Abstract
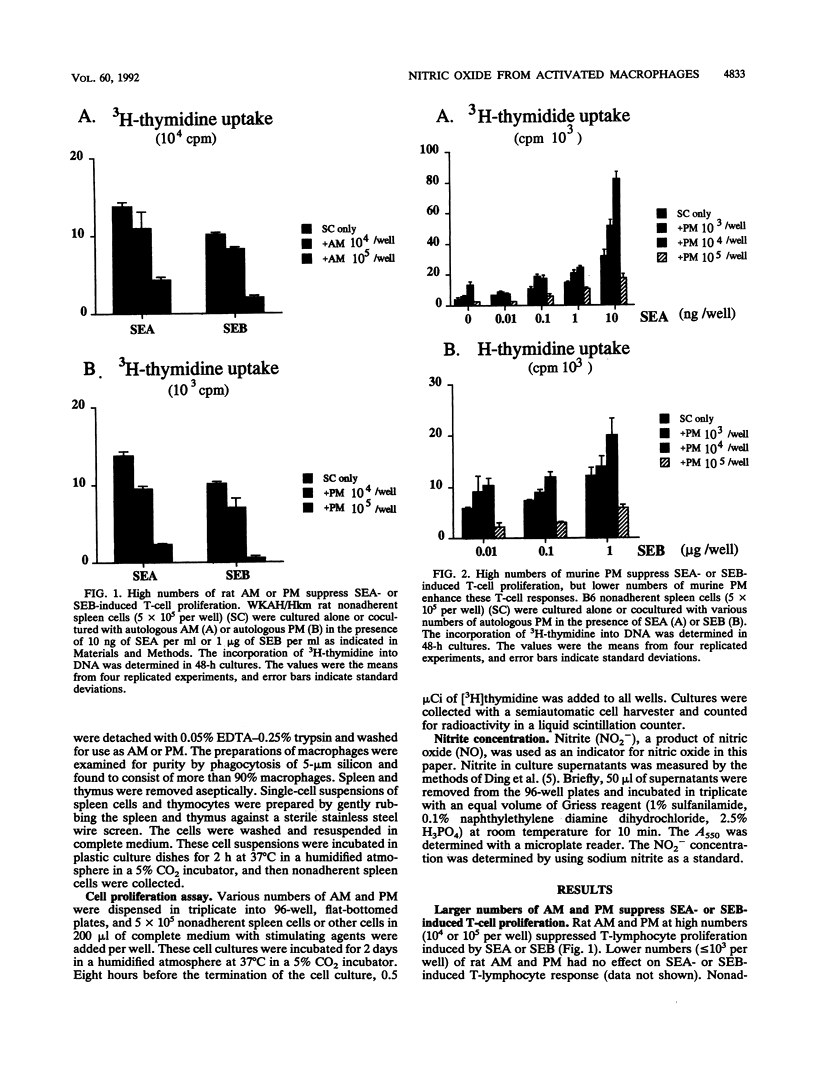
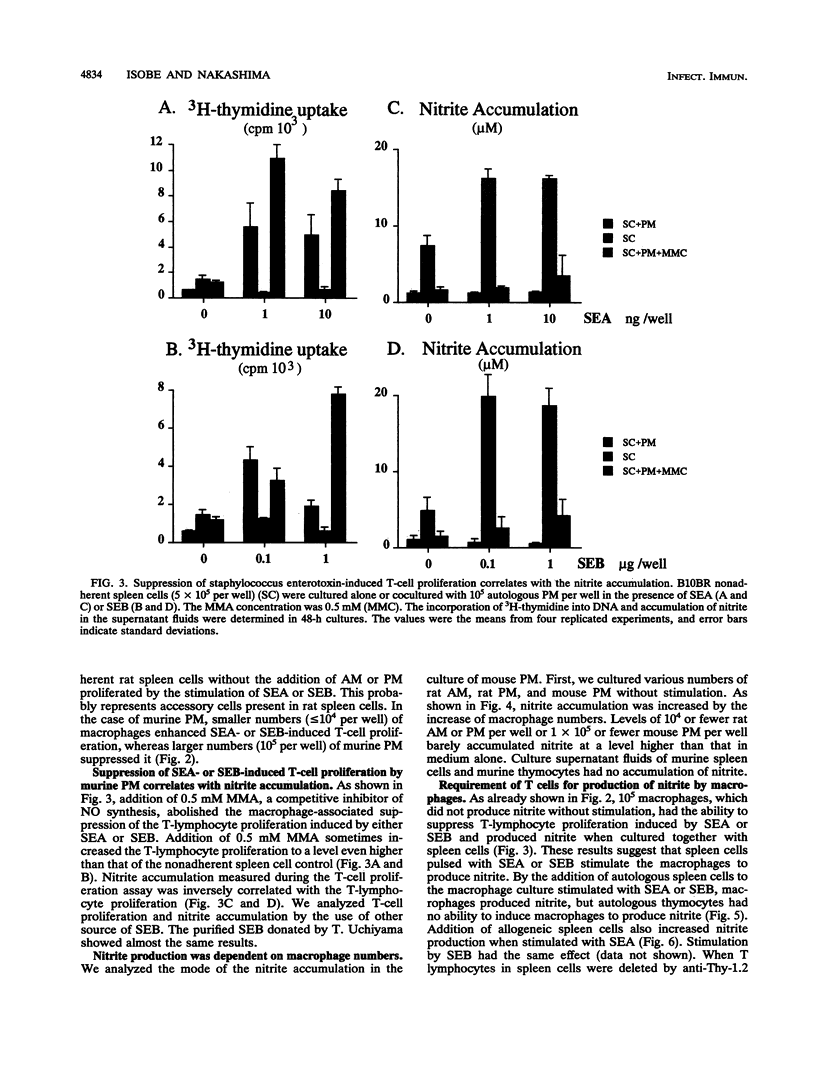
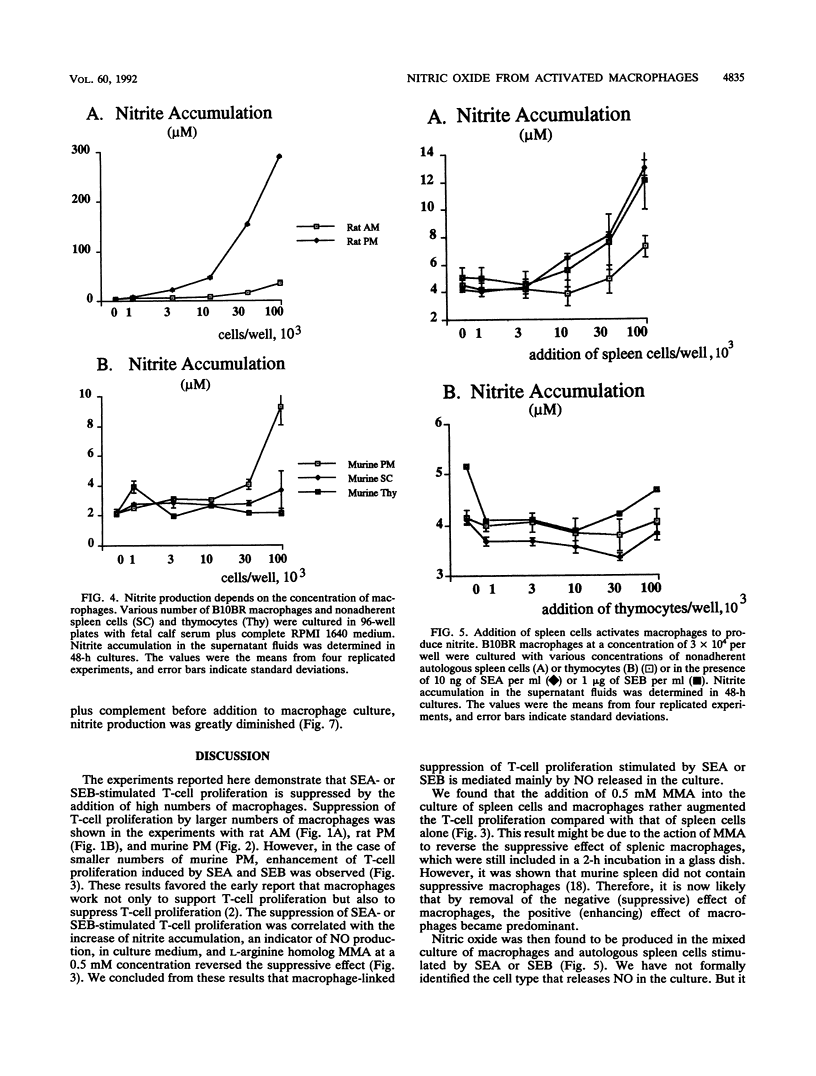
Staphylococcal enterotoxin A (SEA)- or SEB-stimulated T-lymphocyte proliferation was suppressed by the addition of high numbers of murine peritoneal macrophages or rat peritoneal or alveolar macrophages, whereas lower numbers of murine peritoneal macrophages enhanced the T-lymphocyte response. Suppression was associated with the increase of accumulation of nitrite, a product of nitric oxide, in the culture supernatants. This macrophage-mediated suppression was totally reversed by the addition of NG-monomethyl-L-arginine, a homolog of L-arginine, indicating that macrophage-mediated suppression of T-lymphocyte proliferation was mediated through the nitric oxide-synthesizing pathway activity. Macrophages in large numbers spontaneously produced nitric oxide in culture supernatant fluids. By the addition of autologous or allogeneic spleen cells but not thymocytes to SEA- or SEB-stimulated macrophage culture, nitric oxide production was greatly increased. When T lymphocytes in spleen cells were killed by antibody before addition to macrophage culture, nitric oxide production was diminished to the basal level. These results suggest that in addition to the action to support the process of T-lymphocyte activation by SEA or SEB, macrophages display a feedback regulatory action on the SEA- or SEB-stimulated T-cell proliferative response by releasing nitric oxide through interaction between macrophages and activated T lymphocytes.
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Albina J. E., Abate J. A., Henry W. L., Jr Nitric oxide production is required for murine resident peritoneal macrophages to suppress mitogen-stimulated T cell proliferation. Role of IFN-gamma in the induction of the nitric oxide-synthesizing pathway. J Immunol. 1991 Jul 1;147(1):144–148. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bredt D. S., Hwang P. M., Glatt C. E., Lowenstein C., Reed R. R., Snyder S. H. Cloned and expressed nitric oxide synthase structurally resembles cytochrome P-450 reductase. Nature. 