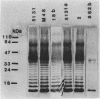
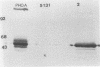
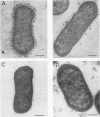
Abstract
Escherichia coli strains of serogroup O115:K(-):F165 have been associated with septicemia in calves and piglets. These strains express a capsular antigen referred to as K"V165" which inhibits agglutination of the O antigen by anti-O115 serum. We used hybrid transposon TnphoA mutants M48, 18b, and 2, and a spontaneous O-agglutinable mutant, 5131a, to evaluate the role of K"V165" in the pathogenicity of E. coli O115. Mutant M48 was as resistant to 90% rabbit serum and as virulent in day-old chickens as the parent strain 5131, mutants 18b and 5131a were less resistant to serum and less virulent in chickens, and mutant 2 was serum sensitive and avirulent. Analysis of outer membrane protein and lipopolysaccharide profiles failed to show any difference between the transposon mutants and the parent strain. In contrast, the spontaneous O-agglutinable mutant showed additional bands in the 16-kDa region of the polysaccharide ladder-like pattern. Mutants 2 and 5131a produced significantly less K"V165" capsular antigen than the parent strain, as demonstrated by a competitive enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay with adsorbed anti-K"V165" serum. In addition, electron microscopic analysis revealed that mutants 2 and 5131a had lost the capsular layer observed in the parent strain after fixation with glutaraldehyde-lysine. This capsule contained carbohydrate compounds and resembled an O-antigen capsule since it prevented O-antigen agglutination before the bacteria were heated at 100 degrees C and induced bacterial serum resistance. The capsule-defective mutants colonized the intestinal epithelium of experimentally infected gnotobiotic pigs but failed to induce clinical signs of septicemia. We concluded that E. coli strains of serogroup O115 expressed a polysaccharide capsular antigen which induced serum resistance and consequently contributed to the pathogenicity of the bacteria.
Full text
PDF




Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bayer M. E. Visualization of the bacterial polysaccharide capsule. Curr Top Microbiol Immunol. 1990;150:129–157. doi: 10.1007/978-3-642-74694-9_7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blum G., Ott M., Cross A., Hacker J. Virulence determinants of Escherichia coli O6 extraintestinal isolates analysed by Southern hybridizations and DNA long range mapping techniques. Microb Pathog. 1991 Feb;10(2):127–136. doi: 10.1016/0882-4010(91)90073-j. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Boulnois G. J., Roberts I. S. Genetics of capsular polysaccharide production in bacteria. Curr Top Microbiol Immunol. 1990;150:1–18. doi: 10.1007/978-3-642-74694-9_1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Broes A., Fairbrother J. M., Mainil J., Harel J., Lariviere S. Phenotypic and genotypic characterization of enterotoxigenic Escherichia coli serotype O8:KX105 and O8:K"2829" strains isolated from piglets with diarrhea. J Clin Microbiol. 1988 Nov;26(11):2402–2409. doi: 10.1128/jcm.26.11.2402-2409.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brubaker R. R. Mechanisms of bacterial virulence. Annu Rev Microbiol. 1985;39:21–50. doi: 10.1146/annurev.mi.39.100185.000321. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Contrepois M., Dubourguier H. C., Parodi A. L., Girardeau J. P., Ollier J. L. Septicaemic Escherichia coli and experimental infection of calves. Vet Microbiol. 1986 Jul;12(2):109–118. doi: 10.1016/0378-1135(86)90073-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cross A. S., Gemski P., Sadoff J. C., Orskov F., Orskov I. The importance of the K1 capsule in invasive infections caused by Escherichia coli. J Infect Dis. 1984 Feb;149(2):184–193. doi: 10.1093/infdis/149.2.184. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cross A. S. The biologic significance of bacterial encapsulation. Curr Top Microbiol Immunol. 1990;150:87–95. doi: 10.1007/978-3-642-74694-9_5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- FREDERICQ P. Colicins. Annu Rev Microbiol. 1957;11:7–22. doi: 10.1146/annurev.mi.11.100157.000255. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fairbrother J. M., Broes A., Jacques M., Larivière S. Pathogenicity of Escherichia coli O115:K"V165" strains isolated from pigs with diarrhea. Am J Vet Res. 1989 Jul;50(7):1029–1036. