Abstract
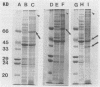
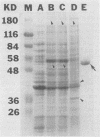
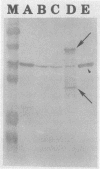
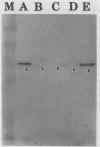
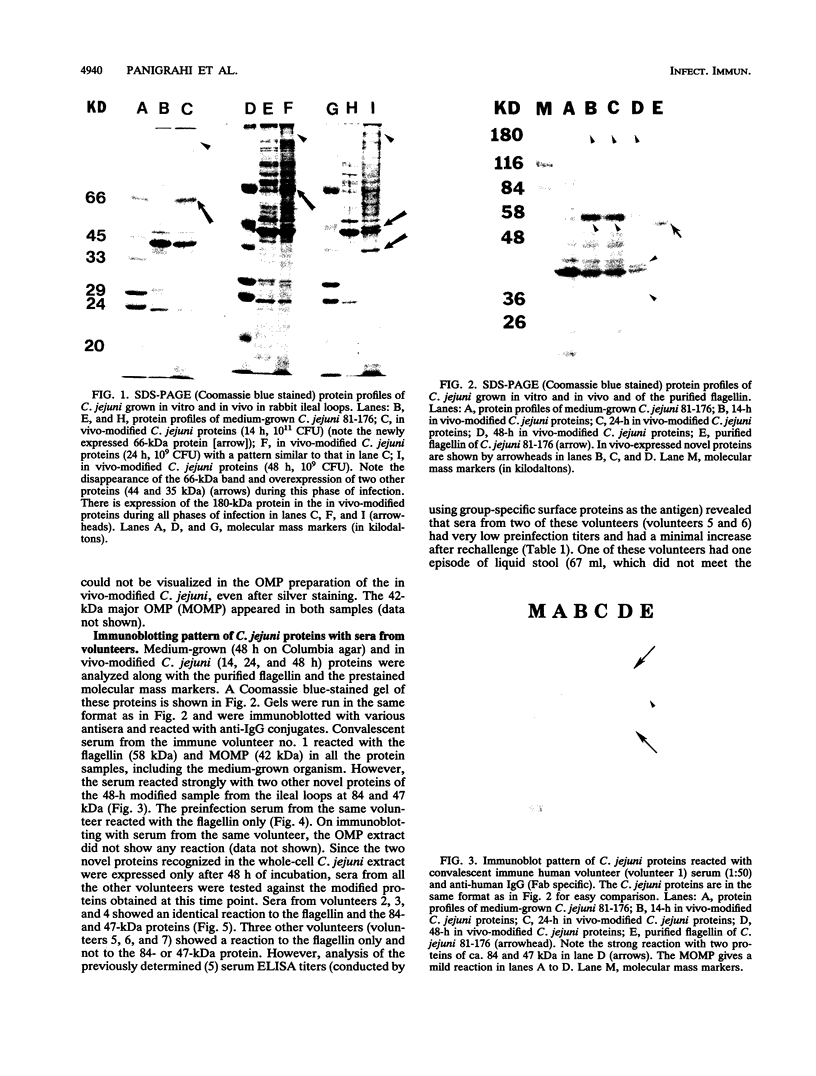
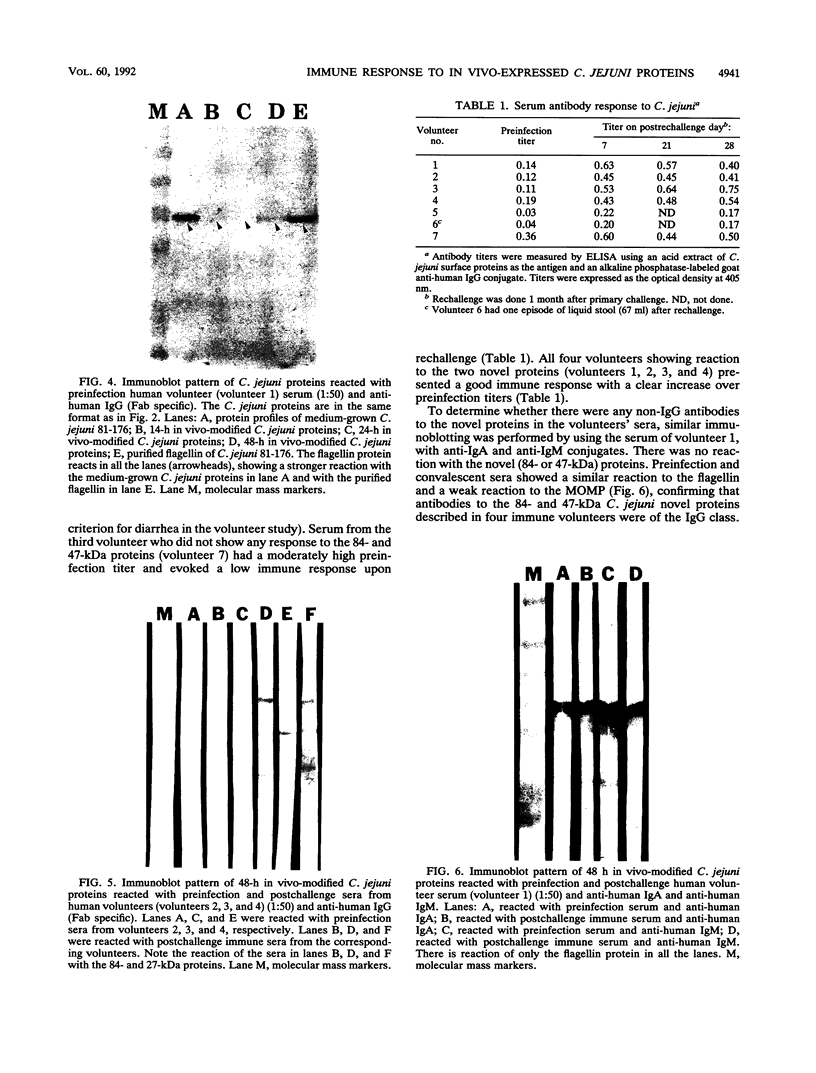
Campylobacter jejuni 81-176 grown in vivo in rabbit ileal loops expresses novel proteins that are not expressed under standard laboratory culture conditions. A new protein with a molecular mass of ca. 180 kDa is expressed at 14, 24, and 48 h of infection. Three other proteins, with molecular masses of ca. 66, 43, and 35 kDa, are overexpressed during different phases of infection. Expression of these proteins stops immediately during the first passage in laboratory media, and they do not elicit a human immune response. Two other proteins, with molecular masses of ca. 84 and 47 kDa, expressed 48 h after infection can be identified by using convalescent sera from human volunteers who were immune to C. jejuni infection upon rechallenge; these proteins were not visualized on sodium dodecyl sulfate-polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis gels by Coomassie blue staining or silver staining. Antibodies to the 84- and 47-kDa proteins are of the immunoglobulin G class. Both preinfection and convalescent human sera react strongly to the C. jejuni flagellin (a 58-kDa protein), suggesting the presence of cross-reactive antibodies to this protein in healthy humans. Major outer membrane protein and flagella may play a role in providing protection against C. jejuni disease, but our data suggest that there are other proteins expressed only during in vivo growth of the organism that elicit a strong immune response in human C. jejuni infections.
Full text
PDF




Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Abimiku A. G., Dolby J. M. Cross-protection of infant mice against intestinal colonisation by Campylobacter jejuni: importance of heat-labile serotyping (Lior) antigens. J Med Microbiol. 1988 Aug;26(4):265–268. doi: 10.1099/00222615-26-4-265. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Aguero-Rosenfeld M. E., Yang X. H., Nachamkin I. Infection of adult Syrian hamsters with flagellar variants of Campylobacter jejuni. Infect Immun. 1990 Jul;58(7):2214–2219. doi: 10.1128/iai.58.7.2214-2219.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Almeida R. A., Rosenbusch R. F. Capsulelike surface material of Mycoplasma dispar induced by in vitro growth in culture with bovine cells is antigenically related to similar structures expressed in vivo. Infect Immun. 1991 Sep;59(9):3119–3125. doi: 10.1128/iai.59.9.3119-3125.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ani E. A., Takahashi T., Shonekan R. A. Campylobacter jejuni antibodies in Nigerian children. J Clin Microbiol. 1988 Mar;26(3):605–606. doi: 10.1128/jcm.26.3.605-606.