Abstract
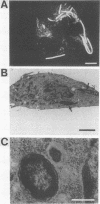
Proteus mirabilis causes serious kidney infections which can involve invasion of host urothelial cells. We present data showing that the ability to invade host urothelial cells is closely coupled to swarming, a form of cyclical multicellular behavior in which vegetative bacteria differentiate into hyperflagellated, filamentous swarm cells capable of coordinated and rapid population migration. Entry into the human urothelial cell line EJ/28 by P. mirabilis U6450 isolated at different stages throughout the swarming cycle was measured by the antibiotic protection assay method and confirmed by electron microscopy. Differentiated filaments entered urothelial cells within 30 min and were 15-fold more invasive (ca. 0.18% entry in 2 h) than an equivalent dry weight of vegetative cells isolated before differentiation, which attained only ca. 0.012% entry in the 2-h assay. The invasive ability of P. mirabilis was modulated in parallel with flagellin levels throughout two cycles of swarming. Septation and division of intracellular swarm cells produced between 50 and 300 vegetative bacteria per human cell, compared with 4 to 12 intracellular bacteria after incubation with vegetative cells. Transposon (Tn5) mutants of P. mirabilis with specific defects in motility and multicellular behavior were compared with the wild-type for the ability to invade. Mutants which lacked flagella (nonmotile nonswarming) were entirely noninvasive, and those which were motile but defective in swarm cell formation (motile nonswarming) were 25-fold less invasive than wild-type vegetative cells. Mutants with defects in the coordination of multicellular migration and the temporal control of consolidation (cyclical reversion of swarm cells to vegetative cells) were reduced ca. 3- to 12-fold in the ability to enter urothelial cells. In contrast, a nonhemolytic transposon mutant which swarmed normally retained over 80% of wild-type invasive ability. Swarm cells and early consolidation cells were at least 10-fold more cytolytic than vegetative cells as a result of their high-level production of hemolysin.
Full text
PDF




Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Allison C., Hughes C. Bacterial swarming: an example of prokaryotic differentiation and multicellular behaviour. Sci Prog. 1991;75(298 Pt 3-4):403–422. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Allison C., Hughes C. Closely linked genetic loci required for swarm cell differentiation and multicellular migration by Proteus mirabilis. Mol Microbiol. 1991 Aug;5(8):1975–1982. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2958.1991.tb00819.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Allison C., Lai H. C., Hughes C. Co-ordinate expression of virulence genes during swarm-cell differentiation and population migration of Proteus mirabilis. Mol Microbiol. 1992 Jun;6(12):1583–1591. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2958.1992.tb00883.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BRAUDE A. I., SIEMIENSKI J. Role of bacterial urease in experimental pyelonephritis. J Bacteriol. 1960 Aug;80:171–179. doi: 10.1128/jb.80.2.171-179.1960. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bahrani F. K., Johnson D. E., Robbins D., Mobley H. L. Proteus mirabilis flagella and MR/P fimbriae: isolation, purification, N-terminal analysis, and serum antibody response following experimental urinary tract infection. Infect Immun. 1991 Oct;59(10):3574–3580. doi: 10.1128/iai.59.10.3574-3580.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Belas R., Erskine D., Flaherty D. Proteus mirabilis mutants defective in swarmer cell differentiation and multicellular behavior. J Bacteriol. 1991 Oct;173(19):6279–6288. doi: 10.1128/jb.173.19.6279-6288.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brooks H. J., O'Grady F., McSherry M. A., Cattell W. R. Uropathogenic properties of Escherichia coli in recurrent urinary-tract infection. J Med Microbiol. 1980 Feb;13(1):57–68. doi: 10.1099/00222615-13-1-57. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clerc P., Sansonetti P. J. Entry of Shigella flexneri into HeLa cells: evidence for directed phagocytosis involving actin polymerization and myosin accumulation. Infect Immun. 1987 Nov;55(11):2681–2688. doi: 10.1128/iai.55.11.2681-2688.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dick H., Murray R. G., Walmsley S. Swarmer cell differentiation of Proteus mirabilis in fluid media. Can J Microbiol. 