1991 Jun 27;351(6329):714–718. doi: 10.1038/351714a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bredt D. S., Snyder S. H. Isolation of nitric oxide synthetase, a calmodulin-requiring enzyme. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1990 Jan;87(2):682–685. doi: 10.1073/pnas.87.2.682. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ding A. H., Nathan C. F., Stuehr D. J. Release of reactive nitrogen intermediates and reactive oxygen intermediates from mouse peritoneal macrophages. Comparison of activating cytokines and evidence for independent production. J Immunol. 1988 Oct 1;141(7):2407–2412. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fleming S. D., Iandolo J. J., Chapes S. K. Murine macrophage activation by staphylococcal exotoxins. Infect Immun. 1991 Nov;59(11):4049–4055. doi: 10.1128/iai.59.11.4049-4055.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Garthwaite J., Charles S. L., Chess-Williams R. Endothelium-derived relaxing factor release on activation of NMDA receptors suggests role as intercellular messenger in the brain. Nature. 1988 Nov 24;336(6197):385–388. doi: 10.1038/336385a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hibbs J. B., Jr, Taintor R. R., Vavrin Z. Macrophage cytotoxicity: role for L-arginine deiminase and imino nitrogen oxidation to nitrite. Science. 1987 Jan 23;235(4787):473–476. doi: 10.1126/science.2432665. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Holt P. G. Alveolar macrophages. IV. Interspecies differences in activity in proliferating lymphocyte cultures. Cell Immunol. 1980 Mar 1;50(1):210–215. doi: 10.1016/0008-8749(80)90020-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Imanishi K., Igarashi H., Uchiyama T. Activation of murine T cells by streptococcal pyrogenic exotoxin type A. Requirement for MHC class II molecules on accessory cells and identification of V beta elements in T cell receptor of toxin-reactive T cells. J Immunol. 1990 Nov 15;145(10):3170–3176. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kappler J., Kotzin B., Herron L., Gelfand E. W., Bigler R. D., Boylston A., Carrel S., Posnett D. N., Choi Y., Marrack P. V beta-specific stimulation of human T cells by staphylococcal toxins. Science. 