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Black R. E., Levine M. M., Clements M. L., Hughes T. P., Blaser M. J. Experimental Campylobacter jejuni infection in humans. J Infect Dis. 1988 Mar;157(3):472–479. doi: 10.1093/infdis/157.3.472. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blaser M. J., Black R. E., Duncan D. J., Amer J. Campylobacter jejuni-specific serum antibodies are elevated in healthy Bangladeshi children. J Clin Microbiol. 1985 Feb;21(2):164–167. doi: 10.1128/jcm.21.2.164-167.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blaser M. J., Duncan D. J. Human serum antibody response to Campylobacter jejuni infection as measured in an enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay. Infect Immun. 1984 May;44(2):292–298. doi: 10.1128/iai.44.2.292-298.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blaser M. J., Smith P. F., Kohler P. F. Susceptibility of Campylobacter isolates to the bactericidal activity of human serum. J Infect Dis. 1985 Feb;151(2):227–235. doi: 10.1093/infdis/151.2.227. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blaser M. J., Taylor D. N., Echeverria P. Immune response to Campylobacter jejuni in a rural community in Thailand. J Infect Dis. 1986 Feb;153(2):249–254. doi: 10.1093/infdis/153.2.249. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Burr D. H., Caldwell M. B., Bourgeois A. L., Morgan H. R., Wistar R., Jr, Walker R. I. Mucosal and systemic immunity to Campylobacter jejuni in rabbits after gastric inoculation. Infect Immun. 1988 Jan;56(1):99–105. doi: 10.1128/iai.56.1.99-105.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Caldwell M. B., Walker R. I., Stewart S. D., Rogers J. E. Simple adult rabbit model for Campylobacter jejuni enteritis. Infect Immun. 1983 Dec;42(3):1176–1182. doi: 10.1128/iai.42.3.1176-1182.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dolby J. M., Newell D. G. The protection of infant mice from colonization with Campylobacter jejuni by vaccination of the dams. J Hyg (Lond) 1986 Apr;96(2):143–151. doi: 10.1017/s0022172400065918. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dunn B. E., Blaser M. J., Snyder E. L. Two-dimensional gel electrophoresis and immunoblotting of Campylobacter outer membrane proteins. Infect Immun. 1987 Jul;55(7):1564–1572. doi: 10.21236/ada265461. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Echeverria P., Taylor D. N., Lexsomboon U., Bhaibulaya M., Blacklow N. R., Tamura K., Sakazaki R. Case-control study of endemic diarrheal disease in Thai children. J Infect Dis. 1989 Mar;159(3):543–548. doi: 10.1093/infdis/159.3.543. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Field L. H., Headley V. L., Underwood J. L., Payne S. M., Berry L. J. The chicken embryo as a model for campylobacter invasion: comparative virulence of human isolates of Campylobacter jejuni and Campylobacter coli. Infect Immun. 1986 Oct;54(1):118–125. doi: 10.1128/iai.54.1.118-125.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fujimoto S., Umeda A., Takade A., Murata K., Amako K. Hexagonal surface layer of Campylobacter fetus isolated from humans. Infect Immun. 