1985 Nov;31(11):1041–1050. doi: 10.1139/m85-196. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Falkinham J. O., 3rd, Hoffman P. S. Unique developmental characteristics of the swarm and short cells of Proteus vulgaris and Proteus mirabilis. J Bacteriol. 1984 Jun;158(3):1037–1040. doi: 10.1128/jb.158.3.1037-1040.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Falkow S. Bacterial entry into eukaryotic cells. Cell. 1991 Jun 28;65(7):1099–1102. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(91)90003-h. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Finlay B. B., Falkow S. Common themes in microbial pathogenicity. Microbiol Rev. 1989 Jun;53(2):210–230. doi: 10.1128/mr.53.2.210-230.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Finlay B. B., Ruschkowski S., Dedhar S. Cytoskeletal rearrangements accompanying salmonella entry into epithelial cells. J Cell Sci. 1991 Jun;99(Pt 2):283–296. doi: 10.1242/jcs.99.2.283. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gaillard J. L., Berche P., Frehel C., Gouin E., Cossart P. Entry of L. monocytogenes into cells is mediated by internalin, a repeat protein reminiscent of surface antigens from gram-positive cocci. Cell. 1991 Jun 28;65(7):1127–1141. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(91)90009-n. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Harmon R. C., Rutherford R. L., Wu H. M., Collins M. S. Monoclonal antibody-mediated protection and neutralization of motility in experimental Proteus mirabilis infection. Infect Immun. 1989 Jul;57(7):1936–1941. doi: 10.1128/iai.57.7.1936-1941.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Henrichsen J. Bacterial surface translocation: a survey and a classification. Bacteriol Rev. 1972 Dec;36(4):478–503. doi: 10.1128/br.36.4.478-503.1972. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hoffman P. S., Falkinham J. O., 3rd Induction of tryptophanase in short cells and swarm cells of Proteus vulgaris. J Bacteriol. 1981 Nov;148(2):736–738. doi: 10.1128/jb.148.2.736-738.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Holmgren K., Danielson B. G., Fellström B. Infection-induced urinary calculi and renal failure. Scand J Urol Nephrol. 1987;21(3):219–223. doi: 10.3109/00365598709180325. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Isberg R. R. Discrimination between intracellular uptake and surface adhesion of bacterial pathogens. Science. 1991 May 17;252(5008):934–938. doi: 10.1126/science.1674624. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Isberg R. R., Leong J. M. Multiple beta 1 chain integrins are receptors for invasin, a protein that promotes bacterial penetration into mammalian cells. Cell. 1990 Mar 9;60(5):861–871. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(90)90099-z. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Isberg R. R., Voorhis D. L., Falkow S. Identification of invasin: a protein that allows enteric bacteria to penetrate cultured mammalian cells. Cell. 1987 Aug 28;50(5):769–778. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(87)90335-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jones B. D., Lee C. A., Falkow S. Invasion by Salmonella typhimurium is affected by the direction of flagellar rotation. Infect Immun. 1992 Jun;60(6):2475–2480. doi: 10.1128/iai.60.6.2475-2480.1992. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Koronakis V., Cross M., Senior B., Koronakis E., Hughes C. The secreted hemolysins of Proteus mirabilis, Proteus vulgaris, and Morganella morganii are genetically related to each other and to the alpha-hemolysin of Escherichia coli. J Bacteriol. 1987 Apr;169(4):1509–1515. doi: 10.1128/jb.169.4.1509-1515.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laemmli U. K. Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature. 1970 Aug 15;227(5259):680–685. doi: 10.1038/227680a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Liu S. L., Ezaki T., Miura H., Matsui K., Yabuuchi E. Intact motility as a Salmonella typhi invasion-related factor. Infect Immun. 1988 Aug;56(8):1967–1973. doi: 10.1128/iai.56.8.1967-1973.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Loomes L. M., Senior B. W., Kerr M. A. A proteolytic enzyme secreted by Proteus mirabilis degrades immunoglobulins of the immunoglobulin A1 (IgA1), IgA2, and IgG isotypes. Infect Immun. 1990 Jun;58(6):1979–1985. doi: 10.1128/iai.58.6.1979-1985.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McCarter L., Silverman M. Surface-induced swarmer cell differentiation of Vibrio parahaemolyticus. Mol Microbiol. 