding subunit. FEBS Lett. 1986 Aug 18;204(2):336–340. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(86)80839-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chong P., Klein M. Single-step purification of pertussis toxin and its subunits by heat-treated fetuin-sepharose affinity chromatography. Biochem Cell Biol. 1989 Jul;67(7):387–391. doi: 10.1139/o89-061. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chong P., Sydor M., Wu E., Zobrist G., Boux H., Klein M. Structural and functional analysis of the S1 subunit of pertussis toxin using synthetic peptides. Mol Immunol. 1991 Mar;28(3):239–245. doi: 10.1016/0161-5890(91)90068-u. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chou P. Y., Fasman G. D. Empirical predictions of protein conformation. Annu Rev Biochem. 1978;47:251–276. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.47.070178.001343. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cieplak W., Burnette W. N., Mar V. L., Kaljot K. T., Morris C. F., Chen K. K., Sato H., Keith J. M. Identification of a region in the S1 subunit of pertussis toxin that is required for enzymatic activity and that contributes to the formation of a neutralizing antigenic determinant. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Jul;85(13):4667–4671. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.13.4667. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DeLisi C., Berzofsky J. A. T-cell antigenic sites tend to be amphipathic structures. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Oct;82(20):7048–7052. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.20.7048. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dyrberg T., Oldstone M. B. Peptides as antigens. Importance of orientation. J Exp Med. 1986 Oct 1;164(4):1344–1349. doi: 10.1084/jem.164.4.1344. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Geerligs H. J., Weijer W. J., Bloemhoff W., Welling G. W., Welling-Wester S. The influence of pH and ionic strength on the coating of peptides of herpes simplex virus type 1 in an enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay. J Immunol Methods. 1988 Feb 10;106(2):239–244. doi: 10.1016/0022-1759(88)90203-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gillenius P., Jätmaa E., Askelöf P., Granström M., Tiru M. The standardization of an assay for pertussis toxin and antitoxin in microplate culture of Chinese hamster ovary cells. J Biol Stand. 1985 Jan;13(1):61–66. doi: 10.1016/s0092-1157(85)80034-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hopp T. P., Woods K. R. Prediction of protein antigenic determinants from amino acid sequences. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1981 Jun;78(6):3824–3828. doi: 10.1073/pnas.78.6.3824. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Iwasa S., Ishida S., Asakawa S., Akama K. A curious histamine-sensitizing activity shown by the newly-developed Japanese acellular pertussis vaccine. Dev Biol Stand. 1985;61:453–460. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lang A. B., Ganss M. T., Cryz S. J., Jr Monoclonal antibodies that define neutralizing epitopes of pertussis toxin: conformational dependence and epitope mapping. Infect Immun. 1989 Sep;57(9):2660–2665. doi: 10.1128/iai.57.9.2660-2665.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Liu F. T., Zinnecker M., Hamaoka T., Katz D. H. New procedures for preparation and isolation of conjugates of proteins and a synthetic copolymer of D-amino acids and immunochemical characterization of such conjugates. Biochemistry. 1979 Feb 20;18(4):690–693. doi: 10.1021/bi00571a022. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Locht C., Keith J. M. Pertussis toxin gene: nucleotide sequence and genetic organization. Science. 1986 Jun 6;232(4755):1258–1264. doi: 10.1126/science.3704651. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Loosmore S. M., Zealey G. R., Boux H. A., Cockle S. A., Radika K., Fahim R. E., Zobrist G. J., Yacoob R. K., Chong P. C., Yao F. L. Engineering of genetically detoxified pertussis toxin analogs for development of a recombinant whooping cough vaccine. Infect Immun. 1990 Nov;58(11):3653–3662. doi: 10.1128/iai.58.11.3653-3662.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nicosia A., Perugini M., Franzini C., Casagli M. C., Borri M. G., Antoni G., Almoni M., Neri P., Ratti G., Rappuoli R. Cloning and sequencing of the pertussis toxin genes: operon structure and gene duplication. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Jul;83(13):4631–4635. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.13.4631. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nogimori K., Tamura M., Nakamura T., Yajima M., Ito K., Ui M. Dual mechanisms involved in the development of diverse biological activities of islet-activating protein, (pertussis toxin) as revealed by chemical modification of the toxin molecule. Dev Biol Stand. 1985;61:51–61. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Oksenberg J. R., Ko C., Judd A. K., Lim M., Kent A., Schoolnik G. K., Steinman L. Multiple T and B cell epitopes in the S1 subunit ("A"-monomer) of the pertussis toxin molecule. J Immunol. 1989 Dec 15;143(12):4227–4231. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rhodes G., Houghten R., Taulane J. P., Carson D., Vaughan J. The immune response to Epstein-Barr nuclear antigen: conformational and structural features of antibody binding to synthetic peptides. Mol Immunol. 1984 Nov;21(11):1047–1054. doi: 10.1016/0161-5890(84)90114-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rothbard J. B., Taylor W. R. A sequence pattern common to T cell epitopes. EMBO J. 1988 Jan;7(1):93–100. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1988.tb02787.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sato H., Ito A., Chiba J., Sato Y. Monoclonal antibody against pertussis toxin: effect on toxin activity and pertussis infections. Infect Immun. 1984 Nov;46(2):422–428. doi: 10.1128/iai.46.2.422-428.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sato H., Sato Y., Ito A., Ohishi I. Effect of monoclonal antibody to pertussis toxin on toxin activity. Infect Immun. 1987 Apr;55(4):909–915. doi: 10.1128/iai.55.4.909-915.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schmidt M. A., Raupach B., Szulczynski M., Marzillier J. Identification of linear B-cell determinants of pertussis toxin associated with the receptor recognition site of the S3 subunit. Infect Immun. 1991 Apr;59(4):1402–1408. doi: 10.1128/iai.59.4.1402-1408.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schmidt M. A., Schmidt W. Inhibition of pertussis toxin binding to model receptors by antipeptide antibodies directed at an antigenic domain of the S2 subunit. Infect Immun. 1989 Dec;57(12):3828–3833. doi: 10.1128/iai.57.12.3828-3833.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schmidt W., Schmidt M. A. Mapping of linear B-cell epitopes of the S2 subunit of pertussis toxin. Infect Immun. 1989 Feb;57(2):438–445. doi: 10.1128/iai.57.2.438-445.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sia D. Y., Chou J. L. In vivo activated lymphoid cells (IVALC) affect the cloning efficiency of human T lymphocytes reactive to a soluble antigen, purified protein derivative. Scand J Immunol. 1987 Dec;26(6):683–690. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-3083.1987.tb02304.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stille C. J., Thomas L. J., Reyes V. E., Humphreys R. E. Hydrophobic strip-of-helix algorithm for selection of T cell-presented peptides. Mol Immunol. 1987 Oct;24(10):1021–1027. doi: 10.1016/0161-5890(87)90068-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tamura M., Nogimori K., Murai S., Yajima M., Ito K., Katada T., Ui M., Ishii S. Subunit structure of islet-activating protein, pertussis toxin, in conformity with the A-B model. Biochemistry. 1982 Oct 26;21(22):5516–5522. doi: 10.1021/bi00265a021. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Towbin H., Staehelin T., Gordon J. Electrophoretic transfer of proteins from polyacrylamide gels to nitrocellulose sheets: procedure and some applications. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Sep;76(9):4350–4354. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.9.4350. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