1989 Aug;57(8):2563–2565. doi: 10.1128/iai.57.8.2563-2565.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Glass R. I., Stoll B. J., Huq M. I., Struelens M. J., Blaser M., Kibriya A. K. Epidemiologic and clinical features of endemic Campylobacter jejuni infection in Bangladesh. J Infect Dis. 1983 Aug;148(2):292–296. doi: 10.1093/infdis/148.2.292. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hall R. H., Vial P. A., Kaper J. B., Mekalanos J. J., Levine M. M. Morphological studies on fimbriae expressed by Vibrio cholerae 01. Microb Pathog. 1988 Apr;4(4):257–265. doi: 10.1016/0882-4010(88)90086-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Humphrey C. D., Montag D. M., Pittman F. E. Experimental infection of hamsters with Campylobacter jejuni. J Infect Dis. 1985 Mar;151(3):485–493. doi: 10.1093/infdis/151.3.485. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jonson G., Svennerholm A. M., Holmgren J. Vibrio cholerae expresses cell surface antigens during intestinal infection which are not expressed during in vitro culture. Infect Immun. 1989 Jun;57(6):1809–1815. doi: 10.1128/iai.57.6.1809-1815.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Korlath J. A., Osterholm M. T., Judy L. A., Forfang J. C., Robinson R. A. A point-source outbreak of campylobacteriosis associated with consumption of raw milk. J Infect Dis. 1985 Sep;152(3):592–596. doi: 10.1093/infdis/152.3.592. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laemmli U. K. Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature. 1970 Aug 15;227(5259):680–685. doi: 10.1038/227680a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lane E. M., Batchelor R. A., Bourgeois A. L., Burr D. H., Olson J. G. Urine and faecal IgA response during naturally acquired infection with Campylobacter jejuni. Lancet. 1987 May 16;1(8542):1141–1141. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(87)91694-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Martin P. M., Mathiot J., Ipero J., Kirimat M., Georges A. J., Georges-Courbot M. C. Immune response to Campylobacter jejuni and Campylobacter coli in a cohort of children from birth to 2 years of age. Infect Immun. 1989 Aug;57(8):2542–2546. doi: 10.1128/iai.57.8.2542-2546.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McSweegan E., Burr D. H., Walker R. I. Intestinal mucus gel and secretory antibody are barriers to Campylobacter jejuni adherence to INT 407 cells. Infect Immun. 1987 Jun;55(6):1431–1435. doi: 10.1128/iai.55.6.1431-1435.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mills S. D., Bradbury W. C. Human antibody response to outer membrane proteins of Campylobacter jejuni during infection. Infect Immun. 1984 Feb;43(2):739–743. doi: 10.1128/iai.43.2.739-743.