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fairbrother J. M., Larivière S., Lallier R. New fimbrial antigen F165 from Escherichia coli serogroup O115 strains isolated from piglets with diarrhea. Infect Immun. 1986 Jan;51(1):10–15. doi: 10.1128/iai.51.1.10-15.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Finlay B. B., Starnbach M. N., Francis C. L., Stocker B. A., Chatfield S., Dougan G., Falkow S. Identification and characterization of TnphoA mutants of Salmonella that are unable to pass through a polarized MDCK epithelial cell monolayer. Mol Microbiol. 1988 Nov;2(6):757–766. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2958.1988.tb00087.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Glantz P. J., Kradel D. C. Escherichia coli serogroup 115 isolated from animals: isolation from natural cases of disease. Am J Vet Res. 1967 Nov;28(127):1891–1895. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goldman R. C., Joiner K., Leive L. Serum-resistant mutants of Escherichia coli O111 contain increased lipopolysaccharide, lack an O antigen-containing capsule, and cover more of their lipid A core with O antigen. J Bacteriol. 1984 Sep;159(3):877–882. doi: 10.1128/jb.159.3.877-882.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goldman R. C., White D., Orskov F., Orskov I., Rick P. D., Lewis M. S., Bhattacharjee A. K., Leive L. A surface polysaccharide of Escherichia coli O111 contains O-antigen and inhibits agglutination of cells by O-antiserum. J Bacteriol. 1982 Sep;151(3):1210–1221. doi: 10.1128/jb.151.3.1210-1221.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hitchcock P. J., Brown T. M. Morphological heterogeneity among Salmonella lipopolysaccharide chemotypes in silver-stained polyacrylamide gels. J Bacteriol. 1983 Apr;154(1):269–277. doi: 10.1128/jb.154.1.269-277.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jann B., Jann K. Structure and biosynthesis of the capsular antigens of Escherichia coli. Curr Top Microbiol Immunol. 1990;150:19–42. doi: 10.1007/978-3-642-74694-9_2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Johnson J. R., Moseley S. L., Roberts P. L., Stamm W. E. Aerobactin and other virulence factor genes among strains of Escherichia coli causing urosepsis: association with patient characteristics. Infect Immun. 1988 Feb;56(2):405–412. doi: 10.1128/iai.56.2.405-412.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Johnson J. R. Virulence factors in Escherichia coli urinary tract infection. Clin Microbiol Rev. 1991 Jan;4(1):80–128. doi: 10.1128/cmr.4.1.80. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Joiner K. A. Complement evasion by bacteria and parasites. Annu Rev Microbiol. 1988;42:201–230. doi: 10.1146/annurev.mi.42.100188.001221. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Joiner K. A., Grossman N., Schmetz M., Leive L. C3 binds preferentially to long-chain lipopolysaccharide during alternative pathway activation by Salmonella montevideo. J Immunol. 1986 Jan;136(2):710–715. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Joiner K. A., Schmetz M. A., Goldman R. C., Leive L., Frank M. M. Mechanism of bacterial resistance to complement-mediated killing: inserted C5b-9 correlates with killing for Escherichia coli O111B4 varying in O-antigen capsule and O-polysaccharide coverage of lipid A core oligosaccharide. Infect Immun. 1984 Jul;45(1):113–117. doi: 10.1128/iai.45.1.113-117.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Korhonen T. K., Virkola R., Westurlund B., Holthöfer H., Parkkinen J. Tissue tropism of Escherichia coli adhesins in human extraintestinal infections. Curr Top Microbiol Immunol. 1990;151:115–127. doi: 10.1007/978-3-642-74703-8_6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laemmli U. K. Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature. 1970 Aug 15;227(5259):680–685. doi: 10.1038/227680a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lee C. J. Bacterial capsular polysaccharides--biochemistry, immunity and vaccine. Mol Immunol. 1987 Oct;24(10):1005–1019. doi: 10.1016/0161-5890(87)90067-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Levine M. M. Escherichia coli that cause diarrhea: enterotoxigenic, enteropathogenic, enteroinvasive, enterohemorrhagic, and enteroadherent. J Infect Dis. 1987 Mar;155(3):377–389. doi: 10.1093/infdis/155.3.377. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miller I., Maskell D., Hormaeche C., Johnson K., Pickard D., Dougan G. Isolation of orally attenuated Salmonella typhimurium following TnphoA mutagenesis. Infect Immun. 