1990 Jul;4(7):1057–1062. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2958.1990.tb00678.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mekalanos J. J. Environmental signals controlling expression of virulence determinants in bacteria. J Bacteriol. 1992 Jan;174(1):1–7. doi: 10.1128/jb.174.1.1-7.1992. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moayeri N., Collins C. M., O'Hanley P. Efficacy of a Proteus mirabilis outer membrane protein vaccine in preventing experimental Proteus pyelonephritis in a BALB/c mouse model. Infect Immun. 1991 Oct;59(10):3778–3786. doi: 10.1128/iai.59.10.3778-3786.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mobley H. L., Chippendale G. R., Swihart K. G., Welch R. A. Cytotoxicity of the HpmA hemolysin and urease of Proteus mirabilis and Proteus vulgaris against cultured human renal proximal tubular epithelial cells. Infect Immun. 1991 Jun;59(6):2036–2042. doi: 10.1128/iai.59.6.2036-2042.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mobley H. L., Hausinger R. P. Microbial ureases: significance, regulation, and molecular characterization. Microbiol Rev. 1989 Mar;53(1):85–108. doi: 10.1128/mr.53.1.85-108.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pazin G. J., Braude A. I. Immobilizing antibodies in urine. II. Prevention of ascending spread of Proteus mirabilis. Invest Urol. 1974 Sep;12(2):129–133. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Peerbooms P. G., Marian A., Verweij J. J., MacLaren D. M. Urinary virulence of Proteus mirabilis in two experimental mouse models. Infect Immun. 1982 Jun;36(3):1246–1248. doi: 10.1128/iai.36.3.1246-1248.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Peerbooms P. G., Verweij A. M., MacLaren D. M. Investigation of the haemolytic activity of Proteus mirabilis strains. Antonie Van Leeuwenhoek. 1983 Apr;49(1):1–11. doi: 10.1007/BF00457874. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Peerbooms P. G., Verweij A. M., MacLaren D. M. Vero cell invasiveness of Proteus mirabilis. Infect Immun. 1984 Mar;43(3):1068–1071. doi: 10.1128/iai.43.3.1068-1071.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Richardson K. Roles of motility and flagellar structure in pathogenicity of Vibrio cholerae: analysis of motility mutants in three animal models. Infect Immun. 1991 Aug;59(8):2727–2736. doi: 10.1128/iai.59.8.2727-2736.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sareneva T., Holthöfer H., Korhonen T. K. Tissue-binding affinity of Proteus mirabilis fimbriae in the human urinary tract. Infect Immun. 1990 Oct;58(10):3330–3336. doi: 10.1128/iai.58.10.3330-3336.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Senior B. W. The special affinity of particular types of Proteus mirabilis for the urinary tract. J Med Microbiol. 1979 Feb;12(1):1–8. doi: 10.1099/00222615-12-1-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stamm W. E., Martin S. M., Bennett J. V. Epidemiology of nosocomial infection due to Gram-negative bacilli: aspects relevant to development and use of vaccines. J Infect Dis. 1977 Aug;136 (Suppl):S151–S160. doi: 10.1093/infdis/136.supplement.s151. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Swihart K. G., Welch R. A. Cytotoxic activity of the Proteus hemolysin HpmA. Infect Immun. 1990 Jun;58(6):1861–1869. doi: 10.1128/iai.58.6.1861-1869.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wassenaar T. M., Bleumink-Pluym N. M., van der Zeijst B. A. Inactivation of Campylobacter jejuni flagellin genes by homologous recombination demonstrates that flaA but not flaB is required for invasion. EMBO J. 1991 Aug;10(8):2055–2061. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1991.tb07736.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wick M. J., Madara J. L., Fields B. N., Normark S. J. Molecular cross talk between epithelial cells and pathogenic microorganisms. Cell. 1991 Nov 15;67(4):651–659. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(91)90061-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Williams F. D., Anderson D. M., Hoffman P. S., Schwarzhoff R. H., Leonard S. Evidence against the involvement of chemotaxis in swarming of Proteus mirabilis. J Bacteriol. 1976 Jul;127(1):237–248. doi: 10.1128/jb.127.1.237-248.1976. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Williams F. D., Schwarzhoff R. H. Nature of the swarming phenomenon in Proteus. Annu Rev Microbiol. 1978;32:101–122. doi: 10.1146/annurev.mi.32.100178.000533. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]