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mizuno S., Maki S., Honda T., Miwatani T., Arita K. Appearance in patients' sera of antibodies against purified antigen of Campylobacter jejuni and its relation to the bacterium-excreting period. J Infect Dis. 1985 Apr;151(4):742–742. doi: 10.1093/infdis/151.4.742. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nachamkin I., Hart A. M. Western blot analysis of the human antibody response to Campylobacter jejuni cellular antigens during gastrointestinal infection. J Clin Microbiol. 1985 Jan;21(1):33–38. doi: 10.1128/jcm.21.1.33-38.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nachamkin I., Yang X. H. Human antibody response to Campylobacter jejuni flagellin protein and a synthetic N-terminal flagellin peptide. J Clin Microbiol. 1989 Oct;27(10):2195–2198. doi: 10.1128/jcm.27.10.2195-2198.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nuijten P. J., van Asten F. J., Gaastra W., van der Zeijst B. A. Structural and functional analysis of two Campylobacter jejuni flagellin genes. J Biol Chem. 1990 Oct 15;265(29):17798–17804. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pavlovskis O. R., Rollins D. M., Haberberger R. L., Jr, Green A. E., Habash L., Strocko S., Walker R. I. Significance of flagella in colonization resistance of rabbits immunized with Campylobacter spp. Infect Immun. 1991 Jul;59(7):2259–2264. doi: 10.1128/iai.59.7.2259-2264.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pennie R. A., Pearson R. D., Barrett L. J., Lior H., Guerrant R. L. Susceptibility of Campylobacter jejuni to strain-specific bactericidal activity in sera of infected patients. Infect Immun. 1986 Jun;52(3):702–706. doi: 10.1128/iai.52.3.702-706.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Russell R. G., Blaser M. J., Sarmiento J. I., Fox J. Experimental Campylobacter jejuni infection in Macaca nemestrina. Infect Immun. 1989 May;57(5):1438–1444. doi: 10.1128/iai.57.5.1438-1444.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Siddique A. B., Akhtar S. Q. Study on the pathogenicity of Campylobacter jejuni by modifying the medium. J Trop Med Hyg. 1991 Jun;94(3):175–179. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ueki Y., Umeda A., Fujimoto S., Mitsuyama M., Amako K. Protection against Campylobacter jejuni infection in suckling mice by anti-flagellar antibody. Microbiol Immunol. 1987;31(12):1161–1171. doi: 10.1111/j.1348-0421.1987.tb01350.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Walker R. I., Caldwell M. B., Lee E. C., Guerry P., Trust T. J., Ruiz-Palacios G. M. Pathophysiology of Campylobacter enteritis. Microbiol Rev. 1986 Mar;50(1):81–94. doi: 10.1128/mr.50.1.81-94.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Winsor D. K., Jr, Mathewson J. J., DuPont H. L. Western blot analysis of intestinal secretory immunoglobulin A response to Campylobacter jejuni antigens in patients with naturally acquired Campylobacter enteritis. Gastroenterology. 1986 May;90(5 Pt 1):1217–1222. doi: 10.1016/0016-5085(86)90388-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]