1989 May 19;244(4906):811–813. doi: 10.1126/science.2524876. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kawabe T., Isobe K. I., Hasegawa Y., Nakashima I., Shimokata K. Immunosuppressive activity induced by nitric oxide in culture supernatant of activated rat alveolar macrophages. Immunology. 1992 May;76(1):72–78. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Knowles R. G., Palacios M., Palmer R. M., Moncada S. Formation of nitric oxide from L-arginine in the central nervous system: a transduction mechanism for stimulation of the soluble guanylate cyclase. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 Jul;86(13):5159–5162. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.13.5159. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kung J. T., Brooks S. B., Jakway J. P., Leonard L. L., Talmage D. W. Suppression of in vitro cytotoxic response by macrophages due to induced arginase. J Exp Med. 1977 Sep 1;146(3):665–672. doi: 10.1084/jem.146.3.665. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Langford M. P., Stanton G. J., Johnson H. M. Biological effects of staphylococcal enterotoxin A on human peripheral lymphocytes. Infect Immun. 1978 Oct;22(1):62–68. doi: 10.1128/iai.22.1.62-68.1978. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Liew F. Y., Cox F. E. Nonspecific defence mechanism: the role of nitric oxide. Immunol Today. 1991 Mar;12(3):A17–A21. doi: 10.1016/S0167-5699(05)80006-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Metzger Z., Hoffeld J. T., Oppenheim J. J. Macrophage-mediated suppression. I. Evidence for participation of both hdyrogen peroxide and prostaglandins in suppression of murine lymphocyte proliferation. J Immunol. 1980 Feb;124(2):983–988. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mills C. D. Molecular basis of "suppressor" macrophages. Arginine metabolism via the nitric oxide synthetase pathway. J Immunol. 1991 Apr 15;146(8):2719–2723. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nathan C. F., Stuehr D. J. Does endothelium-derived nitric oxide have a role in cytokine-induced hypotension? J Natl Cancer Inst. 1990 May 2;82(9):726–728. doi: 10.1093/jnci/82.9.726. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Palmer R. M., Ferrige A. G., Moncada S. Nitric oxide release accounts for the biological activity of endothelium-derived relaxing factor. Nature. 1987 Jun 11;327(6122):524–526. doi: 10.1038/327524a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Peavy D. L., Adler W. H., Smith R. T. The mitogenic effects of endotoxin and staphylococcal enterotoxin B on mouse spleen cells and human peripheral lymphocytes. J Immunol. 1970 Dec;105(6):1453–1458. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Role of macrophages in the immune response. Immunol Rev. 1978;40:1–255. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rosenthal A. S., Shevach E. M. Function of macrophages in antigen recognition by guinea pig T lymphocytes. I. Requirement for histocompatible macrophages and lymphocytes. J Exp Med. 1973 Nov 1;138(5):1194–1212. doi: 10.1084/jem.138.5.1194. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stuehr D. J., Gross S. S., Sakuma I., Levi R., Nathan C. F. Activated murine macrophages secrete a metabolite of arginine with the bioactivity of endothelium-derived relaxing factor and the chemical reactivity of nitric oxide. J Exp Med. 1989 Mar 1;169(3):1011–1020. doi: 10.1084/jem.169.3.1011. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stuehr D. J., Nathan C. F. Nitric oxide. A macrophage product responsible for cytostasis and respiratory inhibition in tumor target cells. J Exp Med. 1989 May 1;169(5):1543–1555. doi: 10.1084/jem.169.5.1543. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Unanue E. R., Allen P. M. The basis for the immunoregulatory role of macrophages and other accessory cells. Science. 1987 May 1;236(4801):551–557. doi: 10.1126/science.2437650. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- White J., Herman A., Pullen A. M., Kubo R., Kappler J. W., Marrack P. The V beta-specific superantigen staphylococcal enterotoxin B: stimulation of mature T cells and clonal deletion in neonatal mice. Cell. 1989 Jan 13;56(1):27–35. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(89)90980-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


