Abstract
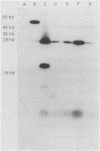
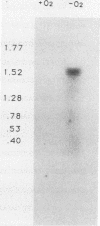
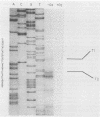
When grown under anaerobic conditions, Neisseria gonorrhoeae, the etiologic agent of the sexually transmitted disease gonorrhea, expresses several novel outer membrane proteins. One of these, Pan 1, has an apparent molecular mass of 54 kDa in electrophoresis and is recognized by serum samples from patients with gonococcal infection. The presence of antibodies to this protein in patient sera suggests that Pan 1 is expressed during gonococcal infection and, more importantly, that N. gonorrhoeae grows anaerobically in vivo. We have cloned the Pan 1 structural gene, aniA, by screening a gonococcal lambda gt11 expression library with monospecific, polyclonal anti-Pan 1 antiserum. Three distinct immunoreactive recombinants, containing overlapping fragments of DNA, were isolated and confirmed to be coding for Pan 1 protein sequences. Northern (RNA blot) hybridization of an insert from an aniA recombinant to total gonococcal cellular RNA revealed the presence of a 1.5-kb transcript that was specific to RNA from anaerobically grown gonococci, indicating that the aniA gene is regulated at the transcriptional level and is monocistronic. To characterize the aniA gene, we have sequenced the entire 2-kb region spanned by the overlapping recombinants. We have also performed primer extension analysis on RNA isolated from aerobically and anaerobically grown gonococci in order to define the aniA promoter region. Two putative primer extension products specific to organisms grown anaerobically were identified by homology to known Escherichia coli promoter sequences, suggesting that the regulation of aniA expression involves multiple promoter regions.
Full text
PDF







Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Aldea M., Garrido T., Hernández-Chico C., Vicente M., Kushner S. R. Induction of a growth-phase-dependent promoter triggers transcription of bolA, an Escherichia coli morphogene. EMBO J. 1989 Dec 1;8(12):3923–3931. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1989.tb08573.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Aldea M., Garrido T., Pla J., Vicente M. Division genes in Escherichia coli are expressed coordinately to cell septum requirements by gearbox promoters. EMBO J. 1990 Nov;9(11):3787–3794. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1990.tb07592.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bohannon D. E., Connell N., Keener J., Tormo A., Espinosa-Urgel M., Zambrano M. M., Kolter R. Stationary-phase-inducible "gearbox" promoters: differential effects of katF mutations and role of sigma 70. J Bacteriol. 1991 Jul;173(14):4482–4492. doi: 10.1128/jb.173.14.4482-4492.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clark V. L., Campbell L. A., Palermo D. A., Evans T. M., Klimpel K. W. Induction and repression of outer membrane proteins by anaerobic growth of Neisseria gonorrhoeae. Infect Immun. 1987 Jun;55(6):1359–1364. doi: 10.1128/iai.55.6.1359-1364.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clark V. L., Knapp J. S., Thompson S., Klimpel K. W. Presence of antibodies to the major anaerobically induced gonococcal outer membrane protein in sera from patients with gonococcal infections. Microb Pathog. 1988 Nov;5(5):381–390. doi: 10.1016/0882-4010(88)90038-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Collado-Vides J., Magasanik B., Gralla J. D. Control site location and transcriptional regulation in Escherichia coli. Microbiol Rev. 1991 Sep;55(3):371–394. doi: 10.1128/mr.55.3.371-394.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Connell N., Han Z., Moreno F., Kolter R. An E. coli promoter induced by the cessation of growth. Mol Microbiol. 1987 Sep;1(2):195–201. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2958.1987.tb00512.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DiRita V. J., Mekalanos J. J. Genetic regulation of bacterial virulence. Annu Rev Genet. 1989;23:455–482. doi: 10.1146/annurev.ge.23.120189.002323. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Feinberg A. P., Vogelstein B. A technique for radiolabeling DNA restriction endonuclease fragments to high specific activity. Anal Biochem. 1983 Jul 1;132(1):6–13. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(83)90418-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fohn M. J., Mietzner T. A., Hubbard T. W., Morse S. A., Hook E. W., 3rd Human immunoglobulin G antibody response to the major gonococcal iron-regulated protein. Infect Immun. 1987 Dec;55(12):3065–3069. doi: 10.1128/iai.55.12.3065-3069.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gold L., Pribnow D., Schneider T., Shinedling S., Singer B. S., Stormo G. Translational initiation in prokaryotes. Annu Rev Microbiol. 1981;35:365–403. doi: 10.1146/annurev.mi.35.100181.002053. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goodman S. D., Scocca J. J. Identification and arrangement of the DNA sequence recognized in specific transformation of Neisseria gonorrhoeae. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Sep;85(18):6982–6986. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.18.6982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gotschlich E. C., Blake M. S., Koomey J. M., Seiff M., Derman A. Cloning of the structural genes of three H8 antigens and of protein III of Neisseria gonorrhoeae. J Exp Med. 1986 Sep 1;164(3):868–881. doi: 10.1084/jem.164.3.868. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gotschlich E. C., Seiff M. E., Blake M. S., Koomey M. Porin protein of Neisseria gonorrhoeae: cloning and gene structure. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 Nov;84(22):8135–8139. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.22.8135. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Herrmann J., Lee P., Saya H., Nakajima M. Application of polymerase chain reaction for rapid subcloning of cDNA inserts from lambda gt11 clones. Biotechniques. 1990 Apr;8(4):376–381. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hicks C. B., Boslego J. W., Brandt B. Evidence of serum antibodies to Neisseria gonorrhoeae before gonococcal infection. J Infect Dis. 1987 Jun;155(6):1276–1281. doi: 10.1093/infdis/155.6.1276. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hoehn G. T., Clark V. L. Distribution of a protein antigenically related to the major anaerobically induced gonococcal outer membrane protein among other Neisseria species. Infect Immun. 1990 Dec;58(12):3929–3933. doi: 10.1128/iai.58.12.3929-3933.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hoehn G. T., Clark V. L. The major anaerobically induced outer membrane protein of Neisseria gonorrhoeae, Pan 1, is a lipoprotein. Infect Immun. 1992 Nov;60(11):4704–4708. doi: 10.1128/iai.60.11.4704-4708.1992. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Klimpel K. W., Lesley S. A., Clark V. L. Identification of subunits of gonococcal RNA polymerase by immunoblot analysis: evidence for multiple sigma factors. J Bacteriol. 1989 Jul;171(7):3713–3718. doi: 10.1128/jb.171.7.3713-3718.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Knapp J. S., Clark V. L. Anaerobic growth of Neisseria gonorrhoeae coupled to nitrite reduction. Infect Immun. 1984 Oct;46(1):176–181. doi: 10.1128/iai.46.1.176-181.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laemmli U. K. Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature. 1970 Aug 15;227(5259):680–685. doi: 10.1038/227680a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lange R., Hengge-Aronis R. Growth phase-regulated expression of bolA and morphology of stationary-phase Escherichia coli cells are controlled by the novel sigma factor sigma S. J Bacteriol. 1991 Jul;173(14):4474–4481. doi: 10.1128/jb.173.14.4474-4481.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lange R., Hengge-Aronis R. Identification of a central regulator of stationary-phase gene expression in Escherichia coli. Mol Microbiol. 1991 Jan;5(1):49–59. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2958.1991.tb01825.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Loewen P. C., Triggs B. L. Genetic mapping of katF, a locus that with katE affects the synthesis of a second catalase species in Escherichia coli. J Bacteriol. 1984 Nov;160(2):668–675. doi: 10.1128/jb.160.2.668-675.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Manfioletti G., Schneider C. A new and fast method for preparing high quality lambda DNA suitable for sequencing. Nucleic Acids Res. 1988 Apr 11;16(7):2873–2884. doi: 10.1093/nar/16.7.2873. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mierendorf R. C., Percy C., Young R. A. Gene isolation by screening lambda gt11 libraries with antibodies. Methods Enzymol. 1987;152:458–469. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(87)52054-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miller J. F., Mekalanos J. J., Falkow S. Coordinate regulation and sensory transduction in the control of bacterial virulence. Science. 1989 Feb 17;243(4893):916–922. doi: 10.1126/science.2537530. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mulvey M. R., Loewen P. C. Nucleotide sequence of katF of Escherichia coli suggests KatF protein is a novel sigma transcription factor. Nucleic Acids Res. 1989 Dec 11;17(23):9979–9991. doi: 10.1093/nar/17.23.9979. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mulvey M. R., Switala J., Borys A., Loewen P. C. Regulation of transcription of katE and katF in Escherichia coli. J Bacteriol. 1990 Dec;172(12):6713–6720. doi: 10.1128/jb.172.12.6713-6720.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rice P. A., Vayo H. E., Tam M. R., Blake M. S. Immunoglobulin G antibodies directed against protein III block killing of serum-resistant Neisseria gonorrhoeae by immune serum. J Exp Med. 1986 Nov 1;164(5):1735–1748. doi: 10.1084/jem.164.5.1735. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sak B. D., Eisenstark A., Touati D. Exonuclease III and the catalase hydroperoxidase II in Escherichia coli are both regulated by the katF gene product. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 May;86(9):3271–3275. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.9.3271. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sanger F., Nicklen S., Coulson A. R. DNA sequencing with chain-terminating inhibitors. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Dec;74(12):5463–5467. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.12.5463. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sarafian S. K., Tam M. R., Morse S. A. Gonococcal protein I-specific opsonic IgG in normal human serum. J Infect Dis. 1983 Dec;148(6):1025–1032. doi: 10.1093/infdis/148.6.1025. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Short H. B., Clark V. L., Kellogg D. S., Jr, Young F. E. Anaerobic survival of clinical isolates and laboratory strains of Neisseria gonorrhoea: use in transfer and storage. J Clin Microbiol. 1982 May;15(5):915–919. doi: 10.1128/jcm.15.5.915-919.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Summers W. C. A simple method for extraction of RNA from E. coli utilizing diethyl pyrocarbonate. Anal Biochem. 1970 Feb;33(2):459–463. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(70)90316-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Touati E., Dassa E., Boquet P. L. Pleiotropic mutations in appR reduce pH 2.5 acid phosphatase expression and restore succinate utilisation in CRP-deficient strains of Escherichia coli. Mol Gen Genet. 1986 Feb;202(2):257–264. doi: 10.1007/BF00331647. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Towbin H., Staehelin T., Gordon J. Electrophoretic transfer of proteins from polyacrylamide gels to nitrocellulose sheets: procedure and some applications. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Sep;76(9):4350–4354. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.9.4350. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vicente M., Kushner S. R., Garrido T., Aldea M. The role of the 'gearbox' in the transcription of essential genes. Mol Microbiol. 1991 Sep;5(9):2085–2091. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2958.1991.tb02137.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- West S. E., Clark V. L. Genetic loci and linkage associations in Neisseria gonorrhoeae and Neisseria meningitidis. Clin Microbiol Rev. 1989 Apr;2 (Suppl):S92–103. doi: 10.1128/cmr.2.suppl.s92. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Young R. A., Davis R. W. Efficient isolation of genes by using antibody probes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1983 Mar;80(5):1194–1198. doi: 10.1073/pnas.80.5.1194. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]