1989 Sep;57(9):2758–2763. doi: 10.1128/iai.57.9.2758-2763.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miniats O. P., Jol D. Gnotobiotic pigs-derivation and rearing. Can J Comp Med. 1978 Oct;42(4):428–437. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Montgomerie J. Z., Bindereif A., Neilands J. B., Kalmanson G. M., Guze L. B. Association of hydroxamate siderophore (aerobactin) with Escherichia coli isolated from patients with bacteremia. Infect Immun. 1984 Dec;46(3):835–838. doi: 10.1128/iai.46.3.835-838.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moon H. W. Colonization factor antigens of enterotoxigenic Escherichia coli in animals. Curr Top Microbiol Immunol. 1990;151:147–165. doi: 10.1007/978-3-642-74703-8_8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moxon E. R., Kroll J. S. The role of bacterial polysaccharide capsules as virulence factors. Curr Top Microbiol Immunol. 1990;150:65–85. doi: 10.1007/978-3-642-74694-9_4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nilius A. M., Savage D. C. Serum resistance encoded by colicin V plasmids in Escherichia coli and its relationship to the plasmid transfer system. Infect Immun. 1984 Mar;43(3):947–953. doi: 10.1128/iai.43.3.947-953.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nnalue N. A., Lindberg A. A. Salmonella choleraesuis strains deficient in O antigen remain fully virulent for mice by parenteral inoculation but are avirulent by oral administration. Infect Immun. 1990 Aug;58(8):2493–2501. doi: 10.1128/iai.58.8.2493-2501.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Orskov I., Orskov F. Escherichia coli in extra-intestinal infections. J Hyg (Lond) 1985 Dec;95(3):551–575. doi: 10.1017/s0022172400060678. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Orskov I., Orskov F., Jann B., Jann K. Serology, chemistry, and genetics of O and K antigens of Escherichia coli. Bacteriol Rev. 1977 Sep;41(3):667–710. doi: 10.1128/br.41.3.667-710.1977. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pluschke G., Mayden J., Achtman M., Levine R. P. Role of the capsule and the O antigen in resistance of O18:K1 Escherichia coli to complement-mediated killing. Infect Immun. 1983 Dec;42(3):907–913. doi: 10.1128/iai.42.3.907-913.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pluschke G., Mercer A., Kusećek B., Pohl A., Achtman M. Induction of bacteremia in newborn rats by Escherichia coli K1 is correlated with only certain O (lipopolysaccharide) antigen types. Infect Immun. 1983 Feb;39(2):599–608. doi: 10.1128/iai.39.2.599-608.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roantree R. J. Salmonella O antigens and virulence. Annu Rev Microbiol. 1967;21:443–466. doi: 10.1146/annurev.mi.21.100167.002303. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Robbins J. B., McCracken G. H., Jr, Gotschlich E. C., Orskov F., Orskov I., Hanson L. A. Escherichia coli K1 capsular polysaccharide associated with neonatal meningitis. N Engl J Med. 1974 May 30;290(22):1216–1220. doi: 10.1056/NEJM197405302902202. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Taylor P. W. Bactericidal and bacteriolytic activity of serum against gram-negative bacteria. Microbiol Rev. 1983 Mar;47(1):46–83. doi: 10.1128/mr.47.1.46-83.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Taylor P. W., Kroll H. P. Killing of an encapsulated strain of Escherichia coli by human serum. Infect Immun. 1983 Jan;39(1):122–131. doi: 10.1128/iai.39.1.122-131.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Taylor R. K., Manoil C., Mekalanos J. J. Broad-host-range vectors for delivery of TnphoA: use in genetic analysis of secreted virulence determinants of Vibrio cholerae. J Bacteriol. 1989 Apr;171(4):1870–1878. doi: 10.1128/jb.171.4.1870-1878.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Taylor R. K., Miller V. L., Furlong D. B., Mekalanos J. J. Use of phoA gene fusions to identify a pilus colonization factor coordinately regulated with cholera toxin. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 May;84(9):2833–2837. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.9.2833. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weinstein R., Young L. S. Phagocytic resistance of Escherichia coli K-1 isolates and relationship to virulence. J Clin Microbiol. 1978 Dec;8(6):748–755. doi: 10.1128/jcm.8.6.748-755.1978. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]